United States territory
United States territory is any extent of region under the sovereign jurisdiction of the federal government of the United States,[1] including all waters (around islands or continental tracts) and all U.S. naval vessels.[2] The United States asserts sovereign rights for exploring, exploiting, conserving, and managing its territory.[3] This extent of territory is all the area belonging to, and under the dominion of, the United States federal government (which includes tracts lying at a distance from the country) for administrative and other purposes.[1] The United States total territory includes a subset of political divisions.
Territory of the United States
The United States territory includes any geography under the control of the United States federal government. Various regions, districts, and divisions are under the supervision of the United States federal government. The United States territory includes clearly defined geographical area and refers to an area of land, air, or sea under jurisdiction of United States federal governmental authority (but is not limited only to these areas). The extent of territory is all the area belonging to, and under the dominion of, the United States of America federal government (which includes tracts lying at a distance from the country) for administrative and other purposes.
Constitution of the United States

Under Article IV of the U.S. Constitution, territory is subject to and belongs to the United States (but not necessarily within the national boundaries or any individual state). This includes tracts of land or water not included within the limits of any State and not admitted as a State into the Union.
The Constitution of the United States states:
The Congress shall have Power to dispose of and make all needful Rules and Regulations respecting the Territory or other Property belonging to the United States; and nothing in this Constitution shall be so construed as to Prejudice any Claims of the United States, or of any particular State.
Congress of the United States
Congress possesses power to set territorial governments within the boundaries of the United States.[4] The power of Congress over such territory is exclusive and universal. Congressional legislation is subject to no control, unless in the case of ceded territory. The U.S. Congress is granted the exclusive and universal power to set a United States territory's political divisions.
Supreme Court of the United States
All territory under the control of the federal government is considered part of the "United States" for purposes of law.[5] From 1901–1905, the U.S. Supreme Court in a series of opinions known as the Insular Cases held that the Constitution extended ex proprio vigore to the territories. However, the Court in these cases also established the doctrine of territorial incorporation. Under the same, the Constitution only applied fully in incorporated territories such as Alaska and Hawaii, whereas it only applied partially in the new unincorporated territories of Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippines.[6][7] A Supreme Court ruling from 1945 stated that the term "United States" can have three different meanings, in different contexts:
The term "United States" may be used in any one of several senses. It may be merely the name of a sovereign occupying the position analogous to that of other sovereigns in the family of nations. It may designate the territory over which the sovereignty of the United States extends, or it may be the collective name of the states which are united by and under the Constitution.
United States Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior is charged with managing federal affairs within U.S. territory.[8] The Interior Department has a wide range of responsibilities (which include the regulation of territorial governments and the basic stewardship for public lands, et al.). The United States Department of the Interior is not responsible for local government or for civil administration except in the cases of Indian reservations, through the Bureau of Indian Affairs, as well as those territories administered through the Office of Insular Affairs. The exception is the "incorporated and unorganized" (see below) United States Territory of Palmyra Island, the legal remnant of the former United States Territory of Hawaii since 1959,[9] in which the local government and civil administration were assigned by the Secretary of the Interior to the Fish and Wildlife Service in 2001.[10]
United States divisions
States, territories, and their subdivisions
The contiguous United States, Hawaii, and Alaska are divided into smaller administrative regions. These are called counties in 48 of the 50 states, and they are called boroughs in Alaska and parishes in Louisiana. A county can include a number of cities and towns, or just a portion of either type. These counties have varying degrees of political and legal significance. A township in the United States refers to a small geographic area. The term is used in two ways: a survey township is simply a geographic reference used to define property location for deeds and grants; a civil township is a unit of local government, originally rural in application.
Territories are subdivided into legally administered tracts—e.g., geographic areas that are under the authority of a government.[11] The District of Columbia and territories are under the direct authority of Congress, although each is allowed home rule.[12] The United States Government, rather than individual states or territories, conducts foreign relations under the U.S. Constitution.
Federal enclaves, such as domestic military bases and national parks, are administered directly by the federal government. To varying degrees, the federal government exercises concurrent jurisdiction with the states where federal land is part of the territory previously granted to a state.
