Enolase
| phosphopyruvate hydratase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Yeast enolase dimer.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.2.1.11 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9014-08-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Enolase, N-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 x-ray structure and catalytic mechanism of lobster enolase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Enolase_N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03952 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0227 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR020811 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00148 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1els | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1els | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Enolase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Enolase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00113 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000941 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00148 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Enolase, also known as phosphopyruvate hydratase, is a metalloenzyme responsible for the catalysis of the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the ninth and penultimate step of glycolysis. The chemical reaction catalyzed by enolase is:
- 2-phospho-D-glycerate phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O
Enolase belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the hydro-lyases, which cleave carbon-oxygen bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme is 2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase (phosphoenolpyruvate-forming).
The reaction is reversible, depending on environmental concentrations of substrates.[3] The optimum pH for the human enzyme is 6.5.[4] Enolase is present in all tissues and organisms capable of glycolysis or fermentation. The enzyme was discovered by Lohmann and Meyerhof in 1934,[5] and has since been isolated from a variety of sources including human muscle and erythrocytes.[4] In humans, deficiency of ENO1 is linked to hereditary haemolytic anemia while ENO3 deficiency is linked to glycogen storage disease XIII.
Isozymes
In humans there are three subunits of enolase, α, β, and γ, each encoded by a separate gene that can combine to form five different isoenzymes: αα, αβ, αγ, ββ, and γγ.[3][6] Three of these isoenzymes (all homodimers) are more commonly found in adult human cells than the others:
- αα or non-neuronal enolase (NNE), which is found in a variety of tissues, including liver, brain, kidney, spleen, adipose. It is present at some level in all normal human cells. Also known as enolase 1
- ββ or muscle specific enolase (MSE). Also known as enolase 3. This enzyme is largely restricted to muscle where it is present at very high levels in muscle
- γγ or neuron-specific enolase (NSE). Also known as enolase 2. Expressed at very high levels in neurons and neural tissues, where it can account for as much as 3% of total soluble protein. It is expressed at much lower levels in most mammalian cells.
When present in the same cell, different isozymes readily form heterodimers.
Structure
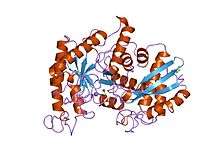
Enolase has a molecular weight of 82,000-100,000 Daltons depending on the isoform.[3][4] In human alpha enolase, the two subunits are antiparallel in orientation so that Glu20 of one subunit forms an ionic bond with Arg414 of the other subunit.[3] Each subunit has two distinct domains. The smaller N-terminal domain consists of three α-helices and four β-sheets.[3][6] The larger C-terminal domain starts with two β-sheets followed by two α-helices and ends with a barrel composed of alternating β-sheets and α-helices arranged so that the β-beta sheets are surrounded by the α-helices.[3][6] The enzyme’s compact, globular structure results from significant hydrophobic interactions between these two domains.
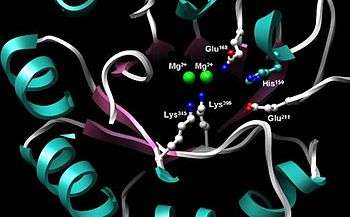
Enolase is a highly conserved enzyme with five active-site residues being especially important for activity. When compared to wild-type enolase, a mutant enolase that differs at either the Glu168, Glu211, Lys345, or Lys396 residue has an activity level that is cut by a factor of 105.[3] Also, changes affecting His159 leave the mutant with only 0.01% of its catalytic activity.[3] An integral part of enolase are two Mg2+ cofactors in the active site, which serve to stabilize negative charges in the substrate.[3][6]
Recently, moonlighting functions of several enolases, such as interaction with plasminogen, have brought interest to the enzymes' catalytic loops and their structural diversity.[7][8]
|
Mechanism

Using isotopic probes, the overall mechanism for converting 2-PG to PEP is proposed to be an E1cb elimination reaction involving a carbanion intermediate.[9] The following detailed mechanism is based on studies of crystal structure and kinetics.[3][10][11][12][13][14][15] When the substrate, 2-phosphoglycerate, binds to α-enolase, its carboxyl group coordinates with two magnesium ion cofactors in the active site. This stabilizes the negative charge on the deprotonated oxygen while increasing the acidity of the alpha hydrogen. Enolase’s Lys345 deprotonates the alpha hydrogen, and the resulting negative charge is stabilized by resonance to the carboxylate oxygen and by the magnesium ion cofactors. Following the creation of the carbanion intermediate, the hydroxide on C3 is eliminated as water with the help of Glu211, and PEP is formed.
