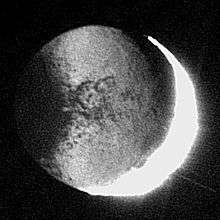
Planetshine

Planetshine is the illumination, by reflected sunlight from a planet, of part of the otherwise dark side of one of its moons. The best known example of planetshine is earthshine, which can be seen from Earth when the Moon is new,[1] or nearly so. Typically, this results in the side of the Moon opposite the Sun being bathed in a soft, faint light. Planetshine has been observed elsewhere in the solar system: in particular, it has recently been used by the Cassini space probe to image portions of the moons of Saturn even when they are not directly lit by the Sun.
Earthshine

Earthshine is reflected earthlight visible on Moon's night side. It is also known as the Moon's ashen glow or as the old Moon in the new Moon's arms.

Earthshine is most readily observable from shortly before until shortly after a new moon, during the waxing or waning crescent phase. When the Moon is new as viewed from Earth, Earth is nearly fully lit up as viewed from the Moon. Sunlight is reflected from the Earth to the night side of the Moon. The night side appears to glow faintly and the entire orb of the Moon is dimly visible.

Leonardo da Vinci explained the phenomenon in the early 16th century when he realized that both Earth and the Moon reflect sunlight at the same time. Light is reflected from the Earth to the Moon and back to the Earth as earthshine.
Earthshine is used to help determine the current albedo of the Earth. The data are used to analyze global cloud cover, a climate factor. Oceans reflect the least amount of light, roughly 10%. Land reflects anywhere from 10–25% of the Sun's light, and clouds reflect around 50%. So, the part of the Earth where it is daytime and from which the Moon is visible determines how bright the Moon's earthshine appears at any given time.

Studies of earthshine can be used to show how the Earth's cloud cover varies over time. Preliminary results show a 6.5% dip in cloud cover between 1985 and 1997 and a corresponding increase between 1997 and 2003. This has implications for climate research, especially with regards to global warming. All clouds contribute to an increased albedo, however some clouds have a net warming effect because they trap more heat than they reflect, while others have a net cooling effect because their increased albedo reflects more radiation than they trap heat. So while the Earth's albedo is measurably increasing, the uncertainty over the amount of heat trapped means the overall effect on global temperature remains unclear.[2]
Retroreflection
The Earth, Moon, and some other bodies have, to some extent, the property of retroreflection. Light which strikes them is reflected preferentially back in the direction from which it has come, rather than in other directions. If the light comes from the Sun, it is reflected back toward the Sun and in nearby directions. For example, when its phase is full, the Moon reflects light preferentially toward the Sun, and toward the Earth, which is in almost the same direction. The full Moon therefore appears brighter, when seen from Earth, than it would if it diffused light uniformly in all directions. Similarly, near new moon, earthshine which has been retroreflected by the Earth toward the Sun, or toward the Moon which is in almost the same direction, and then retroreflected again by the Moon toward the Earth appears much brighter, seen from Earth, than it would without the retroreflective effects. The retroreflection is produced by spheres of transparent material on the reflecting surface. When it encounters a transparent sphere, light is preferentially reflected and refracted in a path, within the sphere, which exits it in the direction from which it entered. On the Earth, the spheres are droplets of water in clouds. On the Moon, large numbers of solid glassy spheres are found on the surface. They are thought to have been formed from drops of molten rock, produced by impacts, which cooled and solidified before falling back to the surface.
Ringshine

Ringshine is when sunlight is reflected by a planet's ring system onto the planet or onto the moons of the planet. This has been observed in many of the photos from the Cassini orbiter.[3]
Search for terrestrial planets

Scientists at NASA's Navigator Program, which specializes in the detection of terrestrial planets, have backed the launch of a Terrestrial Planet Finder (TPF) mission.[4] TPF would detect light reflected by planets orbiting stars to investigate whether they could harbor life. It would use advanced telescope technologies to look for life-marks in the light reflected from the planets, including water, oxygen and methane.
The European Space Agency has a similar mission, named Darwin, under consideration. This will also study the light from planets to detect the signatures of life.[5]
Unlike many traditional astronomical challenges, the most serious challenge for these missions is not gathering enough photons from the faint planet, but rather detecting a faint planet that is extremely close to a very bright star. For a terrestrial planet, the contrast ratio of planet to its host stars is approximately ~10−6-10−7 in the thermal infrared or ~10−9-10−10 in the optical/near infrared. For this reason, Darwin and Terrestrial Planet Finder-I will work in the thermal infrared. However, searching for terrestrial planets in the optical/near infrared has the advantage that the diffraction limit corresponds to a smaller angle for a given size telescope. Therefore, NASA is also pursuing a Terrestrial Planet Finder-C mission that will search for and study terrestrial planets using the optical (and near infrared) wavelengths. While Terrestrial Planet Finder-C aims to study the light of extrasolar planets, Darwin and Terrestrial Planet Finder-I will search for thermal infrared light that is reradiated (rather than scattered) by the planet.
In preparation for these missions, astronomers have performed detailed earthshine observations, since earthshine has the spectroscopic characteristics of light reflected by the Earth. Astronomers have paid particular attention to whether earthshine measurement can detect the red edge, a spectral feature that is due to plants. The detection of a similar spectral feature in light from an extrasolar planet would be particularly interesting, since it might be due to a light-harvesting organism. While the red edge is almost certainly the easiest way to directly detect life on Earth via earthshine observations, it could be extremely difficult to interpret a similar feature due to life on another planet, since the wavelength of the spectral feature is not known in advance (unlike most atomic or molecular spectral features).
See also
References
- ↑ "Earthshine". NASA. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ↑ Shiga, David, Moon Study Tracks Changes in Earth’s Cloud Cover, Sky & Telescope, 25 June 2004
- ↑ "Cassini Solstice Mission: Saturn by Ringshine". NASA. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- ↑
- ↑
- Ford, E. B., Turner, E.L. & Seager, S. (2001) ``Characterization of extrasolar terrestrial planets from diurnal photometric variability Nature, Volume 412, Issue 6850, pp. 885–887. link and preprint
- Seager, S., Turner, E. L., Schafer, J., & Ford, E. B. (2005) ``Vegetation's Red Edge: A Possible Spectroscopic Biosignature of Extraterrestrial Plants Astrobiology, Volume 5, Issue 3, pp. 372–390. (link and preprint)
- Qiu J; Goode PR; Palle E; Yurchyshyn V; et al. (2001). "Earthshine and the Earth's albedo: 1. Earthshine observations and measurements of the lunar phase function for accurate measurements of the Earth's Bond albedo". Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 108 (D22): 4709.
Rush - Earthshine from album Vapor Trails (Remastered 2013). Music Lee,Lifeson. Lyrics Peart
External links
- Science@NASA: Earthshine
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day, 19 April 2002
- 'Earthshine' Linked to Solar Cycle, Climate Change, Space.com
- Scientists Watch Dark Side of the Moon to Monitor Earth's Climate, American Geophysical Union
- Earthshine picture gallery on SkyTrip.de