Amyl acetate
Not to be confused with sec-Amyl acetate.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentyl acetate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| 628-63-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| 1744753 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:167899 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL47769 |
| ChemSpider | 11843 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.044 |
| EC Number | 211-047-3 |
| MeSH | Amyl+acetate |
| PubChem | 12348 |
| RTECS number | AJ1925000 |
| UNII | 92Q24NH7AS |
| UN number | UN 1104 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Banana-like |
| Density | 0.876 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −71 °C (−96 °F; 202 K) |
| Boiling point | 149 °C (300 °F; 422 K) |
| Solubility in other solvents | water: 10 g/l (20 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | −70.6 °C (−95.1 °F; 202.6 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.1%-7.5%[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
7400 mg/kg, oral (rabbit) 6500 mg/kg, oral (rat)[2] |
| LCLo (lowest published) |
5200 ppm (rat)[2] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
100 ppm, 8hr TWA (525 mg/m3)[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 100 ppm (525 mg/m3)[1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
1000 ppm[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
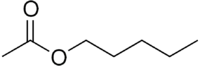
Amyl acetate (pentyl acetate) is an organic compound and an ester with the chemical formula CH3COO[CH2]4CH3 and the molecular weight 130.19 g/mol. It has a scent similar to bananas[3] and apples.[4] The compound is the condensation product of acetic acid and 1-pentanol. However, esters formed from other pentanol isomers (amyl alcohols), or mixtures of pentanols, are often referred to as amyl acetate.
It is used as a flavoring agent, as a paint and lacquer solvent, and in the preparation of penicillin.
See also
- Isoamyl acetate, also known as banana oil.
- Esters, organic molecules with the same functional groups
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0031". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 "n-Amyl acetate". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 4 December 2014. Retrieved 16 February 2015.
- ↑ Stark, Norman (1975). The Formula Book. New York: Sheed and Ward. p. 28. ISBN 0-8362-0630-4.
- ↑ Thickett, Geoffrey (2006). Chemistry 2: HSC Course. Milton, Queensland, Australia: John Wiley & Sons. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-7314-0415-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