Additionally, conformational changes occur within the enzyme that aid catalysis. In human α-enolase, the substrate is rotated into position upon binding to the enzyme due to interactions with the two catalytic magnesium ions, Gln167, and Lys396. Movements of loops Ser36 to His43, Ser158 to Gly162, and Asp255 to Asn256 allow Ser39 to coordinate with Mg2+ and close off the active site. In addition to coordination with the catalytic magnesium ions, the pKa of the substrate’s alpha hydrogen is also lowered due to protonation of the phosphoryl group by His159 and its proximity to Arg374. Arg374 also causes Lys345 in the active site to become deprotonated, which primes Lys345 for its role in the mechanism.
Diagnostic uses
In recent medical experiments, enolase concentrations have been sampled in an attempt to diagnose certain conditions and their severity. For example, higher concentrations of enolase in cerebrospinal fluid more strongly correlated to low-grade astrocytoma than did other enzymes tested (aldolase, pyruvate kinase, creatine kinase, and lactate dehydrogenase).[16] The same study showed that the fastest rate of tumor growth occurred in patients with the highest levels of CSF enolase. Increased levels of enolase have also been identified in patients who have suffered a recent myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident. It has been inferred that levels of CSF neuron-specific enolase, serum NSE, and creatine kinase (type BB) are indicative in the prognostic assessment of cardiac arrest victims.[17] Other studies have focused on the prognostic value of NSE values in cerebrovascular accident victims.[18]
Autoantibodies to alpha-enolase are associated with the rare syndrome called Hashimoto's encephalopathy.[19]
Inhibitors
Small-molecule inhibitors of enolase have been synthesized as chemical probes of the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme. The most potent of these is phosphonoacetohydroxamate, which in its unprotonated form has pM affinity for the enzyme. It has structural similarity to the presumed catalytic intermediate, between PEP and 2-PG. Attempts have been made to use this inhibitor as an anti-trypanosome drug, and more recently, as an anti-cancer agent, specifically, in glioblastoma that are enolase-deficient due to homozygous deletion of the ENO1 gene as part of the 1p36 locus {{PMID:22895339}}. The natural product antibiotic, SF-2312, is an inhibitor of Enolase 4zcw that binds in manner similar to phoshphonoacetohydroxamate 4za0.
Fluoride is a known competitor of enolase’s substrate 2-PG. The fluoride is part of a complex with magnesium and phosphate, which binds in the active site instead of 2-PG.[4] As such, drinking fluoridated water provides fluoride at a level that inhibits oral bacteria enolase activity. Disruption of the bacteria’s glycolytic pathway - and, thus, its normal metabolic functioning - prevents dental caries from forming.[20][21]
References
- ↑ PDB: 2ONE; Zhang E, Brewer JM, Minor W, Carreira LA, Lebioda L (October 1997). "Mechanism of enolase: the crystal structure of asymmetric dimer enolase-2-phospho-D-glycerate/enolase-phosphoenolpyruvate at 2.0 A resolution". Biochemistry. 36 (41): 12526–34. doi:10.1021/bi9712450. PMID 9376357.
- ↑ PDB: 2XSX; Vollmar M, Krysztofinska E, Chaikuad A, Krojer T, Cocking R, Vondelft F, Bountra C, Arrowsmith CH, Weigelt J, Edwards A, Yue WW, Oppermann U (2010). "Crystal structure of human beta enolase ENOB". To be published.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Pancholi V (June 2001). "Multifunctional alpha-enolase: its role in diseases". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 58 (7): 902–20. doi:10.1007/PL00000910. PMID 11497239.
- 1 2 3 4 Hoorn RK, Flickweert JP, Staal GE (1974). "Purification and properties of enolase of human erythroctyes". Int J Biochem. 5 (11–12): 845–52. doi:10.1016/0020-711X(74)90119-0.
- ↑ Lohman K & Meyerhof O (1934) Über die enzymatische umwandlung von phosphoglyzerinsäure in brenztraubensäure und phosphorsäure (Enzymatic transformation of phosphoglyceric acid into pyruvic and phosphoric acid). Biochem Z 273, 60–72.
- 1 2 3 4 Peshavaria M, Day IN (April 1991). "Molecular structure of the human muscle-specific enolase gene (ENO3)". The Biochemical Journal. 275 ( Pt 2) (Pt 2): 427–33. doi:10.1042/bj2750427. PMC 1150071
 . PMID 1840492.
. PMID 1840492. - ↑ Ehinger S, Schubert WD, Bergmann S, Hammerschmidt S, Heinz DW (October 2004). "Plasmin(ogen)-binding alpha-enolase from Streptococcus pneumoniae: crystal structure and evaluation of plasmin(ogen)-binding sites". Journal of Molecular Biology. 343 (4): 997–1005. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.088. PMID 15476816.
