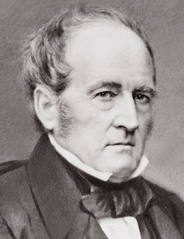United States presidential election, 1860
| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
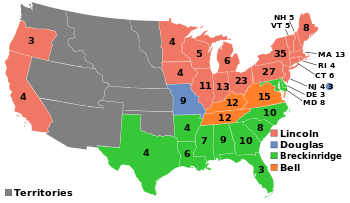
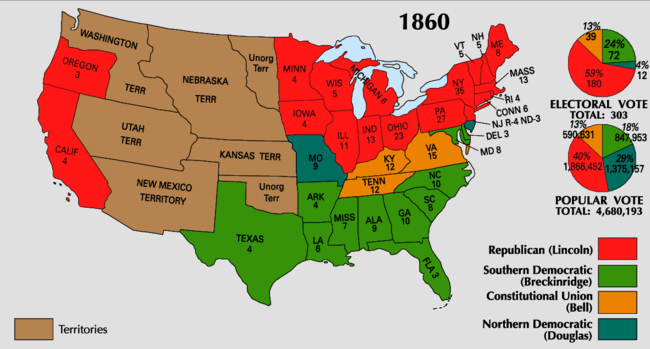
| Presidential Election 1860. Red shows states won by Lincoln, green by Breckinridge, orange by Bell, and blue by Douglas Numbers are Electoral College votes in each state by the 1850 Census. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The United States presidential election of 1860 was the 19th presidential election. The election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860, and served as the immediate impetus for the outbreak of the American Civil War.
The United States had been divided during the 1850s on questions surrounding the expansion of slavery and the rights of slave owners. Incumbent President James Buchanan, like his predecessor Franklin Pierce, was a northerner with sympathies for the South. He recommended that Supreme Court Justice Robert Grier vote proslavery in the Dred Scott v. Sandford case of 1857. This was so unpopular it backfired on Buchanan's presidency, allowing the Republican Party to win a majority in the House in 1858 and full control of Congress in 1860. Buchanan declined to seek re-election. In 1860, these issues broke the Democratic Party into Northern and Southern factions, and a new Constitutional Union Party appeared. In the face of a divided opposition, the newly created Republican Party (founded in 1854), secured a majority of the electoral votes, putting Abraham Lincoln in the White House with almost no support from the South.
Between Election Day and Lincoln's inauguration, seven slave-holding Southern states declared their secession from the Union and formed the Confederate States of America, with the new polity's capital being placed in Montgomery, Alabama. Military maneuvering between the new Confederacy and the United States, and disputes over US forts in Confederate territory led to the firing on Fort Sumter, which precipitated the civil war that lasted from 1861 to 1865.
Nominations
The 1860 presidential election conventions were unusually tumultuous, due in particular to a split in the Democratic party that led to the meeting of rival conventions.
Democratic (Northern Democratic) Party Nomination

Democratic candidates:
- Stephen Douglas, Senator from Illinois
- James Guthrie, former Secretary Treasury
- Robert Mercer Taliaferro Hunter, Senator from Virginia
- Joseph Lane, Senator from Oregon
- Daniel S. Dickinson, former Senator from New York
- Andrew Johnson, Senator from Tennessee
Democratic Party candidates gallery
-
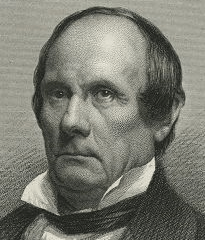
Former Treasury Secretary James Guthrie
-

Senator Joseph Lane from Oregon
-

Former Senator Daniel S. Dickinson from New York
At the Democratic National Convention held in Institute Hall in Charleston, South Carolina, in April 1860, 51 Southern Democrats walked out over a platform dispute. The extreme pro-slavery "Fire-Eater" William Lowndes Yancey and the Alabama delegation first left the hall, followed by the delegates of Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, Texas, three of the four delegates from Arkansas, and one of the three delegates from Delaware.
Six candidates were nominated: Stephen A. Douglas from Illinois, James Guthrie from Kentucky, Robert Mercer Taliaferro Hunter from Virginia, Joseph Lane from Oregon, Daniel S. Dickinson from New York, and Andrew Johnson from Tennessee. Three other candidates, Isaac Toucey from Connecticut, James Pearce from Maryland, and Jefferson Davis from Mississippi (the future president of the Confederate States) also received votes. Douglas, a moderate on the slavery issue who favored "popular sovereignty", was ahead on the first ballot, but needed 56.5 more votes to secure the nomination. On the 57th ballot, Douglas was still ahead, but 51.5 votes short of nomination. In desperation, the delegates agreed on May 3 to stop voting and adjourn the convention.
The Democrats convened again at the Front Street Theater in Baltimore, Maryland, on June 18. This time, 110 Southern delegates (led by "Fire-Eaters") walked out when the convention would not adopt a resolution supporting extending slavery into territories whose voters did not want it. Some considered Horatio Seymour a compromise candidate for the National Democratic nomination at the reconvening convention in Baltimore. Seymour wrote a letter to the editor of his local newspaper declaring unreservedly that he was not a candidate for either spot on the ticket. After two ballots, the remaining Democrats nominated the ticket of Stephen A. Douglas from Illinois for president. Benjamin Fitzpatrick from Alabama was nominated for vice president, but he refused the nomination. That nomination ultimately went instead to Herschel Vespasian Johnson from Georgia.
Southern Democratic Party Nomination

