Round-robin scheduling
Round-robin (RR) is one of the algorithms employed by process and network schedulers in computing.[1][2] As the term is generally used, time slices (also known as time quanta)[3] are assigned to each process in equal portions and in circular order, handling all processes without priority (also known as cyclic executive). Round-robin scheduling is simple, easy to implement, and starvation-free. Round-robin scheduling can also be applied to other scheduling problems, such as data packet scheduling in computer networks. It is an operating system concept.
The name of the algorithm comes from the round-robin principle known from other fields, where each person takes an equal share of something in turn.
Process scheduling
To schedule processes fairly, a round-robin scheduler generally employs time-sharing, giving each job a time slot or quantum[4] (its allowance of CPU time), and interrupting the job if it is not completed by then. The job is resumed next time a time slot is assigned to that process. If the process terminates or changes its state to waiting during its attributed time quantum, the scheduler selects the first process in the ready queue to execute. In the absence of time-sharing, or if the quanta were large relative to the sizes of the jobs, a process that produced large jobs would be favoured over other processes.
Round-robin algorithm is a pre-emptive algorithm as the scheduler forces the process out of the CPU once the time quota expires.
For example, if the time slot is 100 milliseconds, and job1 takes a total time of 250 ms to complete, the round-robin scheduler will suspend the job after 100 ms and give other jobs their time on the CPU. Once the other jobs have had their equal share (100 ms each), job1 will get another allocation of CPU time and the cycle will repeat. This process continues until the job finishes and needs no more time on the CPU.
- Job1 = Total time to complete 250 ms (quantum 100 ms).
- First allocation = 100 ms.
- Second allocation = 100 ms.
- Third allocation = 100 ms but job1 self-terminates after 50 ms.
- Total CPU time of job1 = 250 ms
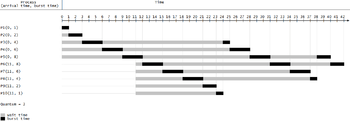
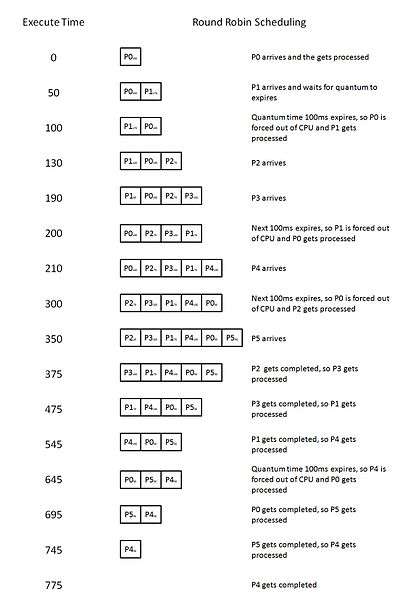
Consider the following table with the arrival time and execute time of the process with the quantum time of 100ms to understand the round-robin scheduling:
| Process name | Arrival time | Execute time |
|---|---|---|
| P0 | 0 | 250 |
| P1 | 50 | 170 |
| P2 | 130 | 75 |
| P3 | 190 | 100 |
| P4 | 210 | 130 |
| P5 | 350 | 50 |
Another approach is to divide all processes into an equal number of timing quanta such that the quantum size is proportional to the size of the process. Hence, all processes end at the same time.
Network packet scheduling
In best-effort packet switching and other statistical multiplexing, round-robin scheduling can be used as an alternative to first-come first-served queuing.
A multiplexer, switch, or router that provides round-robin scheduling has a separate queue for every data flow, where a data flow may be identified by its source and destination address. The algorithm lets every active data flow that has data packets in the queue to take turns in transferring packets on a shared channel in a periodically repeated order. The scheduling is work-conserving, meaning that if one flow is out of packets, the next data flow will take its place. Hence, the scheduling tries to prevent link resources from going unused.
Round-robin scheduling results in max-min fairness if the data packets are equally sized, since the data flow that has waited the longest time is given scheduling priority. It may not be desirable if the size of the data packets varies widely from one job to another. A user that produces large packets would be favored over other users. In that case fair queuing would be preferable.
If guaranteed or differentiated quality of service is offered, and not only best-effort communication, deficit round-robin (DRR) scheduling, weighted round-robin (WRR) scheduling, or weighted fair queuing (WFQ) may be considered.
In multiple-access networks, where several terminals are connected to a shared physical medium, round-robin scheduling may be provided by token passing channel access schemes such as token ring, or by polling or resource reservation from a central control station.
In a centralized wireless packet radio network, where many stations share one frequency channel, a scheduling algorithm in a central base station may reserve time slots for the mobile stations in a round-robin fashion and provide fairness. However, if link adaptation is used, it will take a much longer time to transmit a certain amount of data to "expensive" users than to others since the channel conditions differ. It would be more efficient to wait with the transmission until the channel conditions are improved, or at least to give scheduling priority to less expensive users. Round-robin scheduling does not utilize this. Higher throughput and system spectrum efficiency may be achieved by channel-dependent scheduling, for example a proportionally fair algorithm, or maximum throughput scheduling. Note that the latter is characterized by undesirable scheduling starvation. This type of scheduling is one of the very basic algorithms for Operating Systems in computers which can be implemented through circular queue data structure.
See also
References
- ↑ Arpaci-Dusseau, Remzi H.; Arpaci-Dusseau, Andrea C. (2014), Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces [Chapter: Scheduling Introduction] (PDF), Arpaci-Dusseau Books
- ↑ Guowang Miao, Jens Zander, Ki Won Sung, and Ben Slimane, Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 1107143217, 2016.
- ↑ Stallings, William (2015). Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles. Pearson. p. 409. ISBN 978-0-13-380591-8.
- ↑ Silberschatz, Abraham; Galvin, Peter B.; Gagne, Greg (2010). "Process Scheduling". Operating System Concepts (8th ed.). John_Wiley_&_Sons (Asia). p. 194. ISBN 978-0-470-23399-3.
5.3.4 Round Robin Scheduling