Waggle dance
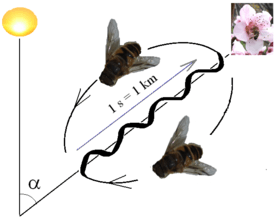
Waggle dance is a term used in beekeeping and ethology for a particular figure-eight dance of the honey bee. By performing this dance, successful foragers can share, with other members of the colony, information about the direction and distance to patches of flowers yielding nectar and pollen, to water sources, or to new nest-site locations.[1][2] A waggle dance with a very short waggle run used to be characterized as a distinct (round) recruitment dance (see below). Austrian ethologist and Nobel laureate Karl von Frisch was one of the first who translated the meaning of the waggle dance.[3]
Description
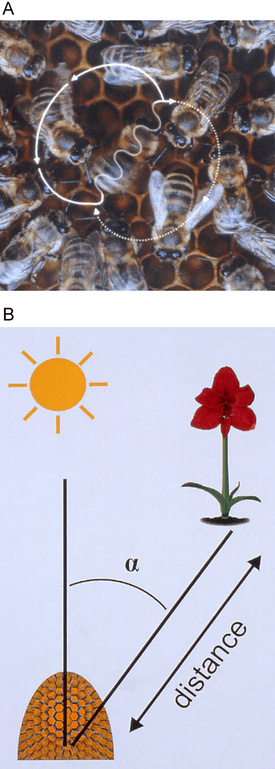
A waggle dance consists of one to 100 or more circuits, each of which consists of two phases: the waggle phase and the return phase. A worker bee's waggle dance involves running through a small figure-eight pattern: a waggle run (aka waggle phase) followed by a turn to the right to circle back to the starting point (aka return phase), another waggle run, followed by a turn and circle to the left, and so on in a regular alternation between right and left turns after waggle runs. Waggle-dancing bees produce and release two alkanes, tricosane and pentacosane, and two alkenes, (Z)-9-tricosene and (Z)-9-pentacosene, onto their abdomens and into the air.[4]
The direction and duration of waggle runs are closely correlated with the direction and distance of the resource being advertised by the dancing bee. The resource can include the location of a food source or a potential nesting site.[5] For cavity-nesting honey bees, like Apis mellifera or Apis nigrocincta, flowers that are located directly in line with the sun are represented by waggle runs in an upward direction on the vertical combs, and any angle to the right or left of the sun is coded by a corresponding angle to the right or left of the upward direction. The distance between hive and recruitment target is encoded in the duration of the waggle runs.[1][6] The farther the target, the longer the waggle phase. The more excited the bee is about the location, the more rapidly it will waggle, so it will grab the attention of the observing bees, and try to convince them. If multiple bees are doing the waggle dance, it's a competition to convince the observing bees to follow their lead, and competing bees may even disrupt other bees' dances or fight each other off. In addition, some open-air nesting honeybees, like Apis andreniformis, whose nests hang from twigs or branches, will perform a horizontal dance on a stage above their nest in order to signal to resources.[7]
Waggle dancing bees that have been in the nest for an extended time adjust the angles of their dances to accommodate the changing direction of the sun. Therefore, bees that follow the waggle run of the dance are still correctly led to the food source even though its angle relative to the sun has changed.
