Typhoon Rammasun
| Typhoon (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 5 (Saffir–Simpson scale) | |
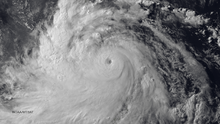
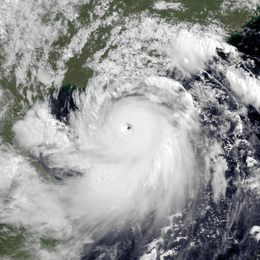 Typhoon Rammasun near peak intensity on July 18 as it skirted Hainan Island | |
| Formed | July 9, 2014 |
| Dissipated | July 20, 2014 |
| Highest winds |
10-minute sustained: 165 km/h (105 mph) 1-minute sustained: 260 km/h (160 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 935 hPa (mbar); 27.61 inHg |
| Fatalities | 195 total |
| Damage | $7.13 billion (2014 USD) |
| Areas affected | |
| Part of the 2014 Pacific typhoon season | |
Typhoon Rammasun, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Glenda, was one of only two Category 5 super typhoons on record in the South China Sea, with the other being Pamela in 1954. Rammasun had destructive impacts across the Philippines, South China, and Vietnam in July 2014. It was the seventh tropical cyclone of the season to be named by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA). Rammasun is a Siamese word for thunder god.[1] After Lingling and Kajiki earlier in 2014, Rammasun became the third tropical cyclone, and first typhoon to directly impact the Philippines in 2014. The storm formed in the Intertropical Convergence Zone, an area near the equator where the northeast and southeast trade winds come together, and slowly drifted northwest. Having passed through the islands of Micronesia, the system turned west and quickly moved under the influence of a subtropical ridge (STR). Rammasun posed a significant threat to the Philippine island of Luzon, as it was expected to reach typhoon intensity before making landfall there.[2] Though initially forecast to make landfall in Cagayan Valley, the storm followed a more westerly path and was later forecast to make landfall in the Bicol Region and then pass through Bataan and Zambales before brushing past Metro Manila.[3]
In preparation for the storm, Governor of Guam Eddie Calvo declared the island in Condition of Readiness 3[4] and later upgraded it to Condition of Readiness 1. On July 11, NASA satellites revealed Rammasun passing directly over Guam.[5] American National Weather Service stated that an unexpected rise in wind shear kept the system from intensifying much further before reaching Guam. Rammasun only made landfall on Guam as a tropical depression, with winds much weaker than earlier anticipated.[6] However, under the system, the island received a substantial amount of rainfall, making that day the wettest in around 3 months. The United States territory received 25 to 50 mm (1 to 2 inches) of rain.[7] Along with the Philippines, Taiwan also expected impact from Rammasun. Moderate to heavy rainfall was predicted through most of the country.[8][9] Chinese meteorologists were focusing on second and/or third landfalls in the Chinese Hainan province and northern Vietnam. Residents of Hong Kong were also warned of rainfall and subsequent landslides.[10]
Following the closure of maritime seaports, more than 100 passengers were reportedly stranded at the Port of Batangas, along with 39 rolling cargoes. Meanwhile, at least 841 passengers were stranded in five ports in the Bicol region, namely Matnog, Tabaco, Bulan, Cataingan and Pilar.[11] A total 50 flights were cancelled and over 100 thousand families were evacuated as the typhoon neared landfall.[12][13] The Philippine Department of Health said that they have prepared all government hospitals to aid the rescue and relief process during and after the typhoon. They claimed that they are much better prepared now, than they were for earlier typhoons.[14] Ahead of the landfall, a city in the province of Albay had declared a state of calamity.[15] At around 17:00 Philippine Standard Time (09:00 UTC), Rammasun's eye passed directly over Rapu-Rapu, Albay while the storm was at its initial peak intensity.[16] Various parts of the National Capital Region reported power outages during the storm. They were reportedly caused by "a temporary system balance at 1:29 a.m. due to a sudden plant outage."[17] At least 6,000 people were stranded at various seaports throughout the country due to the storm.[18]
Throughout its devastating journey through southern Luzon, the powerful typhoon barely weakened but instead maintained its strength and even intensified as it made its way across the Bicol Region.