Southern Democratic candidates:
- John C. Breckinridge, Vice President of the United States
- Daniel S. Dickinson, former Senator from New York
- Robert Mercer Taliaferro Hunter, Senator from Virginia
- Joseph Lane, Senator from Oregon
- Jefferson Davis, Senator from Mississippi
Southern Democratic Party candidates gallery
-

Former Senator
Daniel S. Dickinson from New York -

Senator
Robert M. T. Hunter from Virginia
(Declined to be Nominated) -

Senator Joseph Lane from Oregon
(Declined to be Nominated) -
Senator Jefferson Davis from Mississippi
(Declined to be Nominated)
The Charleston bolters reconvened in Richmond, Virginia on June 11. When the Democrats reconvened in Baltimore, they rejoined (except South Carolina and Florida, who stayed in Richmond).
When the convention seated two replacement delegations on 18 June, they bolted again, now accompanied by nearly all other Southern delegates, as well as erstwhile Convention chair Caleb Cushing, a New Englander and former member of Franklin Pierce's cabinet. This larger group met immediately in Baltimore's Institute Hall, with Cushing again presiding. They adopted the pro-slavery platform rejected at Charleston, and nominated Vice President John C. Breckinridge for President, and Senator Joseph Lane from Oregon for Vice President.[4]
Yancey and some (less than half) of the bolters, almost entirely from the Lower South, met on 28 June in Richmond, along with the South Carolina and Florida delegations. This convention affirmed the nominations of Breckinridge and Lane.[3]
Besides the Democratic Parties in the southern states, the Breckinridge/Lane ticket was also supported by the Buchanan administration. Buchanan's own continued prestige in his home state of Pennsylvania ensured that Breckinridge would be the principal Democratic candidate in that populous state.
Breckinridge will be the last sitting Vice President nominated for President, until Richard Nixon in 1960.
Republican Party Nomination

Republican candidates:
- Abraham Lincoln, former representative from Illinois
- William Seward, Senator from New York
- Simon Cameron, Senator from Pennsylvania
- Salmon P. Chase, Governor of Ohio
- Edward Bates, former representative from Missouri
- John McLean, Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court
- Benjamin Wade, Senator from Ohio
- William L. Dayton, former Senator from New Jersey
Republican Party candidates gallery
-

Former Representative Abraham Lincoln
from Illinois -

Former Representative Edward Bates from Missouri
-

Senator Benjamin Wade from Ohio
-

Former Senator William L. Dayton from New Jersey
The Republican National Convention met in mid-May 1860, after the Democrats had been forced to adjourn their convention in Charleston. With the Democrats in disarray and a sweep of the Northern states possible, the Republicans felt confident going into their convention in Chicago. William H. Seward from New York was considered the front runner, followed by Abraham Lincoln from Illinois, Salmon P. Chase from Ohio, and Missouri's Edward Bates.
As the convention developed, however, it was revealed that Seward, Chase, and Bates had each alienated factions of the Republican Party. Delegates were concerned that Seward was too closely identified with the radical wing of the party, and his moves toward the center had alienated the radicals. Chase, a former Democrat, had alienated many of the former Whigs by his coalition with the Democrats in the late 1840s. He had also opposed tariffs demanded by Pennsylvania, and critically, had opposition from his own delegation from Ohio. Bates outlined his positions on the extension of slavery into the territories and equal constitutional rights for all citizens, positions that alienated his supporters in the border states and Southern conservatives. German Americans in the party opposed Bates because of his past association with the Know Nothings.
Since it was essential to carry the West, and because Lincoln had a national reputation from his debates and speeches as the most articulate moderate, he won the party's nomination for president on the third ballot on May 18, 1860. Senator Hannibal Hamlin from Maine was nominated for vice-president, defeating Cassius Clay from Kentucky.
The party platform[5] promised not to interfere with slavery in the states, but suggested an opposition to slavery in the territories. The platform promised tariffs protecting industry and workers, a Homestead Act granting free farmland in the West to settlers, and the funding of a transcontinental railroad. There was no mention of Mormonism (which had been condemned in the Party's 1856 platform), the Fugitive Slave Act, personal liberty laws, or the Dred Scott decision.[6] While the Seward forces were disappointed at the nomination of a little-known western upstart, they rallied behind Lincoln. Abolitionists, however, were angry at the selection of a moderate and had little faith in Lincoln.[7][8]
Constitutional Union Party Nomination

Constitutional Union candidates:
- John Bell, former Senator from Tennessee
- Sam Houston, Governor of Texas
- John J. Crittenden, Senator from Kentucky
- Edward Everett, former Senator from Massachusetts
- William A. Graham, former Senator from North Carolina
- William C. Rives, former Senator from Virginia
-

Former Senator Edward Everett from Massachusetts
-

Former Senator William A. Graham from North Carolina
-

Former Senator William C. Rives from Virginia
The Constitutional Union Party was formed by remnants of both the defunct Know Nothing and Whig Parties who were unwilling to join either the Republicans or the Democrats. The parties members hoped to stave off Southern secession by avoiding the slavery issue.[9] They met in the Eastside District Courthouse of Baltimore and nominated John Bell from Tennessee for president over Governor Sam Houston of Texas on the second ballot. Edward Everett was nominated for vice-president at the convention on May 9, 1860, one week before Lincoln.[10][11]
John Bell was a former Whig who had opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act and the Lecompton Constitution. Edward Everett had been president of Harvard University and Secretary of State in the Fillmore administration. The party platform advocated compromise to save the Union with the slogan "The Union as it is, and the Constitution as it is."[12]
Liberty (Union) Party nomination
Liberty (Union) candidates:
- Gerrit Smith, former representative from New York
Liberty (Union) candidates gallery
-

