Solar eclipse of June 17, 1909
| Solar eclipse of June 17, 1909 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Hybrid |
| Gamma | 0.8957 |
| Magnitude | 1.0065 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 24 sec (0 m 24 s) |
| Coordinates | 82°54′N 123°36′E / 82.9°N 123.6°E |
| Max. width of band | 51 km (32 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 23:18:38 |
| References | |
| Saros | 145 (16 of 77) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9302 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on June 17, 1909. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This event was a hybrid, starting and ending as an annular eclipse.
The path of totality crossed the Arctic ocean, Canada, Greenland, central Russia, and central Asia.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1906-1909
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 115 | July 21, 1906 Partial |
120 | January 14, 1907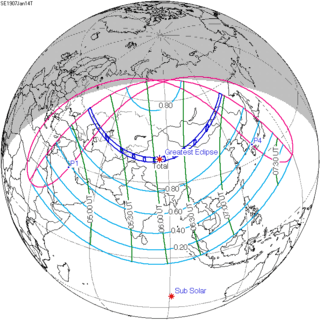 Total | |
| 125 | July 10, 1907 Annular |
130 | January 3, 1908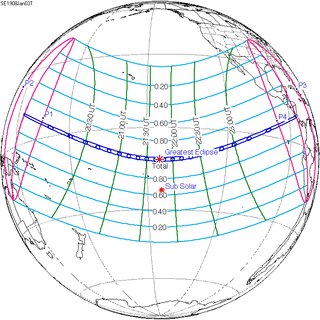 Total | |
| 135 | June 28, 1908 Annular |
140 | December 23, 1908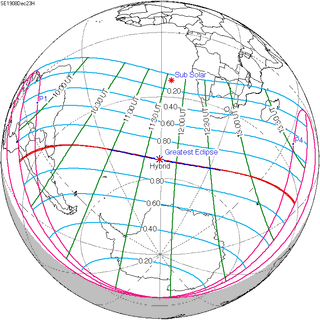 Hybrid | |
| 145 | June 17, 1909 Hybrid |
150 | December 12, 1909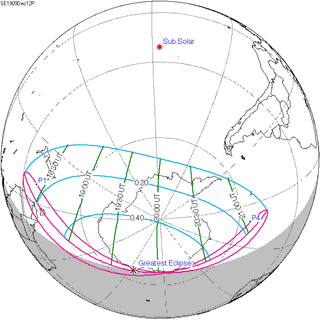 Partial | |
External links
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1909 June 17. |