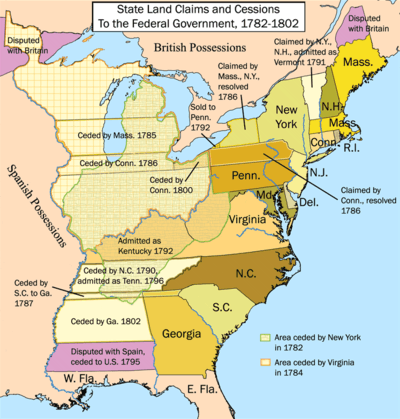
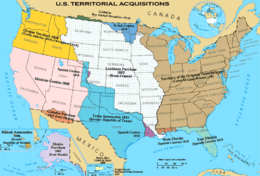
History of United States territory
At times, territories are organized with a separate legislature, under a territorial governor and officers, appointed by the President and approved by the Senate of the United States. A territory has been historically divided into organized territories and unorganized territories.[13][14] An unorganized territory was generally either unpopulated or set aside for Native Americans and other indigenous peoples in the United States by the U.S. federal government, until such time as the growing and restless population encroached into the areas. In recent times, "unorganized" refers to the degree of self-governmental authority exercised by the territory.
As a result of several Supreme Court cases after the Spanish–American War, the United States had to determine how to deal with its newly acquired territories, such as the Philippines,[15][16] Puerto Rico,[17] Guam,[18][19] Wake Island, and other areas that were not part of the North American continent and which were not necessarily intended to become a part of the Union of States. As a consequence of the Supreme Court decisions, the United States has since made a distinction between incorporated and unincorporated territories.[20][21][22] In essence, an incorporated territory is land that has been irrevocably incorporated within the sovereignty of the United States and to which the full corpus of the U.S. Constitution applies. An unincorporated territory is land held by the United States, and to which Congress of the United States applies selected parts of the constitution. At the present time, the only incorporated U.S. territory is the unorganized (and unpopulated) Palmyra Atoll.
|
Insular areas
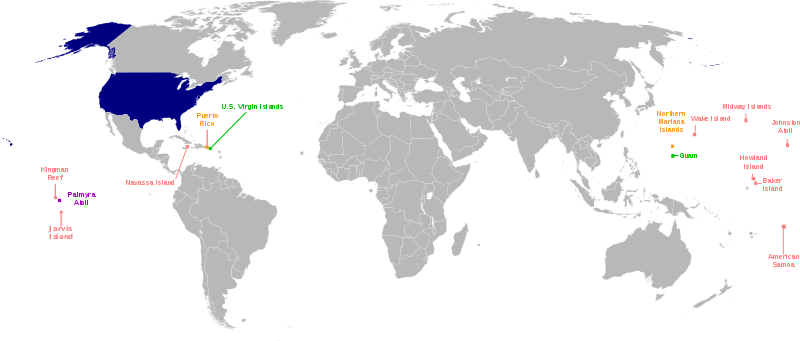
The United States currently administers 16 territories as insular areas:
Palmyra Atoll is the only incorporated territory remaining, and having no government it is also unorganized. The remaining are unincorporated territories of the United States. Puerto Rico and Northern Mariana Islands are styled as commonwealths.
Dependent areas
Several islands in the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea are dependent territories of the United States.[23][24]
The Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, is administered by the United States under a perpetual lease, much as the Panama Canal Zone used to be before the signing of the Torrijos-Carter Treaties and only mutual agreement or U.S. abandonment of the area can terminate the lease.
From July 18, 1947, until October 1, 1994, the United States administered the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, but the Trust ceased to exist when the last member state of Palau gained its independence to become the Republic of Palau. The Panama canal, and the Canal Zone surrounding it, was territory administered by the United States until 1999, when control was relinquished to Panama.
The United States has made no territorial claim in Antarctica but has reserved the right to do so.
Maritime territory of the United States
The government of the United States of America has claims to the oceans in accord with the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, which delineates a zone of territory adjacent to territorial lands and seas. United States protects this marine environment, though not interfering with other lawful uses of this zone. The United States jurisdiction has been established on vessels, ships, and artificial islands (along with other marine structures).
