SMS Novara (1913)
 Novara during World War I | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Novara |
| Namesake: | Battle of Novara in 1849 |
| Builder: | Danubius |
| Laid down: | 9 December 1912 |
| Launched: | 15 February 1913 |
| Commissioned: | 10 January 1915 |
| Fate: | Ceded to France as a war prize, 1920 |
| Name: | Thionville |
| Namesake: | Thionville |
| Acquired: | 1920 |
| Decommissioned: | 1932 |
| Fate: | Scrapped, 1941 |
| General characteristics (as built) | |
| Class and type: | Novara-class scout cruiser |
| Displacement: | 3,500 tonnes (3,400 long tons) |
| Length: | 130.64 m (428 ft 7 in) |
| Beam: | 12.79 m (42 ft 0 in) |
| Draft: | 4.6 m (15 ft 1 in) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 27 knots (50 km/h; 31 mph) |
| Range: | 1,600 nmi (3,000 km; 1,800 mi) at a speed of 24 knots (44 km/h; 28 mph) |
| Complement: | 340 |
| Armament: | 9 × 1 - 10 cm (3.9 in) guns |
| Armor: |
|
SMS Novara was a Novara-class scout cruiser of the Austro-Hungarian Navy which served during World War I. Built by the Danubius shipyard between December 1912 and January 1915, Novara was the third and final member of her class to enter service, some six months after the start of the war. She was armed with a battery of nine 10-centimeter (3.9 in) guns and had a top speed of 27 knots (50 km/h; 31 mph).
The ship saw extensive service during World War I, owing to the cautious strategies adopted by the Austro-Hungarian fleet and their opponents in the Triple Entente. Novara was frequently used to raid enemy shipping and the Otranto Barrage, including a patrol in November 1915 where she destroyed a stranded French submarine. These operations culminated in the Battle of the Strait of Otranto in May 1917, the largest naval battle of the Adriatic Campaign. There, she and her two sisters sank fourteen drifters, though she was badly damaged by a British cruiser and had to be towed back to port. Novara was involved in the Cattaro Mutiny in January 1918 and led the loyalist vessels to safety.
Novara changed hands several times as the war ended, being transferred first to the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, a successor state to Austria-Hungary, and then to France as a war prize under the terms of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye. Commissioned into the French fleet as Thionville, the ship served from 1920 to 1932 as a training ship, and from 1932 to 1941 as a barracks ship in Toulon before being broken up for scrap.
Design
Novara was 130.64 meters (428 ft 7 in) long overall, with a beam of 12.79 meters (42 ft 0 in) and a mean draft of 4.6 meters (15 ft 1 in). She displaced 3,500 metric tons (3,400 long tons) at normal load, and up to 4,017 metric tons (3,954 long tons) at deep load. Her propulsion system consisted of two sets of AEG steam turbines driving two propeller shafts. They were designed to provide 25,600 shaft horsepower (19,100 kW) and were powered by 16 Yarrow water-tube boilers. These gave the ship a top speed of 27 knots (50 km/h; 31 mph). Novara carried about 710 metric tons (700 long tons) of coal that gave her a range of approximately 1,600 nautical miles (3,000 km; 1,800 mi) at 24 knots (44 km/h; 28 mph). The ship had a crew of 340 officers and men.[1][2]
Novara was armed with nine 50-caliber 10-centimeter (3.9 in) guns in single pedestal mounts. Three were placed forward on the forecastle, four were located amidships, two on either side, and two were side by side on the quarterdeck. A 50-caliber 6.6-centimeter (2.6 in) anti-aircraft gun and six 53.3 cm (21.0 in) torpedo tubes in twin mounts were added in 1917. The navy planned to remove the guns on the forecastle and quarterdeck and replace them with a pair of 15-centimeter (5.9 in) guns fore and aft, but nothing was done before the end of the war. The ship was protected by a waterline armored belt that was 60 mm (2.4 in) thick amidships and a 20 mm (0.79 in) thick deck. The conning tower had 60 mm thick sides, and the guns had 40 mm (1.6 in) thick shields.[1][2]
Service history
Construction and early World War I
_Stapellauf.jpg)
Novara was laid down at the Danubius shipyard in Fiume on 9 December 1912, the last member of her class to begin construction. She was launched on 15 February 1913; the ship was still undergoing fitting-out work when World War I broke out in July 1914. The ship was completed on 10 January 1915 and commissioned into the Austro-Hungarian fleet.[2] The commander of the Austro-Hungarian fleet, Admiral Anton Haus, adopted a cautious strategy to preserve his fleet, since he was outnumbered by the Anglo-French fleets in the Mediterranean, and the attitude of Austria-Hungary's erstwhile ally Italy remained unknown. Haus decided the best course of action would be to act as a fleet in being, which would tie down Allied naval forces, while torpedo boats, mines, and raids with fast cruisers like Novara could be used to reduce the numerical superiority of the enemy fleets before a decisive battle could be fought.[3]
