Adelaide–Darwin railway
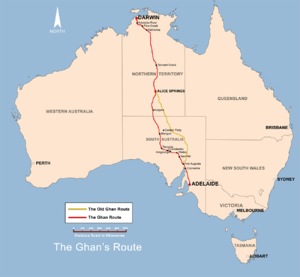
The Adelaide–Darwin railway is a north–south transcontinental railway in Australia, between the cities of Adelaide, South Australia and Darwin, Northern Territory. Between 2000-2004 the line was extended from Alice Springs to Darwin as a Build, Own, Operate and Transfer back (BOOT) project by the AustralAsia Rail Corporation.
The line sees the Great Southern Rail operated passenger train 'The Ghan' as well as goods trains operated by Genesee & Wyoming Australia.
History


- See Central Australian Railway for details of history of the first route - the Adelaide-Darwin railway is a different gauge and route
- 18 January 1878: South: Construction from Port Augusta starts
- 1879: South: Quorn reached
- 1883: South: Maree reached
- 1883: North: Construction of the North Australia Railway from Palmerston (Darwin) starts
- 1888: North: Pine Creek reached
- 1891: South: Oodnadatta reached, and known as the Great Northern Railway
- 1910: First promise by federal government to complete the line in the Acceptance Act (but no date given)
- 1926: Line acquired by Commonwealth Railways
- 1926: North: Katherine reached
- 1929: North: Birdum reached, terminus at Larrimah, and known as the North Australia Railway
- 6 August 1929: South: Alice Springs reached, and officially renamed the Central Australia Railway, but popularly known as The Ghan. The northern and southern parts are not connected.
- 1957: South: Marree line from Stirling North (near Port Augusta) to Marree rebuilt and connected to Adelaide
- Some sections of the narrow-gauge line remain in operation as the Pichi Richi Railway
- 1976: North: line closed
- October 1980: South: New line from Tarcoola (a siding on the Trans-Australian Railway) to Alice Springs opens[1]
- 31 December 1980: South: Marree to Alice Springs (narrow gauge) line closed
Alice Springs to Darwin
In 2000, the AustralAsia Rail Corporation (a company owned by the Northern Territory and South Australian Governments) awarded the contract to build and operate the Adelaide to Darwin railway line as a Build, Own, Operate and Transfer back (BOOT) project to the Asia Pacific Transport Consortium. The Asia Pacific Transport Consortium contracted FreightLink to implement the project and to operate the railway.
It cost $1.2 billion to build.[2]
The Australian Government contributed $165 million from the Centenary of Federation Fund, the Northern Territory Government contributed $165 million and the South Australian Government contributed $150 million to the AustralAsia Rail Corporation for the construction of assets by Asia Pacific Transport Consortium and FreightLink that were later leased for a peppercorn rent to FreightLink in addition, the three Governments contributed about $26 million each, a total of $79 million in further funding to support the Asia Pacific Transport Consortium directly, by way of mezzanine debt financing (subordinated debt), equity, and contingent equity.
The complex agreements were negotiated by Adelaide-based lawyer and public servant, Pamela Martin.
Construction

- July 2001: North: Construction of Alice Springs – Darwin line starts
- 17 September 2003: Darwin reached, the line from Adelaide to Darwin is complete
- 17 January 2004: First freight train reaches Darwin
- 4 February 2004: First passenger train reaches Darwin from Adelaide, travelling 2970 km in 47 hours.[3]
Bankruptcy and sale
The Freightlink board, shareholders and lenders on 19 May 2008 agreed to sell its ownership of the Adelaide to Darwin rail link after failing to make a profit since the railway line commenced operation.[4][5] Then on 6 November 2008 Freightlink went into voluntary administration after failing to reach agreement with creditors on the terms of a sale of the business.[6] Genesee & Wyoming agreed to purchase the assets of FreightLink on 10 June 2010 for $334 million,[2] and the sale meant that the 50-year lease on the Adelaide–Darwin railway was transferred to Genesee & Wyoming Australia.[7]
Infrastructure
- 1420 km
- 6 major bridges crossing the Katherine, Elizabeth, Adelaide, Cullen, Fergusson and Edith rivers[8]
- 87 minor bridges
- 1,500 culverts[9]
- 145,000 tonnes of rail[9]
- 2.8 million tonnes of ballast
- 2 million sleepers
- 8 million sleeper fastenings
Services
Freight services operate on the line in addition to The Ghan passenger service, which is operated by Great Southern Railway. Genesee & Wyoming Australia is the main freight operator. The line has facilitated bulk commodity exports from iron ore and copper mines in central Australia, including Oz Minerals' Prominent Hill copper mine.[10] Following a derailment event in December 2011,[11] Oz Minerals has elected to use the line to export to the south via Port Adelaide,[12] rather than their previous outport, Darwin.
Dry bulk exports from Darwin's port (serviced by rail) exceeded 3 million tonnes for the first time in financial year 2010-2011 and comprised iron ore, manganese and copper concentrate.[13]
Stations
The original narrow gauge railway served, indeed often created, the towns at the stations along the way.
The new standard-gauge railway has stations at Tennant Creek and Katherine, plus passing loops at Illoquara and Newcastle Waters.[14]
See also
References
- ↑ Standard Gauge to Alice Springs – Construction of Tarcoola–Alice Springs Railway Buckland, John L. Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin, June 1981 pp117–39
- 1 2
- ↑
- ↑ Vesna Poljak and Michael Smith (19 May 2008). "Banks force sale of $1.2bn Adelaide- Darwin rail link". The Australian Financial Review. p. 1 and 19.
- ↑ Calacouras, Nick (20 May 2008). "Railway up for sale". Northern Territory News. News Ltd. Retrieved 20 May 2008.
- ↑ "End of the line as train sale derailed". Northern Territory News. News Ltd. 7 November 2008. Retrieved 12 November 2008.
- ↑ "FreightLink-owned Adelaide-Darwin railway to be sold to US company Genesee & Wyoming". The Advertiser. 9 June 2010. Retrieved 9 June 2010.
- ↑
- 1 2
- ↑ "First Prominent Hill shipment set for export". ABC News. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ↑ "Train derailment copper concentrate recovered". ABC News. Retrieved 2016-04-10.
- ↑ "Oz Minerals - Intermodal Solutions Group". Intermodal Solutions Group. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ↑ "Dry Bulk Exports". Darwin Port. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ↑ "Network Operating Guide, Part 32, Tarcoola to Darwin" (PDF). Australia Southern Railroad. 2 January 2004.
Further reading
- Rozycki, Jack (Jan–Mar 2003). "The Never Never Line. Australia's biggest project: the Adelaide-Darwin railway". Australian Geographic 69: 50–67.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Adelaide-Darwin Railway. |
- AustralAsia Railway Corporation
- History of the Adelaide-Darwin Railway
- Tarcoola To Alice Springs Railway Act 1974