Meteorological history
On July 9, the United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) started to monitor a tropical disturbance, that had developed to the east of the Micronesian State of Chuuk.[19] At this time the system had a broad and ill defined circulation center which was associated with flaring and disorganized atmospheric convection.[19] Over the next day the system gradually consolidated within an area of favorable conditions, with convection wrapping around the systems obscured low level circulation center.[20] The system was subsequently declared a tropical depression during the next day, by both the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and the JTWC with the latter assigning it the designation 09W.[21][22]

Early on July 11, the JTWC reported that the system had intensified into a tropical storm, after they had assessed the intensity slightly higher than the Dvorak estimates from various agencies.[23] Later that day as the system approached Guam, the JTWC reported that the system had not intensified into a tropical storm and downgraded it to a tropical depression.[24] This was because of the lack of supporting Dvorak estimates from various agencies and various observations from Guam, that showed the system was a poorly defined low level circulation center with deep convection sheared to the northwest of the center.[24] Early on July 12, the JMA reported that the depression had become a tropical storm and named it Rammasun, as the system passed through the Rota Channel to the north of Guam.[25][26] Later that day as Rammasun moved westwards under the influence of the subtropical ridge of high pressure, the JTWC reported that it had regained tropical storm status after Dvorak estimates from various agencies supported it and the low level structure of the system had improved.[27]
Rammasun entered the Philippine area of responsibility and was given a local name, Glenda on July 13.[28] The storm maintained intensity while a burst of deep central convection developed and the LLCC became slightly more well defined.[29] Over the next couple of hours, vertical wind shear decreased gradually. Rammasun tracked in a westerly direction along the periphery of the steering subtropical ridge. Outflow improved along the southwestern quadrant[30] and Rammasun became a typhoon.[31] The LLCC consolidated while convective banding became well defined and tightly wrapped. During July 14, both the JTWC and the JMA upgraded Rammassun to a typhoon after Dvorak estimates from various agencies suggested a minimum windspeed of 65 knots (120 km/h; 75 mph).[32][33]
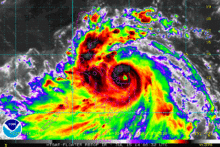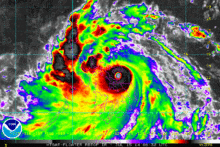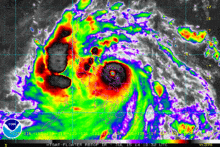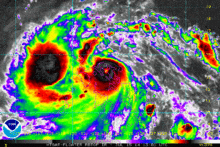
Shortly before its Philippine landfall, Rammasun developed a 10 nautical miles (19 km; 12 mi) wide eye. The storm had vigorous equatorward and westward outflow. At that time, the storm was peaking at 80 knots (150 km/h; 92 mph) 1-minute sustained winds[34] and 75 knots (139 km/h; 86 mph) 10-minute sustained winds.[35] Though initially expect to maintain that intensity and make landfall before weakening into a tropical storm again due to land interaction, Rammasun further intensified. Some six hours later, the JTWC spotted a 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi) eye, twice as wide as previously reported. The 1-minute sustained winds were set at 100 knots (190 km/h; 120 mph), equivalent to Category 3 of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale (SSHWS).[36] Rammasun continued to strengthen, despite land interaction. Post landfall, the storm's windspeed continued to rise, as it was located in a very favorable environment. JTWC initially reported winds of 110 knots (200 km/h; 130 mph) 1-minute sustained winds[37] before correcting it to 115 knots (213 km/h; 132 mph) in their best track, making it a Category-4 equivalent typhoon.[38]
By 00:00 UTC on July 16, Rammasun's eye had re-emerged into the South China Sea. The typhoon lost its eye feature due to its interaction with Philippine's rugged terrain. The convective structure had slightly degraded. However, convective banding remained tightly wrapped around the LLCC.[39]
