Trigeminal cave
| Trigeminal cave | |
|---|---|
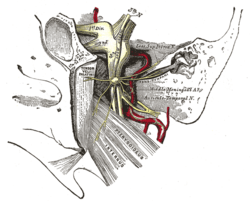 The trigeminal ganglion and its branches represented here as 1st division, 2nd division, and 3rd division. The Trigeminal Cave houses this ganglion. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cavum Meckeli, cavum trigeminale |
| TA | A14.1.01.108 |
The trigeminal cave (also known as Meckel's cave or cavum trigeminale) is an arachnoidal pouch containing cerebrospinal fluid.
Structure
The trigeminal cave is formed by two layers of dura mater which are part of an evagination of the tentorium cerebelli near the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone. It envelops the trigeminal ganglion. It is bounded by the dura overlying four structures:
- The cerebellar tentorium superolaterally
- The lateral wall of the cavernous sinus superomedially
- The clivus medially
- The posterior petrous face inferolaterally
History
Etymology
It is named for Johann Friedrich Meckel, the Elder.[1][2]
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ synd/2133 at Who Named It?
- ↑ J. F. Meckel. Tractatus anatomico physiologicus de quinto pare nervorum cerebri. Göttingen 1748.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.