Former Representative Gerrit Smith from New York
The Liberty Party as formed in 1860 was a splinter (or remnant) of the former Liberty Party of the 1840s, after most of its membership left to join the Free Soil Party in 1848 and nearly all of what remained of it joined the Republicans in 1854. A convention of 100 delegates was held in Convention Hall, Syracuse, New York, on August 29, 1860. Delegates were in attendance from New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Michigan, Illinois, Ohio, Kentucky, and Massachusetts. Several of the delegates were women.
Gerrit Smith, a prominent abolitionist and the 1848 presidential nominee of the original Liberty Party, had sent a letter in which he stated that his health had been so poor that he had not been able to be away from home since 1858. Nonetheless, he remained popular in the party because he had helped inspire some of John Brown's supporters at the Raid on Harpers Ferry. In his letter, Smith donated $50 to pay for the printing of ballots in the various states.
There was quite a spirited contest between the friends of Gerrit Smith and William Goodell in regard to the nomination for the presidency. In spite of his professed ill health, Gerrit Smith was nominated for president and Samuel McFarland from Pennsylvania was nominated for vice president.
In Ohio, a slate of presidential electors pledged to Smith ran with the name of the Union Party.[13]
People's Party nomination
The People's Party was a loose association of the supporters of Governor Samuel Houston. On April 20, 1860, the party held what it termed a national convention to nominate Houston for president on the San Jacinto Battlefield in Texas. Houston's supporters at the gathering did not nominate a vice-presidential candidate, since they expected later gatherings to carry out that function. Later mass meetings were held in northern cities, such as New York City on May 30, 1860, but they too failed to nominate a vice-presidential candidate. Houston withdrew from the race on August 16, convinced that his candidacy would only make it easier for the Republican candidate to win, and urged the formation of a Unified "Union" ticket in opposition to it.[14][15]
Results

