TFDP2
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
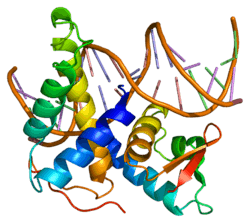
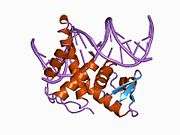
Transcription factor Dp-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFDP2 gene.[4][5][6]
References
- ↑ "Diseases that are genetically associated with TFDP2 view/edit references on wikidata".
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Zhang Y, Chellappan SP (Jul 1995). "Cloning and characterization of human DP2, a novel dimerization partner of E2F". Oncogene. 10 (11): 2085–93. PMID 7784053.
- ↑ Zhang Y, Venkatraj VS, Fischer SG, Warburton D, Chellappan SP (Mar 1997). "Genomic cloning and chromosomal assignment of the E2F dimerization partner TFDP gene family". Genomics. 39 (1): 95–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4473. PMID 9027491.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: TFDP2 transcription factor Dp-2 (E2F dimerization partner 2)".
Further reading
- Wu CL, Zukerberg LR, Ngwu C, et al. (1995). "In vivo association of E2F and DP family proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (5): 2536–46. doi:10.1128/mcb.15.5.2536. PMC 230484
 . PMID 7739537.
. PMID 7739537. - Rogers KT, Higgins PD, Milla MM, et al. (1996). "DP-2, a heterodimeric partner of E2F: identification and characterization of DP-2 proteins expressed in vivo". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (15): 7594–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.15.7594. PMC 38791
 . PMID 8755520.
. PMID 8755520. - Loiseau L, Pasteau S, Brun G (1998). "Molecular cloning and expression pattern of the DP members of the chicken E2F transcription factor". Gene Expr. 6 (5): 259–73. PMID 9368098.
- Trimarchi JM, Fairchild B, Verona R, et al. (1998). "E2F-6, a member of the E2F family that can behave as a transcriptional repressor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (6): 2850–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.6.2850. PMC 19658
 . PMID 9501179.
. PMID 9501179. - Gaubatz S, Wood JG, Livingston DM (1998). "Unusual proliferation arrest and transcriptional control properties of a newly discovered E2F family member, E2F-6". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (16): 9190–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.16.9190. PMC 21314
 . PMID 9689056.
. PMID 9689056. - Zheng N, Fraenkel E, Pabo CO, Pavletich NP (1999). "Structural basis of DNA recognition by the heterodimeric cell cycle transcription factor E2F–DP". Genes Dev. 13 (6): 666–74. doi:10.1101/gad.13.6.666. PMC 316551
 . PMID 10090723.
. PMID 10090723. - Korz C, Pscherer A, Benner A, et al. (2002). "Evidence for distinct pathomechanisms in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma by quantitative expression analysis of cell cycle and apoptosis-associated genes". Blood. 99 (12): 4554–61. doi:10.1182/blood.V99.12.4554. PMID 12036888.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Park KK, Deok Ahn J, Lee IK, et al. (2003). "Inhibitory effects of novel E2F decoy oligodeoxynucleotides on mesangial cell proliferation by coexpression of E2F/DP". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 308 (4): 689–97. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01455-4. PMID 12927774.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. - Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/3/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.