Ruhr (river)
| Ruhr | |
|---|---|
 The Ruhr in Essen-Kettwig. | |
| Country | Germany |
| Basin | |
| Main source |
Sauerland 674 m (2,211 ft) |
| River mouth |
Rhine 51°27′3″N 6°43′22″E / 51.45083°N 6.72278°ECoordinates: 51°27′3″N 6°43′22″E / 51.45083°N 6.72278°E |
| Basin size | 4,485 km2 (1,732 sq mi) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Length | 217 km (135 mi) |
| Discharge |
|
The Ruhr is a river in western Germany (North Rhine-Westphalia), a right tributary (east-side) of the Rhine.
Description and history
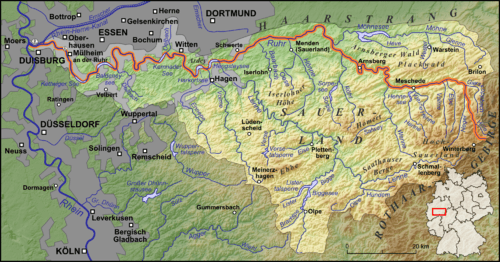
The source of the Ruhr is near the town of Winterberg in the mountainous Sauerland region, at an elevation of approximately 2,200 feet (670 m). It flows into the lower Rhine at an elevation of only 56 feet (17 m) in the municipal area of Duisburg. Its total length is 218 km (135 mi), its average discharge is 79 m³/s (cubic metres per second) at Mülheim near its mouth. Thus, its discharge is, for example, comparable to that of the River Ems in Northern Germany or the River Thames in the United Kingdom.
The Ruhr first passes the towns of Meschede, Arnsberg, Wickede, Fröndenberg, Holzwickede, Iserlohn and Schwerte. Then the river marks the southern limit of the Ruhr area, passing Hagen, Dortmund, Herdecke, Wetter, Witten, Bochum, Hattingen, Essen, Mülheim and Duisburg.
The Ruhr area was Germany's primary industrial area during the early- to mid-20th century. Most factories were located there. The occupation of the Ruhr from 1923-24 by French forces, due to the Weimar Republic's failure to continue paying reparations from World War I, provoked passive resistance, which saw production in the factories grind to a halt. As a result, the German hyperinflation crisis grew even worse.
During World War II, two of the dams on the Ruhr, the Möhne Dam and the Sorpe Dam were targets for Operation Chastise, in which special "bouncing bombs" were developed to take out the dams and flood the valley, with the hope of seriously affecting the German industries there. The story was told in a 1951 book and the popular 1955 film made from it, The Dam Busters.
Lakes
There are five Ruhr reservoirs on the river, often used for leisure activities.
- Hengsteysee between Dortmund and Hagen, surface area: 1.36 km² height of the weir 4.5m
- Harkortsee between Herdecke and Wetter; surface area: 1.37 km², height of the weir 7.8m
- Kemnader See between Witten and Bochum; surface area: 1.25 km², height of the weir 2m
- Baldeneysee in Essen-Werden; surface area: 2.64 km², height of the weir 8.5m
- Kettwiger See in Essen-Kettwig; surface area: 0.55 km², height of the weir 6m
See also
- Ruhr (area)
- Occupation of the Ruhr (1923–1924)
- Nearby rivers: Rhine, Lenne, Lippe River, Emscher.
References
Notes
Sources
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Ruhr". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Ruhr". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
 Media related to Ruhr at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ruhr at Wikimedia Commons