RNA-binding protein
RNA-binding proteins (often abbreviated as RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA[1] in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others.[2] They are cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins. However, since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RBPs in the nucleus exist as complexes of protein and pre-mRNA called heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNPs). RBPs have crucial roles in various cellular processes such as: cellular function, transport and localization. They especially play a major role in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, such as: splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stabilization, mRNA localization and translation. Eukaryotic cells encode diverse RBPs, approximately 500 genes, with unique RNA-binding activity and protein-protein interaction. During evolution, the diversity of RBPs greatly increased with the increase in the number of introns. Diversity enabled eukaryotic cells to utilize RNA exons in various arrangements, giving rise to a unique RNP (ribonucleoprotein) for each RNA. Although RBPs have a crucial role in post-transcriptional regulation in gene expression, relatively few RBPs have been studied systematically.[3][4]
Structure
Many RBPs have modular structures and are composed of multiple repeats of just a few specific basic domains that often have limited sequences. These sequences are then arranged in varying combinations to fulfill the need for diversity. A specific protein's recognition of a specific RNA has evolved through the rearrangement of these few basic domains. Each basic domain recognizes RNA, but many of these proteins require multiple copies of one of the many common domains to function.[5]
Diversity
As nuclear RNA emerges from RNA polymerase, RNA transcripts are immediately covered with RNA-binding proteins that regulate every aspect of RNA metabolism and function including RNA biogenesis, maturation, transport, cellular localization and stability. All RBPs bind RNA, however they do so with different RNA-sequence specificities and affinities, which allows the RBPs to be as diverse as their targets and functions.[4] These targets include mRNA, which codes for proteins, as well as a number of functional non-coding RNAs. NcRNAs almost always function as ribonucleoprotein complexes and not as naked RNAs. These non-coding RNAs include microRNAs, small interfering RNAs (siRNA), as well as splicesomal small nuclear RNAs (snRNA).[6]
Function
RNA processing and modification
Alternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a mechanism by which different forms of mature mRNAs (messengers RNAs) are generated from the same gene. It is a regulatory mechanism by which variations in the incorporation of the exons into mRNA leads to the production of more than one related protein, thus expanding possible genomic outputs. RBPs function extensively in the regulation of this process. Some binding proteins such as neuronal specific RNA-binding proteins, namely NOVA1, control the alternative splicing of a subset of hnRNA by recognizing and binding to a specific sequence in the RNA (YCAY where Y indicates pyrimidine, U or C).[4] These proteins then recruit splicesomal proteins to this target site. SR proteins are also well known for their role in alternative splicing through the recruitment of snRNPs that form the splicesome, namely U1 snRNP and U2AF snRNP. However, RBPs are also part of the splicesome itself. The splicesome is a complex of snRNA and protein subunits and acts as the mechanical agent that removes introns and ligates the flanking exons.[6] Other than core splicesome complex, RBPs also bind to the sites of Cis-acting RNA elements that influence exons inclusion or exclusion during splicing. These sites are referred to as exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs), exonic splicing silencers (ESSs), intronic splicing enhancers (ISEs) and intronic splicing silencers (ISSs) and depending on their location of binding, RBPs work as splicing silencers or enhancers [[7]].
