Betamethadol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 17199-55-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 10064061 |
| ChemSpider | 8239601 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL162243 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H29NO |
| Molar mass | 311.461 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
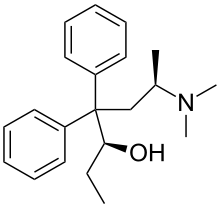
Betamethadol (INN), or β-methadol, also known as betametadol, is a synthetic opioid analgesic.[1] It is an isomer of dimepheptanol (methadol), the other being alphamethadol (α-methadol).[2] Betamethadol is composed of two isomers itself, L-β-methadol, and D-β-methadol.[2] Based on structure-activity relationships it can be inferred that both isomers are likely to be active as opioid analgesics, similarly to those of betacetylmethadol (β-acetylmethadol).[3]
See also
References
- ↑ F.. Macdonald (1997). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 1294. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 15 May 2012.
- 1 2 United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2006). Dictionnaire Multilingue Des Stupéfiants Et Des Substances Psychotropes Placés Sous Contrôle International. United Nations Publications. p. 103. ISBN 978-92-1-048117-5. Retrieved 15 May 2012.
- ↑ Newman JL, Vann RE, May EL, Beardsley PM (October 2002). "Heroin discriminative stimulus effects of methadone, LAAM and other isomers of acetylmethadol in rats". Psychopharmacology. 164 (1): 108–14. doi:10.1007/s00213-002-1198-8. PMID 12373424.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/14/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.