the Capitol, March 4, 1861
by Electoral College vote
The election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860, and was noteworthy for exaggerated sectionalism in a country that was soon to dissolve into civil war. Voter turnout was 81.2%, the highest in American history up to that time, and the second-highest overall (exceeded only in the election of 1876).[16][17] All six Presidents elected since Andrew Jackson won re-election in 1832 had been one-term presidents, the last four with a popular vote under 51 percent.[18] Lincoln won the Electoral College with less than 40 percent of the popular vote nationwide by carrying states above the Mason–Dixon line and north of the Ohio River, plus the states of California and Oregon in the Far West. Unlike all of his predecessors, he did not carry even one slave-holding state, and he received no votes at all in ten of the fifteen slave states.
The Republican victory resulted from the concentration of votes in the free states, which together controlled a majority of the presidential electors.[19] Population increases in the free states had far exceeded those seen in the slave states for many years before the election of 1860, hence their dominance in the Electoral College. The split in the Democratic party is sometimes held responsible for Lincoln's victory,[20] but he would still have won in the Electoral College, 169 to 134, even if all of the anti-Lincoln voters had united behind a single candidate. In the three states in which anti-Lincoln votes did combine into fusion tickets, Lincoln still won in two states and split the electoral vote of New Jersey. At most, a single opponent nationwide would only have deprived Lincoln of California and Oregon (both of which he only won via a plurality of the statewide vote), whose combined total of seven electoral votes would have made no difference to the result; every other state won by the Republicans was won by a clear majority of the vote.[21]
Like Lincoln, Breckinridge and Bell won no electoral votes outside of their respective sections. While Bell retired to his family business, quietly supporting his state's secession, Breckinridge served as a Confederate general. He finished second in the Electoral College with 72 votes, carrying 11 of 15 slave states (including South Carolina, whose electors were chosen by the state legislature, not popular vote). He won a distant third in national popular vote at 18 percent, but he accrued 50–75 percent in the first seven states that would become the Confederate States of America and took nine of the eleven states that eventually joined.[22]
Bell carried three slave states (Tennessee, Kentucky, and Virginia) and lost Maryland by only 722 votes. Nevertheless, he finished a remarkable second in all the slave states won by Breckinridge and Douglas. He won 45–47 percent for Maryland, Tennessee and North Carolina and he canvassed respectably with 36–40 percent in Missouri, Arkansas, Louisiana, Georgia, and Florida. Nonetheless, he came in last in the national popular vote at 12 percent.
Douglas was the only candidate who won electoral votes in both slave and free states (free New Jersey and slave Missouri). His support was the most widespread geographically; he finished second behind Lincoln in the popular vote with 29.5 percent, but last in the Electoral College. Douglas attained a 28–47 percent share in the states of the Mid-Atlantic, Midwest and Trans-Mississippi West, but slipped to 19–39 percent in New England. Outside his regional section, Douglas took 15–17 percent of the popular vote total in the slave states of Kentucky, Alabama and Louisiana, then 10 percent or less in the nine remaining slave states. Douglas, in his "Norfolk Doctrine", reiterated in North Carolina, promised to keep the Union together by coercion if states proceeded to secede. The popular vote for Lincoln and Douglas combined was 70% of the turnout.
An election for disunion
In their campaigning, Bell and Douglas both claimed that disunion would not necessarily follow a Lincoln election. Nonetheless, loyal army officers in Virginia, Kansas and South Carolina warned Lincoln of military preparations to the contrary. Secessionists threw their support behind Breckinridge in an attempt either to force the anti-Republican candidates to coordinate their electoral votes or throw the election into the House of Representatives, where the selection of the president would be made by the representatives elected in 1858, before the Republican majorities in both House and Senate achieved in 1860 were seated in the new 37th Congress. Mexican War hero Winfield Scott suggested to Lincoln that he assume the powers of a commander-in-chief before inauguration. But historian Bruce Chadwick observes that Lincoln and his advisors ignored the widespread alarms and threats of secession as mere election trickery.
Indeed, voting in the South was not as monolithic as the Electoral College map would make it seem. Economically, culturally, and politically, the South was made up of three regions. In the states of the "Upper" South, also known as the "Border States" (Delaware, Maryland, Kentucky, and Missouri along with the Kansas territories), unionist popular votes were scattered among Lincoln, Douglas, and Bell, to form a majority in all four. In four of the five "Middle" South states, there was a unionist majority divided between Douglas and Bell in Virginia and Tennessee; in North Carolina and Arkansas, the unionist (Bell and Douglas) vote approached a majority. Texas was the only Middle South state that Breckinridge carried convincingly. In three of the six "Deep" South, unionists (Bell and Douglas) won divided majorities in Georgia and Louisiana or neared it in Alabama. Breckinridge convincingly carried only three of the six states of the Deep South (South Carolina, Florida, and Mississippi).[23] These three Deep South states were all among the four Southern states with the lowest white populations; together, they held only nine-percent of Southern whites.[24]
In the states that would become the Confederacy, the three states with the highest voter turnouts voted the most one-sided. Texas, with five percent of the total wartime South's population, voted 80 percent Breckinridge. Kentucky and Missouri, with one-fourth the total population, voted 68 percent pro-union Bell, Douglas and Lincoln. In comparison, the six states of the Deep South making up one-fourth the Confederate voting population, split 57 percent Breckinridge versus 43 percent for the three pro-union candidates.[25] The four states that were admitted to the Confederacy after Fort Sumter held almost half its population. These voted a narrow combined majority of 53 percent for the pro-union candidates.
In the eleven states that would later declare their secession from the Union and be controlled by Confederate armies, ballots for Lincoln were cast only in Virginia,[26][27] where he received only 1.1 percent of the popular vote.[23][28] In order to distribute ballots in a state, candidates needed citizens in that state who would pledge to vote for the candidate in the Electoral College. In ten southern slave states, no citizens would publicly pledge such support for Lincoln.
In the four slave states that did not secede (Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, and Delaware), Lincoln came in fourth in every state except Delaware (where he finished third). Within the 15 slave states, Lincoln won only two counties out of 996,[23] both in Missouri.[29] (In the 1856 election, the Republican candidate for president had received no votes at all in 10 of the 14 slave states with a popular vote).
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote(a) | Electoral vote |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Pct | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Elect. vote | ||||
| Abraham Lincoln | Republican | Illinois | 1,865,908 | 39.8% | 180 | Hannibal Hamlin | Maine | 180 |
| John C. Breckinridge | Southern Democratic | Kentucky | 848,019 | 18.1% | 72 | Joseph Lane | Oregon | 72 |
| John Bell | Constitutional Union/Whig | Tennessee | 590,901 | 12.6% | 39 | Edward Everett | Massachusetts | 39 |
| Stephen A. Douglas | Northern Democratic | Illinois | 1,380,202 | 29.5% | 12 | Herschel Vespasian Johnson | Georgia | 12 |
| Other | 531 | 0.0% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 4,685,561 | 100% | 303 | 303 | ||||
| Needed to win | 152 | 152 | ||||||
Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. "1860 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved July 27, 2005. Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 31, 2005.
(a) The popular vote figures exclude South Carolina where the Electors were chosen by the state legislature rather than by popular vote.
Geography of results
Cartographic gallery
-

