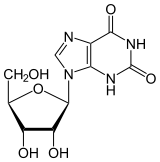
Xanthosine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-3H-purine-2,6-dione | |
| Other names
Xanthine riboside; 9-beta-D-Ribofuranosylxanthine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 146-80-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL402439 |
| ChemSpider | 58484 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.164 |
| PubChem | 64959 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 284.23 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | Decomposes when heated |
| Sparingly soluble in cold water; freely soluble in hot water | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Xanthosine is a nucleoside derived from xanthine and ribose. It is the biosynthetic precursor to 7-methylxanthosine by the action of 7-methylxanthosine synthase. 7-Methylxanthosine in turn is the precursor to theobromine (active alkaloid in chocolate), which in turn is the precursor to caffeine, the alkaloid in coffee and tea.[2]
See also
- Xanthosine monophosphate
- Xanthosine diphosphate
- Xanthosine triphosphate
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9974
- ↑ Ashihara, Hiroshi; Yokota, Takao; Crozier, Alan (2013). "Biosynthesis and catabolism of purine alkaloids". Advances in Botanical Research. 68: 111–138. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-408061-4.00004-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.