Abushiri revolt
| Abushiri revolt | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Scramble for Africa | |||||||
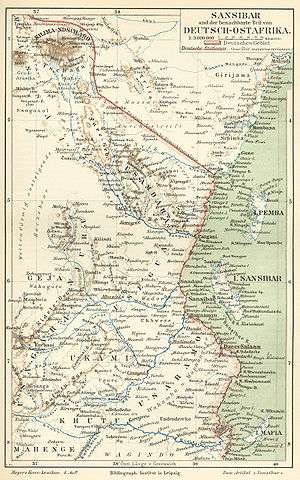 Zanzibar and German East Africa, Meyers Konversations-Lexikon, 1885-90 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| Rebels | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
Abushiri ibn Salim al-Harthi | ||||||

The Abushiri revolt was an insurrection in 1888–1889 by the Arab and Swahili population of the areas of the East African coast which were granted (under protest) to Germany by the Sultan of Zanzibar in 1888. It was eventually suppressed by an Anglo-German blockade of the coast.
Background
In late 1884 an expedition of the Society for German Colonization led by Karl Peters had reached Zanzibar and made the local chiefs on the opposite mainland sign "protection contracts" promising vast areas to his organisation. Once it had gained a foothold, Peters' newly established German East Africa Company acquired further lands in Tanganyika up to the Uluguru and Usambara Mountains. This met with opposition by Sultan Barghash bin Said of Zanzibar, who nevertheless had to give in, after Peters had reached the official support by the Foreign Office in Berlin and a fleet of the Kaiserliche Marine under Konteradmiral Eduard Knorr appeared off the Zanzibar coast. On 28 April 1888 Sultan Khalifah bin Said of Zanzibar finally signed a treaty according to which he ceded the administration of the Tanganyika mainland to the German East Africa Company.
From August 1888 the organisation tried to take over the coastal towns of Tanganyika against the fierce resistance by the Arab elite fearing for the slave and ivory trade, but also by the indigenous population. The attempts by haughty Emil von Zelewski, German administrator in Pangani, to raise the company's flag over the city, sparked the uprising.
Revolt
It was led by the planter Abushiri ibn Salim al-Harthi, who gained the support by both the Arabs of the area and local Swahili tribes. Abushiri's father was an ethnic Arab and his mother a Galla.[1] The rebellion soon spread all along the coast from the town of Tanga in the north to Lindi and Mikindani in the south. The representatives of the German East Africa Company were expelled or killed except for the establishments in Bagamoyo and Dar es Salaam.
In February 1889 the German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck intervened and appointed Lieutenant Hermann Wissmann a Reichskommissar of German East Africa. Wissmann concentrated a Schutztruppe of German officers and native Askari soldiers, who, with support by the Marine and the Royal Navy, subsequently suppressed the revolt.
After Abushiri, on his flight to Mombasa, had been finally betrayed to the Germans in December 1889, he was sentenced to death by a court-martial and publicly hanged in Pangani. By an agreement of 20 November 1890, the East Africa Company had to hand over Tanganyika's administration to the German government. It was however not until early 1891 that Wissmann could report back to Berlin that the rebellion had been fully suppressed.
