Médio Purus Extractive Reserve
| Médio Purus Extractive Reserve | |
|---|---|
| Reserva Extrativista do Médio Purus | |
|
IUCN category VI (protected area with sustainable use of natural resources) | |
 | |
| Nearest city | Lábrea, Amazonas |
| Coordinates | 7°37′34″S 66°16′18″W / 7.62622°S 66.271674°WCoordinates: 7°37′34″S 66°16′18″W / 7.62622°S 66.271674°W |
| Area | 604,209 hectares (1,493,030 acres) |
| Designation | Extractive reserve |
| Created | 8 May 2008 |
| Administrator | Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation |
The Médio Purus Extractive Reserve (Portuguese: Reserva Extrativista do Médio Purus) is an extractive reserve in the state of Amazonas, Brazil.
Location
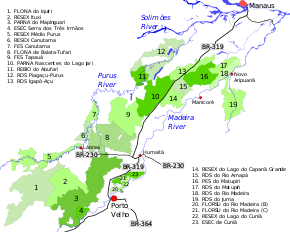
5. Médio Purus Extractive Reserve
The Médio Purus Extractive Reserve is divided between the municipalities of Lábrea (91.41%), Pauini (8.26%) and Tapauá (0.33%) in the state of Amazonas. It has an area of 604,209 hectares (1,493,030 acres).[1] The reserve extends along the Purus River from just below the town of Pauini to the west, down to the town of Lábrea to the east.[2] The Purus River has muddy waters and often shifts its bed.[3] The reserve is largely surrounded by indigenous territories. The Canutama Extractive Reserve is downstream from the Médio Purus Extractive Reserve. The Iquiri National Forest lies to the south.[2]
Temperatures range from 22 to 32 °C (72 to 90 °F) with an average of 25 °C (77 °F). Vegetation includes dense alluvial rainforest and dense tropical lowland rainforest. Tree species include Piranhea trifoliata, Brazil nut (Bertholletia excelsa), rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis), Hevea spruceana and Parkia pendula.[3] The reserve is occupied by about 92 indigenous or riverine communities whose main economic activities are collection of forest products such as Brazil nuts, copaíba, andiroba, rubber, açaí, urucurí and bacaba, and sustainable fishing.[3]
History
The reserve was created in response to a request to IBAMA in 2001 by the local extractive community association for the right to occupy the land and to expel communities that were degrading the environment.[4] The Médio Purus Extractive Reserve was created by federal decree on 8 May 2008.[5] It is administered by the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation (ICMBio).[6] It is classed as IUCN protected area category VI (protected area with sustainable use of natural resources). It aims to protect the livelihoods of the traditional residents and ensure the use and conservation of renewable natural resources traditionally used by these communities.[3]
On 18 September 2008 the Instituto Nacional de Colonização e Reforma Agrária (INCRA – National Institute for Colonisation and Agrarian Reform) recognized the reserve as supporting 900 families, who would qualify for PRONAF support. This was revised to 1,400 families of 30 December 2008. On 29 April 2010 INCRA and ICMBio agreed to incorporate into the reserve the rural properties named Seringal Quichiã, Seringal Parijós I and Seringal Parijós II, with a total area of 23,102 hectares (57,090 acres). The deliberative council was established on 4 November 2010.[5]
An ordnance of 9 January 2012 provided for a consistent and integrated approach to preparing management plans for the conservation units in the BR-319 area of influence. These are the Abufari Biological Reserve, Cuniã Ecological Station, Nascentes do Lago Jari and Mapinguari national parks, Balata-Tufari, Humaitá and Iquiri national forests, and the Lago do Capanã-Grande, Rio Ituxi, Médio Purus and Lago do Cuniã extractive reserves. The usage plan of the reserve was approved on 8 November 2012.[5]
Notes
- ↑ RESEX Médio Purus – ISA, Informações gerais.
- 1 2 RESEX Médio Purus – ISA, Informações gerais (mapa).
- 1 2 3 4 Unidade de Conservação ... MMA.
- ↑ RESEX Médio Purus – ISA, Características.
- 1 2 3 RESEX Médio Purus – ISA, Historico Juridico.
- ↑ Resex do Médio Purus – ICMBio.
Sources
- Resex do Médio Purus (in Portuguese), ICMBio: Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation, retrieved 2016-09-03
- RESEX Médio Purus (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-09-03
- Unidade de Conservação: Reserva Extrativista do Médio Purus (in Portuguese), MMA: Ministério do Meio Ambiente, retrieved 2016-09-03