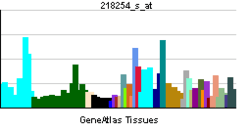
SAR1B
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
SAR1 gene homolog B (S. cerevisiae), also known as SAR1B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SAR1B gene.[3][4]
Function
SAR1B belongs to the Sar1-ADP ribosylation factor family of small GTPases,[5] which govern the intracellular trafficking of proteins in coat protein (COP)-coated vesicles.[6]
Clinical significance
Mutations in the SAR1B gene are associated with chylomicron retention disease (also known as Anderson disease) which is an autosomal recessive disorder of severe fat malabsorption.[7]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: SAR1B SAR1 gene homolog B (S. cerevisiae)".
- ↑ He H, Dai F, Yu L, She X, Zhao Y, Jiang J, Chen X, Zhao S (2002). "Identification and characterization of nine novel human small GTPases showing variable expressions in liver cancer tissues". Gene Expression. 10 (5-6): 231–42. PMID 12450215.
- ↑ Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T (January 2001). "Small GTP-binding proteins". Physiological Reviews. 81 (1): 153–208. PMID 11152757.
- ↑ Schekman R, Orci L (March 1996). "Coat proteins and vesicle budding". Science. 271 (5255): 1526–33. doi:10.1126/science.271.5255.1526. PMID 8599108.
- ↑ Jones B, Jones EL, Bonney SA, Patel HN, Mensenkamp AR, Eichenbaum-Voline S, Rudling M, Myrdal U, Annesi G, Naik S, Meadows N, Quattrone A, Islam SA, Naoumova RP, Angelin B, Infante R, Levy E, Roy CC, Freemont PS, Scott J, Shoulders CC (May 2003). "Mutations in a Sar1 GTPase of COPII vesicles are associated with lipid absorption disorders". Nature Genetics. 34 (1): 29–31. doi:10.1038/ng1145. PMID 12692552.
Further reading
- Jardim DL, da Cunha AF, Duarte Ada S, dos Santos CO, Saad ST, Costa FF (May 2005). "Expression of Sara2 human gene in erythroid progenitors". Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 38 (3): 328–33. PMID 15943909.
- Jones B, Jones EL, Bonney SA, Patel HN, Mensenkamp AR, Eichenbaum-Voline S, Rudling M, Myrdal U, Annesi G, Naik S, Meadows N, Quattrone A, Islam SA, Naoumova RP, Angelin B, Infante R, Levy E, Roy CC, Freemont PS, Scott J, Shoulders CC (May 2003). "Mutations in a Sar1 GTPase of COPII vesicles are associated with lipid absorption disorders". Nature Genetics. 34 (1): 29–31. doi:10.1038/ng1145. PMID 12692552.
- Aguglia U, Annesi G, Pasquinelli G, Spadafora P, Gambardella A, Annesi F, Pasqua AA, Cavalcanti F, Crescibene L, Bagalà A, Bono F, Oliveri RL, Valentino P, Zappia M, Quattrone A (February 2000). "Vitamin E deficiency due to chylomicron retention disease in Marinesco-Sjögren syndrome". Annals of Neurology. 47 (2): 260–4. doi:10.1002/1531-8249(200002)47:2<260::AID-ANA21>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID 10665502.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1-2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1-2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.