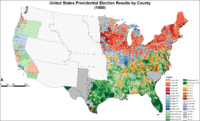
Map of presidential election results by county.
-
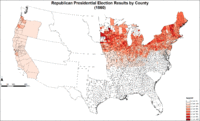
Map of Republican presidential election results by county.
-
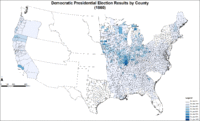
Map of Northern Democratic presidential election results by county.
-
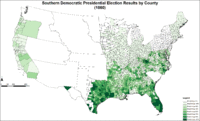
Map of Southern Democratic presidential election results by county.
-
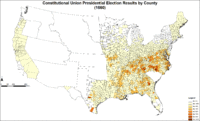
Map of Constitutional Union presidential election results by county.
-
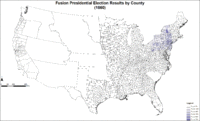
Map of "Fusion" slate presidential election results by county.
-
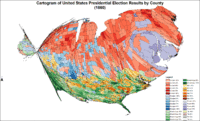
Cartogram of presidential election results by county.
-
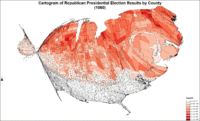
Cartogram of Republican presidential election results by county.
-
Cartogram of Northern Democratic presidential election results by county.
-
Cartogram of Southern Democratic presidential election results by county.
-
Cartogram of Constitutional Union presidential election results by county.
-
Cartogram of "Fusion" slate presidential election results by county.
Results by state
Source: Data from Walter Dean Burnham, Presidential ballots, 1836–1892 (Johns Hopkins University Press, 1955) pp 247-57.
| Abraham Lincoln Republican |
Stephen Douglas (Northern) Democratic |
John Breckinridge (Southern) Democratic |
John Bell Constitutional Union |
Fusion (Non-Republican) (Democratic Fusion) |
State Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | |
| Alabama | 9 | no ballots | 13,618 | 15.1 | - | 48,669 | 54.0 | 9 | 27,835 | 30.9 | - | no ballots | 90,122 | AL | ||||
| Arkansas | 4 | no ballots | 5,357 | 9.9 | - | 28,732 | 53.1 | 4 | 20,063 | 37.0 | - | no ballots | 54,152 | AR | ||||
| California | 4 | 38,733 | 32.3 | 4 | 37,999 | 31.7 | - | 33,969 | 28.4 | - | 9,111 | 7.6 | - | no ballots | 119,812 | CA | ||
| Connecticut | 6 | 43,488 | 58.1 | 6 | 15,431 | 20.6 | - | 14,372 | 19.2 | - | 1,528 | 2.0 | - | no ballots | 74,819 | CT | ||
| Delaware | 3 | 3,822 | 23.7 | - | 1,066 | 6.6 | - | 7,339 | 45.5 | 3 | 3,888 | 24.1 | - | no ballots | 16,115 | DE | ||
| Florida | 3 | no ballots | 223 | 1.7 | - | 8,277 | 62.2 | 3 | 4,801 | 36.1 | - | no ballots | 13,301 | FL | ||||
| Georgia | 10 | no ballots | 11,581 | 10.9 | - | 52,176 | 48.9 | 10 | 42,960 | 40.3 | - | no ballots | 106,717 | GA | ||||
| Illinois | 11 | 172,171 | 50.7 | 11 | 160,215 | 47.2 | - | 2,331 | 0.7 | - | 4,914 | 1.4 | - | no ballots | 339,631 | IL | ||
| Indiana | 13 | 139,033 | 51.1 | 13 | 115,509 | 42.4 | - | 12,295 | 4.5 | - | 5,306 | 1.9 | - | no ballots | 272,143 | IN | ||
| Iowa | 4 | 70,302 | 54.6 | 4 | 55,639 | 43.2 | - | 1,035 | 0.8 | - | 1,763 | 1.4 | - | no ballots | 128,739 | IA | ||
| Kentucky | 12 | 1,364 | 0.9 | - | 25,651 | 17.5 | - | 53,143 | 36.3 | - | 66,058 | 45.2 | 12 | no ballots | 146,216 | KY | ||
| Louisiana | 6 | no ballots | 7,625 | 15.1 | - | 22,681 | 44.9 | 6 | 20,204 | 40.0 | - | no ballots | 50,510 | LA | ||||
| Maine | 8 | 62,811 | 62.2 | 8 | 29,693 | 29.4 | - | 6,368 | 6.3 | - | 2,046 | 2.0 | - | no ballots | 100,918 | ME | ||
| Maryland | 8 | 2,294 | 2.5 | - | 5,966 | 6.4 | - | 42,482 | 45.9 | 8 | 41,760 | 45.1 | - | no ballots | 92,502 | MD | ||
| Massachusetts | 13 | 106,684 | 62.9 | 13 | 34,370 | 20.3 | - | 6,163 | 3.6 | - | 22,331 | 13.2 | - | no ballots | 169,548 | MA | ||
| Michigan | 6 | 88,481 | 57.2 | 6 | 65,057 | 42.0 | - | 805 | 0.5 | - | 415 | 0.3 | - | no ballots | 154,758 | MI | ||
| Minnesota | 4 | 22,069 | 63.4 | 4 | 11,920 | 34.3 | - | 748 | 2.2 | - | 50 | 0.1 | - | no ballots | 34,787 | MN | ||
| Mississippi | 7 | no ballots | 3,282 | 4.7 | - | 40,768 | 59.0 | 7 | 25,045 | 36.2 | - | no ballots | 69,095 | MS | ||||
| Missouri | 9 | 17,028 | 10.3 | - | 58,801 | 35.5 | 9 | 31,362 | 18.9 | - | 58,372 | 35.3 | - | no ballots | 165,563 | MO | ||
| New Hampshire | 5 | 37,519 | 56.9 | 5 | 25,887 | 39.3 | - | 2,125 | 3.2 | - | 412 | 0.6 | - | no ballots | 65,943 | NH | ||
| New Jersey | 7 | 58,346 | 48.1 | 4[nb 1] | no ballots | 3[nb 2] | no ballots | - | no ballots | - | 62,869[nb 3] | 51.9 | -[nb 4] | 121,215 | NJ | |||
| New York | 35 | 362,646 | 53.7 | 35 | no ballots | - | no ballots | - | no ballots | - | 312,510 | 46.3 | -[nb 5] | 675,156 | NY | |||
| North Carolina | 10 | no ballots | 2,737 | 2.8 | - | 48,846 | 50.5 | 10 | 45,129 | 46.7 | - | no ballots | 96,712 | NC | ||||
| Ohio | 23 | 231,709 | 52.3 | 23 | 187,421 | 42.3 | - | 11,406 | 2.6 | - | 12,194 | 2.8 | - | no ballots | 442,730 | OH | ||
| Oregon | 3 | 5,329 | 36.1 | 3 | 4,136 | 28.0 | - | 5,075 | 34.4 | - | 218 | 1.5 | - | no ballots | 14,758 | OR | ||
| Pennsylvania | 27 | 268,030 | 56.3 | 27 | 16,765 | 3.5 | -[nb 6] | no ballots | 12,776 | 2.7 | - | 178,871[nb 7] | 37.5 | -[nb 8] | 476,442 | PA | ||
| Rhode Island | 4 | 12,244 | 61.4 | 4 | 7,707[nb 9] | 38.6 | - | no ballots | no ballots | no ballots | 19,951 | RI | ||||||
| South Carolina | 8 | no popular vote | no popular vote | no popular vote | 8 | no popular vote | no popular vote | - | SC | |||||||||