On July 18, Rammasun entered another area of very warm sea-surface temperatures. Consequently, Rammasun rapidly deepened and was upgraded to a Category 4 super typhoon by the JTWC,[40][41] which was upgraded to Category 5 in post-season reanalysis. Later that day, Rammasun made landfall over Hainan at peak intensity,[42] making it one of only two typhoons to make landfall at Category 5-equivalent intensity in China.[43] The next day, the storm started to weaken. Later that day, both agencies downgraded Rammasun to a tropical storm as it moved to the province of Guangxi and made its third landfall.[44][45] The JTWC made its final warning on the system in the night of the same day. Early on July 20, the JMA reported that Rammasun had weakened into a tropical depression before it was last noted later that day over the Chinese Province of Yunnan.[46][47][48]
Preparations and impact
| Storm | Season | Cost, equivalent to US$ in 2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Mireille | 1991 | $17.4 billion |
| Songda | 2004 | $11.3 billion |
| Fitow | 2013 | $10.6 billion |
| Prapiroon | 2000 | $8.26 billion |
| Herb | 1996 | $7.56 billion |
| Flo | 1990 | $7.26 billion |
| Rammasun | 2014 | $7.14 billion |
| Morakot | 2009 | $6.85 billion |
| Maemi | 2003 | $6.18 billion |
Mariana Islands
On July 10, as the JTWC initiated advisories on the system, the United States National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office in Tiyan, Guam (NWS Guam) issued a tropical storm watch for Guam, Rota, Tinian, Saipan and surrounding waters out to 75 km (45 mi).[49][49] Later that day the Governor of Guam Eddie Calvo, declared the island nation to be in Tropical Cyclone Condition of Readiness 3 (TCCOR 3), as the strongest winds over the island were expected to peak between 80–95 km/h (50–60 mph).[50] Both of these warnings meant that destructive tropical storm force winds were possible on the islands during the next 48 hours.[49] After the system was declared a tropical storm, tropical storm warnings were issued for Guam and Rota, while TCCOR 2 was declared for Guam.[51][52][53] After TCCOR 2 was declared, all of the non essential agencies of the Guam Government and several business were shut down, including the Judiciary and University.[52][53][54][55] Six elementary schools around the island were used as storm shelters, while woman who had been pregnant for more than 38 weeks and or high risk were asked to report to the Guam Memorial Hospital.[52] A TCCOR 1 was subsequently declared during July 11, as destructive winds were expected to impact the island nation within twelve hours.[55] As a result, all outdoor activity was prohibited until early the next day when the watches and warnings were cancelled after the system was downgraded to a tropical depression.[56][57] Eddie Calvo subsequently reverted the TCCOR for Guam to the seasonal TCCOR, as no damaging or destructive winds were expected to affect Guam as the depression moved through the Rota Channel.[58] NWS Guam subsequently noted that heavy thunderstorms had developed near the center of the system as it moved through the Rota Channel and that the weather over Guam could have been a lot worse.[26]
Philippines
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Costliest Philippine typhoons | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
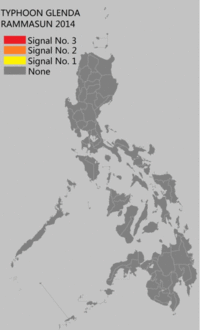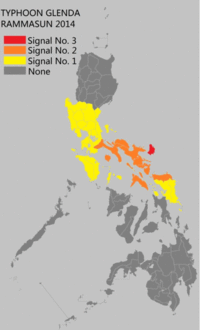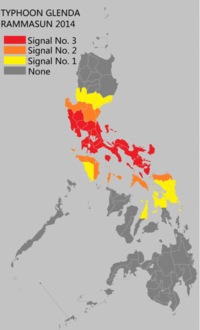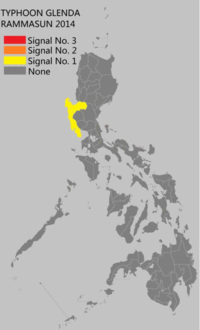
