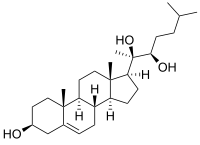
20α,22R-Dihydroxycholesterol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3β)-Cholest-5-ene-3,20,22-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 7977916 |
| PubChem | 9802154 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H46O3 | |
| Molar mass | 418.652 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
20α,22R-Dihydroxycholesterol, or (3β)-cholest-5-ene-3,20,22-triol is an endogenous, metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones from cholesterol.[1][2] Cholesterol ((3β)-cholest-5-en-3-ol) is hydroxylated by cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc) to form 22R-hydroxycholesterol, which is subsequently hydroxlated again by P450scc to form 20α,22R-dihydroxycholesterol, and finally the bond between carbons 20 and 22 is cleaved by P450scc to form pregnenolone ((3β)-3-hydroxypregn-5-en-20-one),[1][2] the precursor to the steroid hormones.
See also
References
- 1 2 CHAUDHURI AC, HARADA Y, SHIMIZU K, GUT M, DORFMAN RI (March 1962). "Biosynthesis of pregnenolone from 22-hydroxycholesterol". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 237: 703–4. PMID 13878470.
- 1 2 Hume R, Kelly RW, Taylor PL, Boyd GS (May 1984). "The catalytic cycle of cytochrome P-450scc and intermediates in the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 140 (3): 583–91. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08142.x. PMID 6723652.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.