The consumption of ethanol by foraging bees has been shown to reduce waggle dance activity and increase occurrence of the tremble dance.[8]
Kevin Abbott and Reuven Dukas of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada discovered that if a dead Apis mellifera bee is placed on a flower, bees performed far fewer waggle dances upon returning to the hive. The scientists explain that the bees associate the dead bee with the presence of a predator at the food source. The reduction of the dance repetition frequency, therefore, indicates that the dancing bees perform and communicate a form of risk/benefit analysis.[9][10]
Though first decoded by Karl von Frisch, dancing behavior in bees had been observed and described multiple times prior. Around 100 years before Frisch's discovery, Nicholas Unhoch described dancing behavior of bees as being an indulgence "in certain pleasures and jollity".[3] He did, however, admit ignorance as to the purpose of the dancing. 35 years prior to Unhoch's observations, Ernst Spitzner observed bees dancing and interpreted it as transmitting forage resource odors to other nestmates.[3] Even Aristotle, in addition to describing flower constancy behavior, suspected that some form of communication occurred between foragers within a nest:
"On each trip the bee does not fly from a flower of one kind to a flower of another, but flies from one violet, say, to another violet, and never meddles with another flower until it has got back to the hive; on reaching the hive they throw off their load, and each bee on her return is followed by three or four companions. What it is that they gather is hard to see, and how they do it has not been observed".[11]
Jürgen Tautz also writes about it in his book "The Buzz about Bees":
Page 112: Many elements of the communication used to recruit miniswarms to feeding sites are also observed in "true" swarming behavior. Miniswarms of foragers are not placed under the same selection pressure as are true swarms, because the fate of the entire colony is not at stake. A truly swarming colony has to be quickly led to a new home, or it will perish. The behavior used to recruit to food sources possibly developed from the "true" swarming behavior.
Tautz,J.: The Buzz about Bees - Biology of a Superorganism (photos by H. R. Heilmann) Springer Heidelberg & Berlin, 2008
Mechanism
Honeybees accumulate an electric charge during flying and when their body parts are moved or rubbed together. Bees emit constant and modulated electric fields during the waggle dance. Both low- and high-frequency components emitted by dancing bees induce passive antennal movements in stationary bees according to Coulomb's Law. The electrically charged flagellum of mechanoreceptor cells are moved by electric fields and more strongly so if sound and electric fields interact. Recordings from axons of the Johnston's organ indicate its sensitivity to electric fields. Therefore, it has been suggested that electric fields emanating from the surface charge of bees stimulate mechanoreceptors and may play a role in social communication during the waggle dance.[12]
Controversy

The dance language vs. the waggle dance
As defined by von Frisch, Tanzsprache (German for "dance language") is the information about direction, distance, and quality of a resource (such as food or nesting sites) contained within the waggle dance.[13] There is supporting evidence of the waggle dance and "Tanzsprache" in Apis dorsata. Similar to other bees, they utilize the dance language to indicate the critical information regarding food resources. The dancer's body points in the direction of the food source and the sound produced during the dance indicates the profitability of the food.[14] Although there is some evidence for a direct connection between the Tanzsprache and the performance of the waggle dance, recent criticism holds that potential foragers need not correctly translate the dance language from the waggle dance to successfully forage.[13] In an experiment on the honeybee Apis mellifera, most individuals who thoroughly followed a waggle dance ignored the resource direction and location information. Instead, 93% of the foragers returned to foraging areas they had previous knowledge of.[13]
Bees that follow a waggle dance can successfully forage without decoding the dance language information in several ways:[15]
- Dance follower may use olfactory information from the dancer and find either the same resource or a different one with a similar scent.
- Following a dance may simply trigger foraging behavior. A forager may then search randomly for resources.
- Following a dance may reactivate private knowledge of a resource. After reactivation, the forager may return to the known resource.
- Using information communicated in the waggle dance is more useful to foragers when private information about resources is lacking.
Dance language as a language
The use of the word "language" may lead to misrepresentations of the waggle dance. The Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure proposed a system of language where a sign is made up two chief components. The signifier is the physical or phonetic representation of a sign. The signified is the conceptual component.[16] If the dance language followed the Saussurian dyadic model of semiotics, the signifier would be the waggle dance and the signified would be the location of the foraging resource. Though the dance language may or may not follow this sort of pattern, it is not considered to be a language with syntactical grammar or a set of symbols.[15]
Efficiency and adaptation
The waggle dance may be less efficient than once thought. Some bees observe over 50 waggle runs without successfully foraging, while others will forage successfully after observing 5 runs.[15] Likewise, studies have found that honeybees rarely make use of the information communicated in the waggle dance and seem to only do so about ten percent of the time.[17][18] Evidently there is a conflict between private information, or individual experience, and social information transmitted through dance communication. This sheds light on the fact that following social information is more energetically costly than foraging independently and is not always advantageous.[19][20] Using olfactory cues and memory of plentiful foraging sites, honeybees are able to successfully forage independently without expending the potentially extensive energy it takes to process and execute the directions communicated by their fellow foragers.