In March, after the beginning of the British Dardanelles Campaign against the Ottoman Empire, Germany began to pressure Austria-Hungary to assist their ally; Haus considered sending Novara with a cargo of munitions. Haus ultimately decided the operation was too risky for what would have been a minimal gain, as the ship would not have been able to carry a particularly large amount.[4] On 2 May, Novara towed the German U-boat UB-8 from Pola out of the Adriatic Sea. They evaded French patrols until 6 May, off Cephalonia, they were spotted by a French vessel. Novara cut the tow and sped north, while UB-8 submerged and evaded the French patrol.[5] Following the Italian declaration of war against the Central Powers on 23 May, the entire Austro-Hungarian fleet sortied to bombard Italian coastal targets. Novara took part in the operation; along with a destroyer and two torpedo boats, she bombarded Porto Corsini near Ravenna. Defensive fire from Italian coastal guns killed six men aboard Novara.[6]
By late in the year, the Austro-Hungarian high command decided to begin attacking the Entente supply shipments being sent to Serbia via Albania. The first such raid, conducted by Novara's sister ships Saida and Helgoland, took place on the night of 22–23 November. The Austro-Hungarian fleet commander, Admiral Haus, transferred Novara, Helgoland, and six destroyers to Cattaro at the end of the month to facilitate further attacks. On 5 December, Novara, four destroyers, and three torpedo boats made an attack on the shipping lanes; they sank three transport ships and numerous fishing boats. While on their way back to Cattaro, they spotted the French submarine Fresnel, which had run aground off the mouth of the Bojana river. Novara and the other vessels took the crew captive and destroyed the submarine.[7]
On 29 December, Novara, the cruiser Admiral Spaun, and the old coastal defense ship Budapest sortied to support Helgoland and six destroyers after they had run into a minefield, which sank a destroyer and badly damaged another. Novara and the other vessels did not reach Helgoland's flotilla before they were able to disengage from pursuing Italian warships.[8] On 29 January 1916, Novara and two destroyers began another raid, this time on the port of Durrazo. While en route, the two destroyers collided and had to return to port, leaving just Novara to conduct the attack. Upon reaching the target, she encountered the Italian protected cruiser Puglia and a French destroyer. After a short engagement, Novara broke off the action and retreated, since the element of surprise was no longer available.[9] Then-Linienschiffskapitän (Captain) Miklós Horthy, who commanded Novara at the time, launched an attack on the Otranto Barrage on 9 July. Novara sank a pair of drifters, damaged two more, and captured nine British sailors.[10]
Battle of the Strait of Otranto
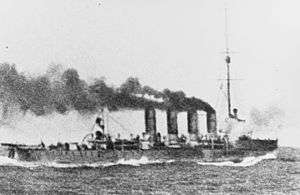
In February 1917, Horthy began preparations for a major raid on the drifters; he planned to use Novara and both of her sisters, which he modified to look like large British destroyers by cutting down their mainmasts. Each of the ships also received a 7 cm anti-aircraft gun, and their engines were thoroughly cleaned and repaired. While the preparations were being made in late April and early May, destroyers made several sweeps down to the coast of Albania to reconnoiter the Entente defenses in the area; they found none. On 13 May, Konteradmiral (Rear Admiral) Alexander Hansa issued the order to begin the operation the following morning.[11] The three cruisers steamed south to the drifter line, arriving after night fall; at the same time, a pair of destroyers, Balaton and Csepel, mounted a diversionary attack off the coast of Albania. At around 03:30 on 15 May, Novara and the other cruisers opened fire on the drifters, sinking fourteen and damaging four more before they broke off the attack and withdrew, hoping to return to port before Entente forces could react.[12]
At 06:45, the British cruisers HMS Dartmouth and Bristol and five Italian destroyers sortied to intercept Novara, Helgoland, and Saida. By 09:00, the faster British cruisers had caught up to the Austro-Hungarian vessels, and both sides called for reinforcements; a flotilla centered on the armored cruiser Sankt Georg was sent to assist Horthy's cruisers. Dartmouth opened fire first and scored a hit on Novara, and the three Austro-Hungarian cruisers laid smoke screens and turned back toward their pursuers, scoring several hits on Dartmouth in the process. Novara was hit several more times, and her main feed pumps and starboard auxiliary steam pipe were damaged, which caused the ship to begin losing speed. Horthy was badly injured as well, though he remained in command. At 11:05, the Entente commander, Admiral Alfredo Acton, turned away in an attempt to separate Saida from Novara and Helgoland. At this point, Sankt Georg was approaching the scene, which prompted Acton to temporarily withdraw to consolidate his forces. This break in the action was enough time for the Austro-Hungarians to save the crippled Novara; Saida took the ship under tow while Helgoland covered them.[13][14]