| Tennessee | 12 | no ballots | 11,281 | 7.7 | - | 65,097 | 44.6 | - | 69,728 | 47.7 | 12 | no ballots | 146,106 | TN | ||||
| Texas | 4 | no ballots | 18 | 0.0 | - | 47,454 | 75.5 | 4 | 15,383 | 24.5 | - | no ballots | 62,855 | TX | ||||
| Vermont | 5 | 33,808 | 75.7 | 5 | 8,649 | 19.4 | - | 218 | 0.5 | - | 1,969 | 4.4 | - | no ballots | 44,644 | VT | ||
| Virginia | 15 | 1,887 | 1.1 | - | 16,198 | 9.7 | - | 74,325 | 44.5 | - | 74,481 | 44.6 | 15 | no ballots | 166,891 | VA | ||
| Wisconsin | 5 | 86,110 | 56.6 | 5 | 65,021 | 42.7 | - | 887 | 0.6 | - | 161 | 0.1 | - | no ballots | 152,179 | WI | ||
| TOTALS: | 303 | 1,865,908 | 39.8 | 180 | 1,004,823 | 21.5 | 12 | 669,148 | 14.3 | 72 | 590,901 | 12.6 | 39 | 554,250 | 11.8 | 0 | 4,685,030 | US |
| TO WIN: | 152 | |||||||||||||||||
Trigger for the Civil War
The election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860 was the immediate cause of southern resolutions of secession. He was the nominee of the Republican party with an anti-slavery expansion platform, he refused to acknowledge the right to secession, and he would not yield federal property within Southern states. Numerous historians have explored the reasons so many white Southerners adopted secessionism in 1860.[32] Bertram Wyatt-Brown argues that secessionists desired independence as necessary for their honor. They could no longer tolerate northern attitudes that regarded slave ownership as a great sin and Northern politicians who insisted on stopping the spread of slavery.[33][34] Avery Craven argues that secessionists believed Lincoln's election meant long-term doom for their peculiar social system. These terms placed issues beyond the democratic process, and they placed "the great masses of men, North and South, helpless before the drift into war".[35]
See also
- American election campaigns in the 19th century
- Electoral history of Abraham Lincoln
- History of the United States (1849–1865)
- History of the United States Democratic Party
- History of the United States Republican Party
- John Hanks
- Third Party System
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1860
- United States Senate elections, 1860
Notes
- ↑ 4 of the electors pledged to Lincoln were elected since the Breckinridge and Bell electors finished behind all other candidates.[30]
- ↑ The 3 Douglas electors were elected.[30]
- ↑ The Fusion vote used here is the vote for the high elector on the slate, who was pledged to Douglas.[30]
- ↑ The Fusion slate consisted of 3 electors pledged to Douglas, and 2 each to Breckinridge and Bell. Nonetheless, different electors appeared in some counties for Breckinridge and Bell, resulting in lower totals for them and a split electoral outcome. The 3 Douglas electors were elected and 4 of those pledged to Lincoln. The Breckinridge and Bell electors finished behind all other candidates.[30]
- ↑ The slate of electors were pledged to 3 different candidates: 18 to Douglas, 10 to Bell, and 7 to Breckinridge.[30]
- ↑ Not all of the Douglas supporters agreed to the Reading slate deal and established a separate Douglas only ticket. This slate comprised the 12 Douglas electoral candidates on the Reading ticket, and 15 additional Douglas supporters. This ticket was usually referred to as the Straight Douglas ticket. Thus 12 electoral candidates appeared on 2 tickets, Reading and Straight Douglas.[31]
- ↑ This vote is listed under the Fusion column, not the Breckinridge column as many other sources do, because this ticket was pledged to either of two candidates based on the national result. Additionally, the slate was almost equally divided between the supporters of Breckinridge and Douglas.[31]
- ↑ The Democratic Party chose its slate of electors before the National Convention in Charleston, SC. Since this was decided before the party split, both Douglas supporters and Breckinridge supporters claimed the right for their man to be considered the party candidate and the support of the electoral slate. Eventually, the state party worked out an agreement: if either candidate could win the national election with Pennsylvania's electoral vote, then all her electoral votes would go to that candidate. Of the 27 electoral candidates, 15 were Breckinridge supporters; the remaining 12 were for Douglas. This was often referred to as the Reading electoral slate, because it was in that city that the state party chose it.[31]
- ↑ The Douglas ticket in Rhode Island was supported by Breckinridge and Bell supporters.[31]
References
- ↑ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
- ↑ Lossing, Benson John. Pictorial history of the civil war in the United States of America, Volume 1 (1866) Poughkeepsie, NY. Free ebook. viewed January 26, 2012. Bolters met at St. Andrew's Hall.
- 1 2 Freehling, William W., The Road to Disunion: Secessionists Triumphant, Vol.2. Oxford University, 2007, p. 321
- ↑ Heidler, p. 157. Baltimore's Institute Hall, not be confused with Charleston's Institute Hall also used by the walk-out delegations.