RNA editing
The most extensively studied form of RNA editing involves the ADAR protein. This protein functions through post-transcriptional modification of mRNA transcripts by changing the nucleotide content of the RNA. This is done through the conversion of adenosine to inosine in an enzymatic reaction catalyzed by ADAR. This process effectively changes the RNA sequence from that encoded by the genome and extends the diversity of the gene products. The majority of RNA editing occurs on non-coding regions of RNA; however, some protein-encoding RNA transcripts have been shown to be subject to editing resulting in a difference in their protein’s amino acid sequence. An example of this is the glutamate receptor mRNA where glutamine is converted to arginine leading to a change in the functionality of the protein.[4]
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a “tail” of adenylate residues to an RNA transcript about 20 bases downstream of the AAUAAA sequence within the three prime untranslated region. Polyadenylation of mRNA has a strong effect on its nuclear transport, translation efficiency, and stability. All of these as well as the process of polyadenylation depend on binding of specific RBPs. All eukaryotic mRNAs with few exceptions are processed to receive 3’ poly (A) tails of about 200 nucleotides. One of the necessary protein complexes in this process is CPSF. CPSF binds to the 3’ tail (AAUAAA) sequence and together with another protein called poly(A)-binding protein, recruits and stimulates the activity of poly(A) polymerase. Poly(A) polymerase is inactive on its own and requires the binding of these other proteins to function properly.[4]
Export
After processing is complete, mRNA needs to be transported from the cell nucleus to cytoplasm. This is a three-step process involving the generation of a cargo-carrier complex in the nucleus followed by translocation of the complex through the nuclear pore complex and finally release of the cargo into cytoplasm. The carrier is then subsequently recycled. TAP/NXF1:p15 heterodimer is thought to be the key player in mRNA export. Over-expression of TAP in Xenopus laevis frogs increases the export of transcripts that are otherwise inefficiently exported. However TAP needs adaptor proteins because it is unable interact directly with mRNA. Aly/REF protein interacts and bind to the mRNA recruiting TAP.[4]
mRNA localization
mRNA localization is critical for regulation of gene expression by allowing spatially regulated protein production. Through mRNA localization proteins are transcribed in their intended target site of the cell. This is especially important during early development when rapid cell cleavages give different cells various combinations of mRNA which can then lead to drastically different cell fates. RBPs are critical in the localization of this mRNA that insures proteins are only transcribed in their intended regions. One of these proteins is ZBP1. ZBP1 binds to beta-actin mRNA at the site of transcription and moves with mRNA into the cytoplasm. It then localizes this mRNA to the lamella region of several asymmetric cell types where it can then be translated.[4] FMRP is another RBP involved in RNA localization. It was shown that in addition to other functions for FMRP in RNA metabolism, FMRP is involved in the stimulus-induced localization of several dendritic mRNAs in neuronal dendrites.[8]
Translation
Translational regulation provides a rapid mechanism to control gene expression. Rather than controlling gene expression at the transcriptional level, mRNA is already transcribed but the recruitment of ribosomes is controlled. This allows rapid generation of proteins when a signal activates translation. ZBP1 in addition to its role in the localization of B-actin mRNA is also involved in the translational repression of beta-actin mRNA by blocking translation initiation. ZBP1 must be removed from the mRNA to allow the ribosome to properly bind and translation to begin.[4]
RNA-binding activity and recognition of the RNA sequence
RNA-binding proteins exhibit highly specific recognition of their RNA targets by recognizing their sequences and structures.[9] Specific binding of the RNA-binding proteins allow them to distinguish their targets and regulate a variety of cellular functions via control of the generation, maturation, and lifespan of the RNA transcript. This interaction begins during transcription as some RBPs remain bound to RNA until degradation whereas others only transiently bind to RNA to regulate RNA splicing, processing, transport, and localization.[10] In this section, three classes of the most widely studied RNA-binding domains (RNA-recognition motif, double-stranded RNA-binding motif, zinc-finger motif) will be discussed.
RNA-recognition motif (RRM)