The waggle dance may be adaptive in some environments and not in others, which provides a plausible explanation as to why the information provided by waggle dances are only used sparingly. Depending on weather, other competitors, and food source characteristics, transmitted information may become obsolete quickly.[21] As a result, foragers reported to be attached to their food sites and continue to revisit a single patch many times after it has become unprofitable.[22] For example, the waggle dance plays a significantly larger role in foraging when food sources are not as abundant.[23][24] In temperate habitats, for instance, honey bee colonies routinely perform the waggle dance, but can still successfully forage when the dance is experimentally obscured. In tropical habitats, honey bee foraging is severely impaired if waggle dancing is prevented. This is thought to be due to the patchiness of resources in tropical environment versus the homogeneity of resources in temperate environments. In the tropics, food resources can come in the form of flowering trees which are rich in nectar but are scattered sparsely and bloom only briefly. Thus, in tropical zones information about forage location might be more valuable than in temperate zones.[25]
Evolution
Ancestors to modern honeybees most likely performed excitatory movements to encourage other nestmates to forage. These excitatory movements include shaking, zig-zagging, buzzing and crashing into nestmates. Similar behavior is observed in other Hymenoptera including stingless bees, wasps, bumblebees and ants.[15]
The waggle dance is thought to have evolved to aid in communicating information about a new nest site, rather than spatial information about foraging sites.[15]
Observations have suggested that different species of honeybees have different "dialects" of the waggle dance, each species or subspecies dance varying by curve or duration.[26][27] A study from 2008 demonstrated that a mixed colony of Asiatic honeybees (Apis cerana cerana) and European honeybees (Apis mellifera ligustica) were gradually able to understand one another's "dialects" of waggle dance.[28]
Applications to operations research
In line with recent work in swarm intelligence research involving optimization algorithms inspired by the behavior of social insects (including bees, ants and termites), and vertebrates such as fish and birds, there has recently been research on using bee waggle dance behavior for efficient fault-tolerant routing.[29] From the abstract of Wedde, Farooq, and Zhang (2004):[30]
In this paper we present a novel routing algorithm, BeeHive, which has been inspired by the communicative and evaluative methods and procedures of honey bees. In this algorithm, bee agents travel through network regions called foraging zones. On their way their information on the network state is delivered for updating the local routing tables. BeeHive is fault tolerant, scalable, and relies completely on local, or regional, information, respectively. We demonstrate through extensive simulations that BeeHive achieves a similar or better performance compared to state-of-the-art algorithms.
Another bee-inspired stigmergic computational technique called bee colony optimization is employed in Internet Server Optimization.[31][32]
The Zigbee RF protocol is named after the waggle dance.
See also
References
- 1 2 Riley, J.; Greggers, U.; Smith, A.; Reynolds, D.; Menzel, R. (2005). "The flight paths of honeybees recruited by the waggle dance". Nature. 435 (7039): 205–207. Bibcode:2005Natur.435..205R. doi:10.1038/nature03526. PMID 15889092.
- ↑ Seeley T.D.; Visscher P.K.; Passino K.M. (2006). "Group decision making in honey bee swarms". American Scientist. 94: 220–229. doi:10.1511/2006.3.220.
- 1 2 3 Frisch, Karl von. (1967) The Dance Language and Orientation of Bees. Cambridge, Mass.: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press.
- ↑ Thom, C.; Gilley, D.; Hooper, J.; Esch, H. (2007). "The scent of the waggle dance". PLoS Biology. 5 (9): e228. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050228. PMC 1994260
 . PMID 17713987.