Rammasun (known as "Glenda" in the Philippines) was the first typhoon to impact the Philippines in over eight months, the previous being Typhoon Haiyan. Preparations for Rammasun started in the island nation, early on July 14.[60] In the wake of the storm, The National Transmission Corporation of the country said in their statement, "Preparations included ensuring the reliability of communications equipment, availability of hardware materials and supplies necessary for the repair of damages to facilities, as well as the positioning of line crews in strategic areas, to facilitate immediate restoration work."[61] Storm warning signal number 3 was hoisted over Catanduanes, while signal number 2 was raised over areas such as Camarines Norte, Burias Island, Ticao Island, Marinduque, and southern Quezon.[62] Several islands in southern Luzon and eastern western, and central Visayas were put under storm signal number 1. Over 12 million people, in all, were asked to brace for the typhoon. Classes on all levels were reportedly suspended for the next two days.[63] Philippine National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council's head Alexander Pama, in an interview, said "We are already warning the public to be on alert for possible effects of the weather disturbance: landslides, flash floods, strong rains and winds." more than 1,300 villages were advised about floods or landslides.[64] The Embassy of the United States in Manila cancelled non-immigrant visa applicant interviews scheduled for July 15 and 16. All applicants were asked to reschedule their interviews.[65] The Philippine Coast Guard asked all shipping vessels to refrain from travelling. Spokesperson Armand Balilo said "Authorities are already on standby to prevent any maritime vessels from sailing as the Philippines braces for Glenda (Ramassun).[66] Department of the Interior and Local Government Director Edgar Tabell said "All DILG offices in Luzon and Eastern Visayas have been activated to prepare for Glenda. Evacuation centers have been prepared and power lines, bridges and roads have also been checked." He also asked all local officials to fully cooperate with them and provide support to the residents.[67] As the typhoon neared the coastline of Philippines, the entire nation was put on red alert.[68] By the early hours of July 15, the government reportedly evacuated eastern coastal areas of the nation. PAGASA said "Storm surges of up to three meters were expected in coastal villages."[69] However, that evening, several other residents fled their homes as the typhoon intensified much more than anticipated.[70] The civil defence chief of Bicol, in an interview said "We are preparing for the worst... it is critical now that we finish the evacuations. About 6,000 residents had already moved to evacuation centres, with authorities aiming to have another 39,000 take shelter before the typhoon hits.[71] Several cities were warned of storm surge ranging from 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) to 3 metres (9.8 ft).[72] Immediately after the landfall, three fishermen were reported missing. They were reported to have gone out fishing a day ago from the Philippine province of Catanduanes, and failed to return.[73] A wall collapse in Quezon City injured two people.[74] At least 90% of the total residents of Metro Manila lost power, as poles were toppled and lines downed. The national grid corporation posted on Twitter, saying "Around 90% of Meralco’s franchise area is experiencing power outage brought about by downed poles, lines and outages of NGCP’s (National Grid Corporation of the Philippines) transmission lines due to Typhoon Glenda."[75] Strong winds from the storm destroyed several homes in the slums. Most of the capital area was also completely shut down.[76] As of July 17, the NDRRMC reported that the damages from the storm had reached 1 billion ($27 million).[77] Hong KongLate on July 16, the Hong Kong Observatory issued the Typhoon Standby Signal No. 1, before issuing the Typhoon Signal Number 3 during the next day as local winds strengthened gradually from the east.[78] Gale force winds were subsequently recorded offshore and on higher ground, before it made its closest point of approach during July 18, as it passed around 390 km (240 mi) to the southwest of Hong Kong.[78] Winds over the region gradually subsided before the signals were cancelled by the HKO early on July 19.[78] Over the region at least 51 trees were blown down while there were several reports of fallen objects including a lamp post on the Tsuen Wan flyover.