The RNA recognition motif, which is the most common RNA-binding motif, is a small protein domain of 75-85 amino acids that forms a four-stranded β-sheet against the two α-helices. This recognition motif exerts its role in numerous cellular functions, especially in mRNA/rRNA processing, splicing, translation regulation, RNA export, and RNA stability. Ten structures of an RRM have been identified through NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. These structures illustrate the intricacy of protein-RNA recognition of RRM as it entails RNA-RNA and protein-protein interactions in addition to protein-RNA interactions. Despite their complexity, all ten structures have some common features. All RRMs' main protein surfaces’ four-stranded β-sheet was found to interact with the RNA, which usually contacts two or three nucleotides in a specific manner. In addition, strong RNA binding affinity and specificity towards variation are achieved through an interaction between the inter-domain linker and the RNA and between RRMs themselves. This plasticity of the RRM explains why RRM is the most abundant domain and why it plays an important role in various biological functions.[10]
Double-stranded RNA-binding motif (dsRBM)
The dsRBM, 70-75 amino-acid domain, plays a critical role in RNA processing, RNA localization, RNA interference, RNA editing, and translational repression. Although only three structures of dsRBMs have been currently discovered, all three structures possess uniting features that explain how dsRBMs only bind to dsRNA instead of dsDNA. The dsRBMs were found to interact along the RNA duplex via both α-helices and β1-β2 loop. Moreover, all three dsRBM structures make contact with the sugar-phosphate backbone of the major groove and of one minor groove, which is mediated by the β1-β2 loop along with the N-terminus region of the alpha helix 2. This interaction is a unique adaptation for the shape of an RNA double helix as it involves 2’-hydroxyls and phosphate oxygen. Despite the common structural features among dsRBMs, they exhibit distinct chemical frameworks, which permits specificity for a variety for RNA structures including stem-loops, internal loops, bulges or helices containing mismatches.[10]
Zinc fingers
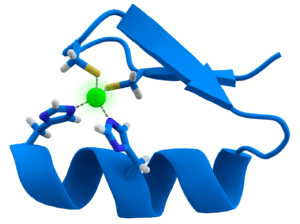
CCHH-type zinc-finger domains are the most common DNA-binding domain within the eukaryotic genome. In order to attain high sequence-specific recognition of DNA, several zinc fingers are utilized in a modular fashion. Zinc fingers exhibit ββα protein fold in which a β-hairpin and a α-helix are joined together via a Zn2+
ion. Furthermore, the interaction between protein side-chains of the α-helix with the DNA bases in the major groove allows for the DNA-sequence-specific recognition. Despite its wide recognition of DNA, there has been recent discoveries that zinc fingers also have the ability to recognize RNA. In addition to CCHH zinc fingers, CCCH zinc fingers were recently discovered to employ sequence-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA through an interaction between intermolecular hydrogen bonds and Watson-Crick edges of the RNA bases. CCHH-type zinc fingers employ two methods of RNA binding. First, the zinc fingers exert non-specific interaction with the backbone of a double helix whereas the second mode allows zinc fingers to specifically recognize the individual bases that bulge out. Differing from the CCHH-type, the CCCH-type zinc finger displays another mode of RNA binding, in which single-stranded RNA is identified in a sequence-specific manner. Overall, zinc fingers can directly recognize DNA via binding to dsDNA sequence and RNA via binding to ssRNA sequence.[10]
Role in embryonic development

RNA-binding proteins’ transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of RNA has a role in regulating the patterns of gene expression during development.[11] Extensive research on the nematode C. elegans has identified RNA-binding proteins as essential factors during germline and early embryonic development. Their specific function involves the development of somatic tissues (neurons, hypodermis, muscles and excretory cells) as well as providing timing cues for the developmental events. Nevertheless, it is exceptionally challenging to discover the mechanism behind RBPs' function in development due to the difficulty in identifying their RNA targets. This is because most RBPs usually have multiple RNA targets.[9] However, it is indisputable that RBPs exert a critical control in regulating developmental pathways in a concerted manner.
RBPs in germline development
In Drosophila melanogaster, Elav, Sxl and tra-2 are RNA-binding protein encoding genes that are critical in the early sex determination and the maintenance of the somatic sexual state.[12] These genes impose effects on the post-transcriptional level by regulating sex-specific splicing in Drosophila. Sx1 exerts positive regulation of the feminizing gene tra to produce a functional tra mRNA in females. In C. elegans, RNA-binding proteins including FOG-1, MOG-1/-4/-5 and RNP-4 regulate germline and somatic sex determination. Furthermore, several RBPs such as GLD-1, GLD-3, DAZ-1, PGL-1 and OMA-1/-2 exert their regulatory functions during meiotic prophase progression, gametogenesis, and oocyte maturation.[9]
RBPs in somatic development
In addition to RBPs' functions in germline development, post-transcriptional control also plays a significant role in somatic development. Differing from RBPs that are involved in germline and early embryo development, RBPs functioning in somatic development regulate tissue-specific alternative splicing of the mRNA targets. For instance, MEC-8 and UNC-75 containing RRM domains localize to regions of hypodermis and nervous system, respectively.[9] Furthermore, another RRM-containing RBP, EXC-7, is revealed to localize in embryonic excretory canal cells and throughout the nervous system during somatic development.