. PMID 17713987. - ↑ "The Waggle Dance". www.pbs.org. Retrieved 2016-01-27.
- ↑ Radloff, Sara E.; Hepburn, H. Randall; Engel, Michael S. (2011). Honeybees of Asia. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3642164217.
- ↑ Raffiudin, Rika; Crozier, Ross H. (2007-05-01). "Phylogenetic analysis of honey bee behavioral evolution". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 43 (2): 543–552. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.10.013.
- ↑ Bozic, J.; Abramson, C.; Bedencic, M. (2006). "Reduced ability of ethanol drinkers for social communication in honeybees (Apis mellifera carnica Poll.)". Alcohol (Fayetteville, N.Y.). 38 (3): 179–183. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2006.01.005. PMID 16905444.
- ↑ Walker, Matt (31 July 2009). "Honeybees warn of Risky Flowers". BBC Earth News. Retrieved 18 January 2010.
- ↑ Abbott, K. R.; Dukas, R. (2009). "Honeybees consider flower danger in their waggle dance". Animal Behaviour. 78 (3): 633–635. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2009.05.029.
- ↑ Aristotle, Historia animalium, IX, 40, Becker 624b; modified from the translation by D.W. Thompson in The Works of Aristotle, Clarendon, Oxford, 1910.
- ↑ Greggers, Uwe; Koch G; Schmidt V; Dürr A; Floriou-Servou A; Piepenbrock D; Göpfert MC; Menzel R (March 2013). "Reception and learning of electric fields". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 280: 20130528. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.0528.
- 1 2 3 Grüter, C.; Balbuena, M.; Farina, W. (2008). "Informational conflicts created by the waggle dance". Proceedings. Biological sciences / the Royal Society. 275 (1640): 1321–1327. doi:10.1098/rspb.2008.0186. PMC 2602683
 . PMID 18331980.
. PMID 18331980. - ↑ Kirchner, Wolfgang. "Acoustic signals in the dance language of the giant honeybee, Apis dorsata". Behavior Ecology and Sociobiology (33): 67–72.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Grüter, C. .; Farina, W. . (2009). "The honeybee waggle dance: can we follow the steps?". Trends in ecology & evolution (Personal edition). 24 (5): 242–247. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2008.12.007. PMID 19307042.
- ↑ Saussure, Ferdinand de (1916), "Nature of the Linguistics Sign", in: Charles Bally & Albert Sechehaye (Ed.), Cours de linguistique générale, McGraw Hill Education.
- ↑ Dornhaus, A.; Chittka, L (2014). "Why do honey bees dance?". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 55: 395–401.
- ↑ Gruter, C.; Balbuena, M. S.; Farina, W. M. (2008). ". Informational conflicts created by the waggle dance". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 275: 1321–1327. doi:10.1098/rspb.2008.0186. PMC 2602683
 . PMID 18331980.
. PMID 18331980. - ↑ Al Toufailia, H.; Gruter, C.; Ratnieks, F. L. W. (2013). "Persistence to unrewarding feeding locations by honeybee foragers (Apis mellifera): the effects of experience, resource profitability and season". Ethology. 119: 1096–1106. doi:10.1111/eth.12170.
- ↑ Gruter, C; Ratnieks, F. L. W. (2011). "Honeybee foragers increase the use of waggle dance information when private information becomes unrewarding". Animal Behaviour. 81: 949–954. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.01.014.
- ↑ Gruter, C.; Farina, W. M. (2009). "The honeybee waggle dance: can we follow the steps?". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 24: 242–247. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2008.12.007. PMID 19307042.
- ↑ name="tle=Persistence to unrewarding feeding locations by honeybee foragers (Apis mellifera): the effects of experience, resource profitability and season"
- ↑ name="The biology of the dance language"
- ↑ name="Informational conflicts created by the waggle dance"
- ↑ Dornhaus, A.; Chittka, L. (2004). "Why do honey bees dance?". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 55 (4): 395–401. doi:10.1007/s00265-003-0726-9.