- ↑ "Republican National Platform, 1860". Central Pacific Railroad Photographic History Museum. CPRR.org. 2003-04-13. Retrieved 2015-04-17.
- ↑ Rhodes (1920) 2:420
- ↑ Rhodes (1920) 2:429
- ↑ Baum, Dale (1984). The Civil War Party System: The Case of Massachusetts, 1848–1876. Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press. p. 49. ISBN 0-8078-1588-8.
- ↑ Schulten, Susan (2010-11-10). "How (And Where) Lincoln Won". New York Times, 10 November 2010. Retrieved from http://opinionator.blogs.nytimes.com/2010/11/10/how-and-where-lincoln-won/.
- ↑ Lossing, Benson John, Pictorial History of the Civil War in the United States of America, Volume 1 (1866) Poughkeepsie, NY. Free ebook. viewed January 26, 2012. p. 29 Bolters met at St. Andrew's Hall.
- ↑ The building had been the First Presbyterian Meeting House (Two Towers Church) on Fayette Street, between Calvert and North Street, demolished before 1866 and occupied by the United States Courthouse.
- ↑ Getting the Message Out! Stephen A. Douglas
- ↑ "Our Campaigns – US President – Liberty (Union) National Convention Race – Aug 30, 1860".
- ↑ "POLITICAL MOVEMENTS.; THE HOUSTON MASS MEETING. Large Gathering of the People in Union-Square--Washington statue Illuminated. The Hero of San Jacinto Nominated for the Presidency. Speeches, Address, Resolutions, Music, Fireworks, Guns, and Fun". The New York Times. May 30, 1860.
- ↑ "Letter from Sam Houston Withdrawing from the Canvass". The New York Times. September 3, 1860.
- ↑ The 1876 election had a turnout of 81.8%, slightly higher than 1860. Between 1828–1928: "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections: 1828–2008". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara. Retrieved 2012-11-09.
- ↑ Data between 1932 and 2008: "Table 397. Participation in Elections for President and U.S. Representatives: 1932 to 2010" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau, Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2012. U.S. Census Bureau.
- ↑ http://www.uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/ Only Franklin Pierce had achieved a statistical majority in the popular vote (50.83 percent).
- ↑ Chadwick, Bruce. "Lincoln for President: an unlikely candidate, an audacious strategy, and the victory no one saw coming" (2009) Ch. 10 The Eleventh Hour. p. 289 ISBN 978-1-4022-2504-8 Lincoln's strategy was deliberately focused, in collaboration with Republican Party Chairman Thurlow Weed, "Find 'em and vote 'em." and based on expanding on the states Fremont had won four years earlier. New York was critical with 35 Electoral College votes, 11.5 percent of the total. The Wide Awakes young Republican men's organization massively expanded registered voter lists. But Lincoln was not even on the ballot in many southern states.
- ↑ e.g. the 1912 Catholic Encyclopedia's article on the United States, vol, 15, p. 171
- ↑ The three states were New York, Rhode Island, and New Jersey. Allan Nevins, The Emergence of Lincoln: Prologue to Civil War (1950), p. 312 notes that if the opposition had formed fusion tickets in every state, Lincoln still would have 169 electoral votes; he needed 152 to win the Electoral College. Potter, The impending crisis, 1848–1861 (1976) p. 437, and Luthin, The First Lincoln Campaign p. 227 both conclude it was impossible for Lincoln's opponents to combine because they hated each other. The fractured Democratic vote did tip California, Oregon, and four New Jersey "New Jersey's Vote in 1860". NY Times. December 26, 1892. electoral votes to Lincoln, giving him 180 Electoral College votes. 1860 election Only in California, Oregon, and Illinois was Lincoln's victory margin less than seven percent. In New England, he won every county.
- ↑ He carried the border slave states of Delaware and Maryland and losing Virginia and Tennessee. Breckinridge received very little support in the free states, showing some strength only in California, Oregon, and Pennsylvania.
- 1 2 3 "HarpWeek 1860 Election Overview". Retrieved 2011-03-20.
- ↑ Freehling, William W., The Road to Disunion: Volume II. Secessionists Triumphant, 1854–1861, Oxford University Press, 2004, p. 447.
- ↑ "Deep South" here in presidential popular votes refers to Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi and Louisiana. It excludes South Carolina from the calculation, because it chose presidential electors in the state legislature in 1860, without a popular vote.
- ↑ "Republican ballot 1860". Retrieved 2011-04-28.
- ↑ "Election of 1860 – "Read Your Ballot"". Retrieved 2011-04-28. Ballots were printed sheets, usually printed by the party, with the name of the candidate(s) and the names of presidential electors who were pledged to that presidential candidate. Voters brought the ballot to the polling station and dropped it publicly into the election box. In order to receive any votes, a candidate (or his party) had to have ballots printed and organize a group of electors pledged to that candidate. Except in some border areas, the Republican party did not attempt any organization in the South and did not print ballots there because almost no one was willing to acknowledge publicly they were voting for Lincoln for fear of violent retribution.