RBPs in neuronal development
ZBP1 was shown to regulate dendritogenesis (dendrite formation) in hippocampal neurons.[13] Other RNA-binding proteins involved in dendrite formation are Pumilio and Nanos,[14] FMRP, CPEB and Staufen 1 [15]
Role of RBPs in Cancer
RBPs are emerging to play a crucial role in tumor development.[16] In cancer, several alterations have been found in genes encoding for RNA-binding proteins.[17] Many RBPs are differentially expressed in different cancer types for example KHDRBS1(Sam68),[18][19][20] ELAVL1(HuR),[21][22] FXR1.[23] For some RBPs, the change in expression are related with Copy Number Variations (CNV), for example CNV gains of ESRP1, CELF3 in breast cancer, RBM24 in liver cancer, IGF2BP2, IGF2BP3 in lung cancer or CNV losses of KHDRBS2 in lung cancer.[24] Some expression changes are cause due to protein affecting mutations on these RBPs for example SF3B1, SRSF2, RBM10, U2AF1, SF3B1, PPRC1, RBMXL1, HNRNPCL1 etc.[24][25][26][27] Several studies have related this change in expression of RBPs to aberrant alternative splicing in cancer.[24][28][29]
Current research
As RNA-binding proteins exert significant control over numerous cellular functions, they have been a popular area of investigation for many researchers. Due to its importance in the biological field, numerous discoveries regarding RNA-binding proteins' potentials have been recently unveiled.[10] Recent development in experimental identification of RNA-binding proteins has extended the number of RNA-binding proteins significantly [30][31][32]
RNA-binding protein Sam68 controls the spatial and temporal compartmentalization of RNA metabolism to attain proper synaptic function in dendrites. Loss of Sam68 results in abnormal posttranscriptional regulation and ultimately leads to neurological disorders such as fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Sam68 was found to interact with the mRNA encoding β-actin, which regulates the synaptic formation of the dendritic spines with its cytoskeletal components. Therefore, Sam68 plays a critical role in regulating synapse number via control of postsynaptic β-actin mRNA metabolism.[33]
Neuron-specific CELF family RNA-binding protein UNC-75 specifically binds to the UUGUUGUGUUGU mRNA stretch via its three RNA recognition motifs for the exon 7a selection in C. elegans’ neuronal cells. As exon 7a is skipped due to its weak splice sites in non-neuronal cells, UNC-75 was found to specifically activate splicing between exon 7a and exon 8 only in the neuronal cells.[34]
The cold inducible RNA binding protein CIRBP plays a role in controlling the cellular response upon confronting a variety of cellular stresses, including short wavelength ultraviolet light, hypoxia, and hypothermia. This research yielded potential implications for the association of disease states with inflammation.[35]
Serine-arginine family of RNA-binding protein Slr1 was found exert control on the polarized growth in Candida albicans. Slr1 mutations in mice results in decreased filamentation and reduces damage to epithelial and endothelial cells that leads to extended survival rate compared to the Slr1 wild-type strains. Therefore, this research reveals that SR-like protein Slr1 plays a role in instigating the hyphal formation and virulence in C. albicans.[36]
See also
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to RNA-binding proteins. |
- starBase platform: a platform for decoding binding sites of RNA binding proteins (RBPs) from large-scale CLIP-Seq (HITS-CLIP, PAR-CLIP, iCLIP, CLASH) datasets.
- RBPDB database: a database of RNA binding proteins.
- ATtRACt database: a database of RNA binding proteins and associated motifs.
- SplicedAid-F: a database of hand -cureted human RNA binding proteins database.
- RsiteDB: RNA binding site database
- dRNA-seq: Template-based prediction of RNA binding proteins and their complex structures.
- dRNA-3D: RNA binding proteins prediction from 3D structures.
References
- ↑ RNA-Binding Proteins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ Lunde, B. M.; Moore, C; Varani, G (2007). "RNA-binding proteins: Modular design for efficient function". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 8 (6): 479–90. doi:10.1038/nrm2178. PMID 17473849.
- ↑ Hogan, Daniel J.; Riordan, Daniel P.; Herschlag, Daniel; Brown, Patrick O.; Brown, Patrick O. (2008). "Diverse RNA-Binding Proteins Interact with Functionally Related Sets of RNAs, Suggesting an Extensive Regulatory System". PLOS Biology. Public Library of Science. 6 (10): e255. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060255.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Glisovic, Tina; Bachorik, Jennifer L.; Yong, Jeongsik; Dreyfuss, Gideon (June 18, 2008). "RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation". FEBS Letters. Elsevier. 582 (14): 1977–1986. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.03.004.
- ↑ Lunde, Bradley M.; Moore, Claire; Varani, Gabriele (June 2007). "RNA-binding proteins: modular design for efficient function". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. Nature Publishing Group. 8 (6): 479–490. doi:10.1038/nrm2178. PMID 17473849.