In 1983 President Ronald Reagan, through Proclamation No. 5030, claimed a 200-mile exclusive economic zone. In December 1988 President Reagan, through Proclamation No. 5928, extended U.S. territorial waters from three nautical miles to twelve nautical miles for national security purposes. However a legal opinion from the Justice Department questioned the President's constitutional authority to extend sovereignty as Congress has the power to make laws concerning the territory belonging to the United States under the U.S. Constitution. In any event, Congress needs to make laws defining if the extended waters, including oil and mineral rights, are under State or Federal control.[25][26]
The primary enforcer of maritime law is the U.S. Coast Guard. Federal and state governments share economic and regulatory jurisdiction over the waters owned by the country. (See tidelands.)

International law
The United States is not restricted from making laws governing its own territory by international law. United States territory can include occupied territory, which is a geographic area that claims sovereignty, but is being forcibly subjugated to the authority of the United States of America. United States territory can also include disputed territory, which is a geographic area claimed by the United States of America and one (or more) rival governments.
Like many nations, the United States of America has acquired territory by force and conquest (Latin, "to seek for"). Under the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907, United States territory can include areas occupied by and controlled by the United States Armed Forces. When de facto military control is maintained and exercised, occupation (and thus possession) extends to that territory. Military personnel in control of the territory have a responsibility to provide for the basic needs of individuals under their control (which includes food, clothing, shelter, medical attention, law maintenance, and social order). To prevent systematic abuse of puppet governments by the occupation forces, they must enforce laws that were in place in the territory prior to the occupation.
Customs territories
The fifty states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico form the main customs territory of the United States. Special rules apply to foreign trade zones in these areas. Separate customs territories are formed by American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, the U.S. Minor Outlying Islands, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Other areas
U.S. sovereignty includes the airspace over its land and territorial waters. No international agreement exists on the vertical limit that separates this from outer space, which is international.
Federal jurisdiction includes federal enclaves like national parks and domestic military bases, even though these are located in the territory of a state. Host states exercise concurrent jurisdiction to some degree.
The United States exercises extraterritoriality on overseas embassies and military bases, including the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base in Cuba. Despite exercise of extraterritorial jurisdiction, these overseas locations remain under the sovereignty of the host countries.
The federal government also exercises property ownership, but not sovereignty over land in various foreign countries. Examples include the John F. Kennedy Memorial built at Runnymede in England,[27] and 13 hectares (32 acres) around Pointe du Hoc in Normandy, France.[28]
See also
Notes
- 1 2 Hurd, John C. (1968) [1858]. The Law of Freedom and Bondage in the United States. New York: Negro Universities Press. pp. 438–439. OCLC 10955.
- ↑ McLaughlin, Andrew C.; Hart, Albert Bushnell (1914). "Influence of the United States on International Law". Cyclopedia of American Government. 2. New York: D. Appleton and Co. pp. 204–209. OCLC 11430802.
- ↑ Smith, Robert W. (1986). Exclusive Economic Zone Claims: An Analysis and Primary Documents. Hingham, Mass.: M. Nijhoff. p. 467. ISBN 90-247-3250-6. OCLC 424143523.
- ↑ An example of this would be the Northwest Ordinance.
- ↑ See 8 U.S.C. § 1101(a)(36) and 8 U.S.C. § 1101(a)(38) Providing the term "State" and "United States" definitions on the U.S. Federal Code, Immigration and Nationality Act. 8 U.S.C. § 1101a
- ↑ CONSEJO DE SALUD PLAYA DE PONCE v JOHNNY RULLAN, SECRETARY OF HEALTH OF THE COMMONWEALTH OF PUERTO RICO Page 6 and 7 (PDF), The United States District Court for the District of Puerto Rico, archived from the original (PDF) on May 10, 2011, retrieved 4 February 2010.
- ↑ The Insular Cases: The Establishment of a Regime of Political Apartheid" (2007) Juan R. Torruella (PDF), retrieved 5 February 2010.
- ↑ Towle, Nathaniel C. (1861). A History and Analysis of the Constitution of the United States. Boston: Little, Brown. pp. 384–385. OCLC 60723860.