- ↑ "1860 Election Returns in Virginia, by County" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-04-28.
- ↑ St. Louis County, Missouri and Gasconade County, Missouri according to http://www.missouridivision-scv.org/election.htm
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dubin, Michael J., United States Presidential Elections, 1788–1860: The Official Results by County and State, McFarland & Company, 2002, p. 187
- 1 2 3 4 Dubin, Michael J., United States Presidential Elections, 1788–1860: The Official Results by County and State, McFarland & Company, 2002, p. 188
- ↑ Mary A. Decredico, "Sectionalism and the Secession Crisis," in John b. Boles, ed., A Companion to the American South (2004) pp. 240
- ↑ Decredico, p. 243
- ↑ Wyatt-Brown, Bertram. Yankee Saints and Southern Sinners (1990)
- ↑ Avery Craven, The Growth of Southern Nationalism, 1848–1861, 1953. ISBN 978-0-8071-0006-6, p. 391, 394, 396.
Bibliography
- Carwardine, Richard (2003). Lincoln. Pearson Education Ltd. ISBN 978-0-582-03279-8.
- Chadwick, Bruce (2010). Lincoln for President: An Unlikely Candidate, An Audacious Strategy, and the Victory No One Saw Coming. Sourcebooks, Inc. ISBN 978-1-4022-2858-2.
- Decredico, Mary A. "Sectionalism and the Secession Crisis," in John b. Boles, ed., A Companion to the American South (2004) pp. 231-248, on the historiography of Southend motivations
- Donald, David Herbert (1996) [1995]. Lincoln. New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-0-684-82535-9.
- Egerton, Douglas (2010). Year of Meteors: Stephen Douglas, Abraham Lincoln, and the Election That Brought on the Civil War. Bloomsbury Press. ISBN 978-1-59691-619-7.
- Foner, Eric (1995) [1970]. Free Soil, Free Labor, Free Men: The Ideology of the Republican Party before the Civil War. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509497-8.
- Fuller, A. James, ed. The Election of 1860 Reconsidered (Kent State Univ Press, 2013); 288pp; essays by scholars; online
- Goodwin, Doris Kearns (2005). Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham Lincoln. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-82490-6.
- Green, Michael S. (2011). Lincoln and the Election of 1860. SIU Press. ISBN 978-0-8093-8636-9.
- Grinspan, Jon, "'Young Men for War': The Wide Awakes and Lincoln's 1860 Presidential Campaign," Journal of American History 96.2 (2009): online.
- Harris, William C. (2007). Lincoln's Rise to the Presidency. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-1520-9.
- Holt, Michael F. (1978). The Political Crisis of the 1850s.
- Holzer, Harold (2004). Lincoln at Cooper Union: The Speech That Made Abraham Lincoln President. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-9964-0.
- Johannsen, Robert W. Stephen A. Douglas (1973), standard biography
- Luebke, Frederick C. (1971). Ethnic Voters and the Election of Lincoln.
- Luthin, Reinhard H. (1944). The First Lincoln Campaign. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-8446-1292-8.along with Nevins, the most detailed narrative of the election
- Mansch, Larry D. (2005). Abraham Lincoln, President-Elect: The Four Critical Months from Election to Inauguration. McFarland. ISBN 0-7864-2026-X.
- Nevins, Allan (1950). Ordeal of the Union; Vol. IV: The Emergence of Lincoln: Prologue to Civil War, 1859–1861. Macmillan Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-684-10416-4.
- Nichols, Roy Franklin. The Disruption of American Democracy (1948), pp. 348–506, focused on the Democratic party
- Parks, Joseph Howard. John Bell of Tennessee (1950), standard biography
- Potter, David M. (1976). The impending crisis, 1848–1861. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-131929-7.
- Rhodes, James Ford (1920). History of the United States from the Compromise of 1850 to the McKinley-Bryan Campaign of 1896. vol. 2, ch. 11. highly detailed narrative covering 1856–60
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States presidential election, 1860. |
- 1860 election: State-by-state Popular vote results
- 1860 popular vote by counties
- United States Presidential Election of 1860 in Encyclopedia Virginia
- Election of 1860 er.lib.virginia.edu/elections/maps/1860.gif Electoral Map from 1860]
- Abraham Lincoln: Original Letters and Manuscripts, 1860 Shapell Manuscript Foundation
- Lincoln's election – details
- Report on 1860 Republican convention
- Overview of Constitutional Union National Convention
- How close was the 1860 election? at the Wayback Machine (archived August 25, 2012) — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Abraham Lincoln: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- Presidential Election of 1860: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- Bill Bigelow, "The Election of 1860 Role Play", 12-page lesson plan for high school students, Zinn Education Project/Rethinking Schools
- Election of 1860 in Counting the Votes






.jpg)