Metaldehyde
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
r-2, c-4, c-6, c-8-tetramethyl- 1,3,5,7-tetroxocane | |
| Other names
2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7- tetraoxocanemetacetaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 108-62-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 54981 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.274 |
| KEGG | C18744 |
| PubChem | 61021 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 176.212 g/mol |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) |
| Boiling point | sublimes at 110 to 120 °C (230 to 248 °F; 383 to 393 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
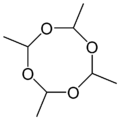
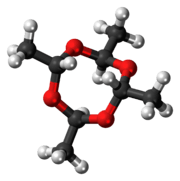
Metaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula (CH3CHO)4. It is commonly used as a pesticide against slugs, snails, and other gastropods. It is the cyclic tetramer of acetaldehyde.[1]
Production and properties
Metaldehyde is obtained in moderate yields by treatment of acetaldehyde with various acid catalysts, such as hydrogen bromide. The reaction is reversible, upon heating to about 80 °C, metaldehyde reverts to acetaldehyde. Metaldehyde exists as a mixture of stereoisomers, molecules that differ with respect to the relative orientation of the methyl groups on the 8-membered ring.
Uses
As a pesticide
It is sold under various trade names as a molluscicide, including Antimilice, Ariotox, Blitzem (in Australia), Cekumeta, Deadline, Defender (in Australia), Halizan, Limatox, Limeol, Meta, Metason, Mifaslug, Namekil, Slug Fest Colloidel 25, and Slugit. Typically it is applied in the form of slug pellets, which normally include a wheat bait. Metaldehyde acts on the pest by contact or ingestion, and the aqueous environment inside the pest's cells readily hydrolyzes metaldehyde into acetaldehyde, the molecule associated with an alcohol hangover.
Other uses
Metaldehyde is also used as a camping fuel, also for military purposes, or solid fuel in lamps. It may be purchased in a tablet form to be used in small stoves, and for preheating of Primus type stoves. It is sold under the trade name of "META" by Lonza Group of Switzerland; it can be included in the field ration of some nation.
Safety
Metaldehyde has a toxicity profile identical to that for acetaldehyde, being mildly toxic[2] and a respiratory irritant at the 50 ppm level.
Metaldehyde-containing slug baits should be used with caution, as they are toxic to dogs and cats.[3] If ingested by dogs or cats, tremors, drooling, and restlessness will proceed to seizures and death within hours to days if treatment is not started quickly. Due to this toxicity, pet owners may want to investigate alternatives which are not toxic to pets.[4] The tablets resemble sweetmeats and do not taste bad, making accidental ingestion possible by children or even by adults unaware of their true nature. Their use was popular during the inter-war period and several cases of poisoning resulted.[5] Baits may contain a bittering agent to prevent accidental consumption by pets or children.
In popular culture
In chapter 5 of Missee Lee from Arthur Ransome's Swallows and Amazons series, Susan of the Swallows is shown using Meta fuel to preheat a Primus stove. The substance is branded "Meta Fuel", but its properties as described in the book — a jelly-like substance that melts when lit and burns with a blue flame leaving no residue — are more suggestive of gelled alcohol in tablet form; genuine metaldehyde fuel tablets are white in colour and brittle, sublime rather than melting, burn with a yellow flame and leave a powdery residue.[6]
References
- ↑ Marc Eckert, Gerald Fleischmann, Reinhard Jira, Hermann M. Bolt, Klaus Golka "Acetaldehyde" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_031.pub2.
- ↑ Toxicology of metaldehyde
- ↑ "Pests in Gardens and Landscapes". University of California, Davis. Retrieved 2010-08-03.
- ↑ "Slugging Out Spring". Dr. Heidi Houchen, DVM.
- ↑ Miller, Reginald (December 1928). "Poisoning by "Meta Fuel" Tablets (Metacetaldehyde)". Archive of Disease in Childhood. 3 (18): 292–295. doi:10.1136/adc.3.18.292. PMC 1975025
 . PMID 21031743.
. PMID 21031743. - ↑ "Meta Fuel - Classic Camp Stoves". Retrieved 2013-08-04.
External links
- National Pesticide Information Center (NPIC) Information about pesticide-related topics.
- Get Rid of Slugs and Snails, Not Puppy Tails! Case Profile - National Pesticide Information Center
- Slugs and Snails - National Pesticide Information Center
- WHO/FAO Data sheet at inchem.org
- Solid Fuel Stoves - Metaldehyde mentioned
- Slug controls (on Wikibooks)
- Metaldehyde in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)