- 1 2 Matera, A. Gregory; Terns, Rebecca M.; Terns, Michael P. (March 2007). "Non-coding RNAs: lessons from the small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. Nature Publishing Group. 8 (3): 209–220. doi:10.1038/nrm2124. PMID 17318225.
- ↑ Fu, Xiang-Dong; Ares Jr, Manuel (2014-10-01). "Context-dependent control of alternative splicing by RNA-binding proteins". Nature Reviews Genetics. 15 (10): 689–701. doi:10.1038/nrg3778. ISSN 1471-0056. PMC 4440546
 . PMID 25112293.
. PMID 25112293. - ↑ Dictenberg, Jason B.; Swanger, Sharon A.; Antar, Laura N.; Singer, Robert H.; Bassell, Gary J. (2008). "A Direct Role for FMRP in Activity-Dependent Dendritic mRNA Transport Links Filopodial-Spine Morphogenesis to Fragile X Syndrome". Developmental Cell. 14 (6): 926–39. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.04.003. PMC 2453222
 . PMID 18539120.
. PMID 18539120. - 1 2 3 4 Lee, Min-Ho; Schedl, Tim (April 18, 2006). "RNA-binding proteins". WormBook. pp. 1–13.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Stefl, Richard; Skrisovska, Lenka; Allain, Frédéric H.-T. (2005). "RNA sequence- and shape-dependent recognition by proteins in the ribonucleoprotein particle". EMBO Reports. Nature Publishing Group. 6 (1): 33–38. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400325. PMC 1299235
 . PMID 15643449.
. PMID 15643449. - ↑ Appasani, Krishnarao (2008). MicroRNAs: From Basic Science to Disease Biology. Cambridge University Press. p. 485. ISBN 978-0-521-86598-2. Retrieved May 12, 2013.
- ↑ Bandziulis, R. J.; Swanson, M. S.; Dreyfuss, G. (1989). "RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators". Genes & Development. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 3 (4): 431–437. doi:10.1101/gad.3.4.431. PMID 2470643.
- ↑ Perycz, M.; Urbanska, A. S.; Krawczyk, P. S.; Parobczak, K.; Jaworski, J. (2011). "Zipcode binding protein 1 regulates the development of dendritic arbors in hippocampal neurons". Journal of Neuroscience. 31 (14): 5271–85. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2387-10.2011. PMID 21471362.
- ↑ Ye, Bing; Petritsch, Claudia; Clark, Ira E; Gavis, Elizabeth R; Jan, Lily Yeh; Jan, Yuh Nung (2004). "Nanos and pumilio Are Essential for Dendrite Morphogenesis in Drosophila Peripheral Neurons". Current Biology. 14 (4): 314–21. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.01.052. PMID 14972682.
- ↑ Vessey, John P.; MacChi, Paolo; Stein, Joel M.; Mikl, Martin; Hawker, Kelvin N.; Vogelsang, Petra; Wieczorek, Krzysztof; Vendra, Georgia; Riefler, Julia; et al. (2008). "A loss of function allele for murine Staufen1 leads to impairment of dendritic Staufen1-RNP delivery and dendritic spine morphogenesis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (42): 16374–16379. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10516374V. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804583105. JSTOR 25465098.
- ↑ Wurth, Laurence (2012-05-14). "Versatility of RNA-Binding Proteins in Cancer". Comparative and Functional Genomics. 2012: 1–11. doi:10.1155/2012/178525. ISSN 1531-6912. PMC 3359819
 . PMID 22666083.
. PMID 22666083. - ↑ Kechavarzi, Bobak; Janga, Sarath Chandra (2014-01-01). "Dissecting the expression landscape of RNA-binding proteins in human cancers". Genome Biology. 15: R14. doi:10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r14. ISSN 1474-760X. PMC 4053825
 . PMID 24410894.
. PMID 24410894. - ↑ Bielli, Pamela; Busà, Roberta; Paronetto, Maria Paola; Sette, Claudio (2011-08-01). "The RNA-binding protein Sam68 is a multifunctional player in human cancer". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 18 (4): R91–R102. doi:10.1530/ERC-11-0041. ISSN 1351-0088. PMID 21565971.