- ↑ Gould; Towne (1989). "On the Evolution of the Dance Language: Response to Dyer and Seeley". American Naturalist. The American Society of Naturalists. 134 (1): 156–159. doi:10.1086/284972. JSTOR 2462282.
- ↑ Dyer; Seeley (1991). "Dance Dialects and Foraging Range in Three Asian Honey Bee Species". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. Springer. 28 (4): 227–233. doi:10.1007/BF00175094. JSTOR 4600541.
- ↑ Su, S.; Cai, F.; Si, A.; Zhang, S.; Tautz, J.; Chen, S.; Giurfa, M. (2008). Giurfa, Martin, ed. "East learns from West: Asiatic honeybees can understand dance language of European honeybees". PLoS ONE. 3 (6): e2365. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.2365S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002365. PMC 2391287
 . PMID 18523550.
. PMID 18523550. - ↑ Crina, Grosan; Abraham Ajith. (2006) Stigmergic Optimization: Inspiration, Technologies and Perspectives. Studies in Computational Intelligence. Vol. 31. pp. 1-24. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. ISBN 978-3-540-34689-0
- ↑ Wedde, H. F.; Farooq, M.; Pannenbaecker, T.; Vogel, B.; Mueller, C.; Meth, J.; Jeruschkat, R. (2005). "BeeAdHoc". Proceedings of the 2005 conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation - GECCO '05. p. 153. doi:10.1145/1068009.1068034. ISBN 1595930108.
- ↑ Nakrani, S.; Tovey, C. (2004). "On Honey Bees and Dynamic Server Allocation in Internet Hosting Centers". Adaptive Behavior. 12 (3–4): 223–240. doi:10.1177/105971230401200308.
- ↑ C. Tovey, (2004) "The Honey Bee Algorithm: A Biological Inspired Approach to Internet Server Optimization". Engineering Enterprise. Spring 2004, pp.13-15.
Further reading
- Gould JL (1975). "Honey bee recruitment: the dance-language controversy" (PDF). Science. 189 (4204): 685−693. doi:10.1126/science.1154023.
- Riley JR, Greggers U, Smith AD, Reynolds DR, Menzel R (2005). "The flight paths of honeybees recruited by the waggle dance". Nature. 435 (7039): 205–207. Bibcode:2005Natur.435..205R. doi:10.1038/nature03526. PMID 15889092.
- Seeley TD (1995). The Wisdom of the Hive. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- von Frisch K (1967). The Dance Language and Orientation of Bees. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Rendell, L; Boyd, R.; Cownden, D; Enquist, M.; Eriksson, K.; Feldman, W. M.; Fogarty, L.; Ghirlanda, S.; Lilicrap, T.; Laland, K. N. (2010). "Why copy others? Insights from the social learning strategies tournament". Science. 328: 208–213. doi:10.1126/science.1184719.
- Gruter, C; Ratnieks, F. L. (2011). "Honeybee foragers increase the use of waggle dance information when private information becomes unrewarding". Animal Behaviour. 81: 949–954. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.01.014.
- Dyer, F. C. (2002). "The biology of the dance language". Annual Review of Entomology. 47: 917–949. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145306.
- Beekman, M.; Golag, R. S.; Even, N.; Wattanchiyingchareon, W.; Olroyd, B. P. (2008). "Dance precision of Apis florae--clues to the evolution of honeybee dance language". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 62: 1259–1265. doi:10.1007/s00265-008-0554-z.
- Al Toufalia, H. M. (2012). "Honey bee foraging: persistence to non-rewarding feeding locations and waggle dance communication". Doctoral thesis, University of Sussexx.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Waggle dance. |
- NATURE, Silence of the Bees, Inside the Hive, PBS on YouTube
- Waggle Dance Infographic - VetSci
- Communication and Recruitment to Food Sources by Apis mellifera — USDA-ARS (accessed 2005-03)
- Honeybee Communication — Kimball's Biology Pages (accessed 2005-09)