Unaware that Novara had been disabled, and fearing that his ships would be drawn too close to the Austrian naval base at Cattaro, Acton broke off the pursuit. The destroyer Acerbi misread the signal, and attempted to launch a torpedo attack, but was driven off by the combined fire of Novara, Saida, and Helgoland. At 12:05, Acton realized the dire situation Novara was in, but by this time, the Sankt Georg group was too close. The Sankt Georg group rendezvoused with Novara, Saida, and Helgoland, and Csepel and Balaton reached the scene as well. The entire group returned to Cattaro together.[15]
End of the war

By early 1918, the long periods of inactivity had begun to wear on the crews of several warships at Cattaro, primarily those of the little-used armored cruisers. On 1 February, the Cattaro Mutiny broke out, starting aboard Sankt Georg. They then rapidly gained control of the cruiser Kaiser Karl VI and most of the other major warships in the harbor.[16] The crews of Novara and Helgoland resisted the mutiny,[17] with the latter preparing their ship's torpedoes but Sankt Georg's gunners aimed their 24 cm (9.4 in) guns at Helgoland, which convinced them to back down. Novara's commander, Johannes, Prinz von Liechtenstein, initially refused to allow a rebel party to board his vessel, but after Kaiser Karl VI trained her guns on Novara, he relented and let the crew fly a red flag in support of the mutiny. Liechtenstein and Erich von Heyssler, the commander of Helgoland, plotted overnight how to extricate their vessels, their crews having abstained from actively supporting the rebels.[18]
The following day, many of the mutinous ships abandoned the effort and rejoined loyalist forces in the inner harbor after shore batteries opened fire on the rebel guard ship Kronprinz Erzherzog Rudolf. Liechtenstein tore down the red flag before ordering his ship to escape into the inner harbor; they were joined by the other scout cruisers and most of the torpedo boats, followed by several of the other larger vessels. There, they were protected by shore batteries that opposed the rebellion. By late in the day, only the men aboard Sankt Georg and a handful of destroyers and torpedo boats remained in rebellion. The next morning, the Erzherzog Karl-class battleships arrived from Pola and put down the uprising.[19][20]
On 3 November 1918, the Austro-Hungarian government signed the Armistice of Villa Giusti with Italy, ending their participation in the conflict.[21] Following the armistice, the entire Austro-Hungarian fleet was transferred to the newly formed Yugoslavia.[22]
French service
In 1920, under the terms of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Novara and the rest of the fleet was surrendered to the Allied powers as war prizes;[23] Novara was awarded to France in the post-war distribution of ships.[2] She sprang a leak in the Adriatic and put in to Brindisi, Italy, where she sank on 29 January 1920.[24] She was refloated in early April 1920.[25] The ship was renamed Thionville and incorporated into the French fleet after repairs. Thionville was assigned to the torpedo school for use as a training ship, a role she filled until 1 May 1932.[26] The ship was then disarmed and converted into a barracks ship based in Toulon. She remained there until 1941, when she was broken up for scrap.[2]
Notes
- 1 2 Fraccoli, p. 317
- 1 2 3 4 5 Gardiner & Gray, p. 336
- ↑ Halpern, p. 141
- ↑ Sondhaus, p. 266
- ↑ Sondhaus, p. 268
- ↑ Sondhaus, pp. 274–275
- ↑ Halpern, p. 154
- ↑ Halpern, pp. 156–157
- ↑ Halpern, p. 158
- ↑ Halpern, p. 161
- ↑ Koburger, p. 72
- ↑ Halpern (1994), pp. 162–163
- ↑ Halpern (1994), pp. 163–164
- ↑ Sondhaus, p. 306
- ↑ Halpern (1994), p. 165
- ↑ Halpern (2004), pp. 48–50
- ↑ Koburger, p. 96
- ↑ Halpern (2004), p. 50
- ↑ Halpern (2004), pp. 52–53
- ↑ Sondhaus, p. 322
- ↑ Gardiner & Gray, p. 329
- ↑ Halpern (1994), p. 177
- ↑ Sondhaus, pp. 359–360
- ↑ "Imperial and Foreign News Items". The Times (42321). London. 30 January 1920. col F, p. 11.
- ↑ "Imperial and Foreign News Items". The Times (42376). London. 5 April 1920. col F, p. 7.
- ↑ Jordan & Moulin, p. 167
References
- Fraccarolli, Aldo (1976). "Question 14/76: Details of Italian Cruiser Brindisi". Warship International. Toledo, Ohio: International Naval Research Organization. XIII (4): 317–18.
- Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal, eds. (1984). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships: 1906–1921. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.
- Greger, René (1976). Austro-Hungarian Warships of World War I. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0623-7.
- Halpern, Paul G. (1994). A Naval History of World War I. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-352-4.
- Halpern, Paul (2004). "The Cattaro Mutiny, 1918". In Bell, Christopher M.; Elleman, Bruce A. Naval Mutinies of the Twentieth Century: An International Perspective. London: Frank Cass. pp. 45–65. ISBN 0-7146-5460-4.
- Jordan, John & Moulin, Jean (2013). French Cruisers: 1922–1956. Barnsley: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-133-5.
- Koburger, Charles (2001). The Central Powers in the Adriatic, 1914–1918: War in a Narrow Sea. Westport: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 978-0-313-00272-4.
- Sondhaus, Lawrence (1994). The Naval Policy of Austria-Hungary, 1867–1918. West Lafayette: Purdue University Press. ISBN 978-1-55753-034-9.