- ↑ Raghunathan K, Harris PT, Spurbeck RR, Arvidson CG, Arvidson DN (June 2014). "Crystal structure of an efficacious gonococcal adherence inhibitor: an enolase from Lactobacillus gasseri". FEBS Letters. 588 (14): 2212–6. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.05.020. PMID 24859038.
- ↑ Dinovo EC, Boyer PD (1971). "Isotopic probes of the enolase reaction mechanism". J Biol Chem. 240: 4586–93.
- ↑ Poyner RR, Laughlin LT, Sowa GA, Reed GH (February 1996). "Toward identification of acid/base catalysts in the active site of enolase: comparison of the properties of K345A, E168Q, and E211Q variants". Biochemistry. 35 (5): 1692–9. doi:10.1021/bi952186y. PMID 8634301.
- ↑ Reed GH, Poyner RR, Larsen TM, Wedekind JE, Rayment I (December 1996). "Structural and mechanistic studies of enolase". Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 6 (6): 736–43. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(96)80002-9. PMID 8994873.
- ↑ Wedekind JE, Reed GH, Rayment I (April 1995). "Octahedral coordination at the high-affinity metal site in enolase: crystallographic analysis of the MgII--enzyme complex from yeast at 1.9 A resolution". Biochemistry. 34 (13): 4325–30. doi:10.1021/bi00013a022. PMID 7703246.
- ↑ Wedekind JE, Poyner RR, Reed GH, Rayment I (August 1994). "Chelation of serine 39 to Mg2+ latches a gate at the active site of enolase: structure of the bis(Mg2+) complex of yeast enolase and the intermediate analog phosphonoacetohydroxamate at 2.1-A resolution". Biochemistry. 33 (31): 9333–42. doi:10.1021/bi00197a038. PMID 8049235.
- ↑ Larsen TM, Wedekind JE, Rayment I, Reed GH (April 1996). "A carboxylate oxygen of the substrate bridges the magnesium ions at the active site of enolase: structure of the yeast enzyme complexed with the equilibrium mixture of 2-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenolpyruvate at 1.8 A resolution". Biochemistry. 35 (14): 4349–58. doi:10.1021/bi952859c. PMID 8605183.
- ↑ Duquerroy S, Camus C, Janin J (October 1995). "X-ray structure and catalytic mechanism of lobster enolase". Biochemistry. 34 (39): 12513–23. doi:10.1021/bi00039a005. PMID 7547999.
- ↑ Royds JA, Timperley WR, Taylor CB (December 1981). "Levels of enolase and other enzymes in the cerebrospinal fluid as indices of pathological change". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 44 (12): 1129–35. doi:10.1136/jnnp.44.12.1129. PMC 491233
 . PMID 7334408.
. PMID 7334408. - ↑ Roine RO, Somer H, Kaste M, Viinikka L, Karonen SL (July 1989). "Neurological outcome after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Prediction by cerebrospinal fluid enzyme analysis". Archives of Neurology. 46 (7): 753–6. doi:10.1001/archneur.1989.00520430047015. PMID 2742544.
- ↑ Hay E, Royds JA, Davies-Jones GA, Lewtas NA, Timperley WR, Taylor CB (July 1984). "Cerebrospinal fluid enolase in stroke". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 47 (7): 724–9. doi:10.1136/jnnp.47.7.724. PMC 1027902
 . PMID 6747647.
. PMID 6747647. - ↑ Fujii A, Yoneda M, Ito T, Yamamura O, Satomi S, Higa H, Kimura A, Suzuki M, Yamashita M, Yuasa T, Suzuki H, Kuriyama M (May 2005). "Autoantibodies against the amino terminal of alpha-enolase are a useful diagnostic marker of Hashimoto's encephalopathy". Journal of Neuroimmunology. 162 (1-2): 130–6. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2005.02.004. PMID 15833368.
- ↑ "Populations receiving optimally fluoridated public drinking water--United States, 2000". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 51 (7): 144–7. February 2002. PMID 11905481.
- ↑ Hüther FJ, Psarros N, Duschner H (April 1990). "Isolation, characterization, and inhibition kinetics of enolase from Streptococcus rattus FA-1". Infection and Immunity. 58 (4): 1043–7. PMC 258580
 . PMID 2318530.
. PMID 2318530.
Further reading
- Holt A, Wold F (December 1961). "The isolation and characterization of rabbit muscle enolase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 236: 3227–31. PMID 13908561.
- Boyer, P.D., Lardy, H. and Myrback, K. (Eds.), The Enzymes, 2nd ed., vol. 5, Academic Press, New York, 1961, p. 471-494.
- Westhead EW, Mclain G (August 1964). "A purification of brewers' and bakers' yeast enolase yielding a single active component". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 239: 2464–8. PMID 14235523.
External links
- Enolase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)