- ↑ "GAO/OGC-98-5 – U.S. Insular Areas: Application of the U.S. Constitution; Appendix II:0.3, footnote 22". U.S. Government Printing Office. November 7, 1997. Retrieved September 6, 2016.
- ↑ Secretary of the Interior Order No. 3224, January 18, 2001.
- ↑ "Geographic Areas Reference Manual". U.S. Census Bureau. 16 September 2005. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ↑ "District of Columbia Home Rule Act". abfa.com. 19 November 1997. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ↑ Berg-Andersson, Richard E. (14 July 2008). "Official Name and Status History of the several States and U.S. Territories". The Green Papers. Retrieved 12 September 2009.
- ↑ "Indian Land Cessions in the United States, 1784–1894". The Library of Congress. 2009. Retrieved 12 September 2009.
- ↑ "Philippines – United States Rule". U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2006-08-22.
- ↑ "Philippines – A Collaborative Philippine Leadership". U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2006-08-22.
- ↑ Treaty of Paris (1898)
- ↑ Paul Carano and Pedro C. Sanchez, A Complete History of Guam (Rutland, VT: C. E. Tuttle, 1964)
- ↑ Howard P Willens and Dirk Ballendorf, The Secret Guam Study: How President Ford's 1975 Approval of Commonwealth Was Blocked by Federal Officials (Mangilao, Guam: Micronesian Area Research Center; Saipan: Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands Division of Historical Preservation, 2004)
- ↑ FindLaw: Downes v. Bidwell, 182 U.S. 244 (1901) regarding the distinction between incorporated and unincorporated territories
- ↑ FindLaw: People of Puerto Rico v. Shell Co., 302 U.S. 253 (1937) regarding application of U.S. law to organized but unincorporated territories
- ↑ FindLaw: United States v. Standard Oil Company, 404 U.S. 558 (1972) regarding application of U.S. law to unorganized unincorporated territories
- ↑ Office of Insular Affairs
- ↑ Department of the Interior Definitions of Insular Area Political Types Archived July 21, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Andrew Rosenthal (29 December 1988). "Reagan Extends Territorial Waters to 12 Miles". New York Times. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ↑ Carol Elizabeth Remy (1992). "U.S. Territorial Sea Extension: Jurisdiction and International Environmental Protection". Fordham International Law Journal. 16 (4): 1208–1252. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ↑ Evans, D. M. Emrys (1965). "John F. Kennedy Memorial Act, 1964". The Modern Law Review. 28 (6): 703–706.
- ↑ "The American Battle Monuments Commission". Retrieved October 29, 2012.
The site, preserved since the war by the French Committee of the Pointe du Hoc, which erected an impressive granite monument at the edge of the cliff, was transferred to American control by formal agreement between the two governments on 11 January 1979 in Paris, with Ambassador Arthur A. Hartman signing for the United States and Secretary of State for Veterans Affairs Maurice Plantier signing for France.
References
- Fleury Graff, Thibaut (2013). Etat et territoire en droit international. L'exemple de la construction du territoire des Etats-Unis (1789-1914) (State and Territory in International Law. The case of United States' Territory (1789-1914)). Paris, France: Pedone. ISBN 978-2-233-00686-8.
- Lalor, John J. (1899). "Territories". Cyclopaedia of Political Science, Political Economy, and of the Political History of the United States. New York: Maynard, Merrill, and Co. OCLC 221087006.
- McFerson, Hazel M. (1997). The Racial Dimension of American Overseas Colonial Policy. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-28996-4. OCLC 36301430.
- Willoughby, Westel W. (1910). The Constitutional Law of the United States. 2. New York: Baker, Voorhis & Company. OCLC 180533376.
Further reading
- Mellander, Gustavo A.; Mellander, Nelly Maldonado (1999). Charles Edward Magoon, the Panama Years. Río Piedras, Puerto Rico: Editorial Plaza Mayor. ISBN 1-56328-155-4. OCLC 42970390.
- Mellander, Gustavo A. (1971). The United States in Panamanian Politics: The Intriguing Formative Years. Danville, Ill.: Interstate Publishers. OCLC 138568.