[78] China_in_Haikou.ogv.jpg) Video of fallen trees in Haikou 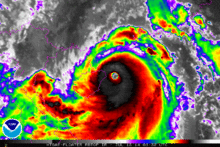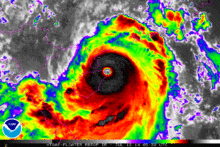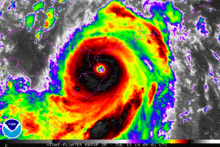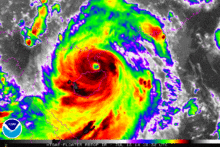 Typhoon Rammasun shows its landfall over China later on July 18 On July 17, Rammasun made landfall near Wenchang City on the island province of Hainan. The city's mayor, Liu Chun-mei, told the Xinhua News Agency that many houses had been damaged and more than 700,000 people evacuated. Qionghai also suffered heavy damage. Hainan closed all its airports while kindergartens and other schools were shut. Resorts in Hainan were ordered to close and the high speed train in Guangdong bound for Hainan suspended. The typhoon killed one person on the island[79] and injured 21. Waves reached up to 13 m (43 ft) on the northern and eastern coasts of the island and the Leizhou Peninsula.[80] The local government dispatched 66 officials in 13 locales to supervise preparations for the typhoon. Xinhua reported that 6,000 people on Hainan were evacuated. Bus companies also suspended operations due to heavy rains and high winds.[81] 51,000 homes were destroyed in Hainan[82] and at least 62 people were killed throughout the country.[83] Economic losses amounted to US$6.25 billion.[83] In Haikou, the capital of Hainan, a large number of trees were blown down throughout the city. Damage to shops, bus stops and vehicles due to rain and flooding was widespread. Large parts of the city were left without power and water. The army was called in to help clear fallen trees from roads. Along the shore of the city, several barges and other vessels ran aground. Rammasun is considered to be the most severe typhoon to hit the city in 41 years. VietnamVietnamese authorities ordered an evacuation of people from parts of the northern coast of the country on July 18 in preparation for Rammasun.[84] Typhoon Rammasun affected the nearby provinces of Haiphong, Thái Bình, and Nam Định. The officials of Quảng Ninh Province have evacuated more than 1,300 people to safe shelters. Prime Minister Nguyễn Tấn Dũng ordered authorities to help in evacuation and "require all boats to remain close to the shore". He commanded the army to install its forces in the areas for possible search and rescue operations.[85] Heavy rains caused minor flooding in urban areas of Hai Phong and the capital, Hanoi. It also submerged the streets of Nguyen Khuyen, Minh Khai, Truong Dinh and Hang Chuoi. Duong Anh Dien, a government official, told Tuoi Tre that he ordered the cancellation of "all administrative meetings". Residents near the coast areas were evacuated to the nearest designated evacuation sites. All vessels and boats were banned from leaving port. The National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting said the eye of the storm was about 210 kilometers east of Hoàng Sa with wind speeds reaching 149 kilometers per hour. The mountainous province of Bắc Kạn, Cao Bằng, Lai Chau, Lạng Sơn and Lào Cai were put on high alert for flash floods and landslides. Over twenty flights by Vietnam Airlines were cancelled or delayed at Noi Bai International Airport. The trade department reserved foods and goods to assure support for at least 250,000 people in case of an emergency.[86][87] Overall, around 500 homes were damaged. Throughout Vietnam, Rammasun is responsible for 27 deaths had caused damages of US$6 million.[88] RetirementAfter the system had caused damage to the Philippines, China and Vietnam, the name Rammasun was retired at the Third Joint Session of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee and WMO/ESCAP Panel on Tropical Cyclones during 2015.[89] The name Glenda was also retired by PAGASA after damages had exceeded 1 billion, while the name Gardo was selected to replace Glenda for the 2018 season.[90][91] In February 2016, Thailand provided replacement names for Rammasun, and a month later, the name Bualoi was chosen to replace it.[92] See also
Notes
References
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||