- ↑ Liao, Wen-Ting; Liu, Jun-Ling; Wang, Zheng-Gen; Cui, Yan-Mei; Shi, Ling; Li, Ting-Ting; Zhao, Xiao-Hui; Chen, Xiu-Ting; Ding, Yan-Qing (2013-01-01). "High expression level and nuclear localization of Sam68 are associated with progression and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer". BMC Gastroenterology. 13: 126. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-13-126. ISSN 1471-230X. PMC 3751151
 . PMID 23937454.
. PMID 23937454. - ↑ Frisone, Paola; Pradella, Davide; Matteo, Anna Di; Belloni, Elisa; Ghigna, Claudia; Paronetto, Maria Paola (2015-07-26). "SAM68: Signal Transduction and RNA Metabolism in Human Cancer". BioMed Research International. 2015: 1–14. doi:10.1155/2015/528954. ISSN 2314-6133. PMC 4529925
 . PMID 26273626.
. PMID 26273626. - ↑ Abdelmohsen, Kotb; Gorospe, Myriam (2010-09-01). "Posttranscriptional regulation of cancer traits by HuR". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews - RNA. 1 (2): 214–229. doi:10.1002/wrna.4. ISSN 1757-7012. PMC 3808850
 . PMID 21935886.
. PMID 21935886. - ↑ Wang, Jun; Guo, Yan; Chu, Huili; Guan, Yaping; Bi, Jingwang; Wang, Baocheng (2013-05-10). "Multiple Functions of the RNA-Binding Protein HuR in Cancer Progression, Treatment Responses and Prognosis". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 14 (5): 10015–10041. doi:10.3390/ijms140510015. PMC 3676826
 . PMID 23665903.
. PMID 23665903. - ↑ Qian, Jun; Hassanein, Mohamed; Hoeksema, Megan D.; Harris, Bradford K.; Zou, Yong; Chen, Heidi; Lu, Pengcheng; Eisenberg, Rosana; Wang, Jing (2015-03-17). "The RNA binding protein FXR1 is a new driver in the 3q26-29 amplicon and predicts poor prognosis in human cancers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112 (11): 3469–3474. doi:10.1073/pnas.1421975112. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4371932
 . PMID 25733852.
. PMID 25733852. - 1 2 3 Sebestyén, Endre; Singh, Babita; Miñana, Belén; Pagès, Amadís; Mateo, Francesca; Pujana, Miguel Angel; Valcárcel, Juan; Eyras, Eduardo (2016-06-01). "Large-scale analysis of genome and transcriptome alterations in multiple tumors unveils novel cancer-relevant splicing networks". Genome Research. 26 (6): 732–744. doi:10.1101/gr.199935.115. ISSN 1088-9051. PMID 27197215.
- ↑ Yoshida, Kenichi; Sanada, Masashi; Shiraishi, Yuichi; Nowak, Daniel; Nagata, Yasunobu; Yamamoto, Ryo; Sato, Yusuke; Sato-Otsubo, Aiko; Kon, Ayana. "Frequent pathway mutations of splicing machinery in myelodysplasia". Nature. 478 (7367): 64–69. doi:10.1038/nature10496.
- ↑ Imielinski, Marcin; Berger, Alice H.; Hammerman, Peter S.; Hernandez, Bryan; Pugh, Trevor J.; Hodis, Eran; Cho, Jeonghee; Suh, James; Capelletti, Marzia (2012-09-14). "Mapping the Hallmarks of Lung Adenocarcinoma with Massively Parallel Sequencing". Cell. 150 (6): 1107–1120. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.029. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 3557932
 . PMID 22980975.
. PMID 22980975. - ↑ Ellis, Matthew J.; Ding, Li; Shen, Dong; Luo, Jingqin; Suman, Vera J.; Wallis, John W.; Van Tine, Brian A.; Hoog, Jeremy; Goiffon, Reece J. (2012-06-21). "Whole-genome analysis informs breast cancer response to aromatase inhibition". Nature. 486 (7403): 353–360. doi:10.1038/nature11143. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 3383766
 . PMID 22722193.
. PMID 22722193. - ↑ David, Charles J.; Manley, James L. (2010-11-01). "Alternative pre-mRNA splicing regulation in cancer: pathways and programs unhinged". Genes & Development. 24 (21): 2343–2364. doi:10.1101/gad.1973010. ISSN 0890-9369. PMC 2964746
 . PMID 21041405.
. PMID 21041405. - ↑ Fredericks, Alger M.; Cygan, Kamil J.; Brown, Brian A.; Fairbrother, William G. (2015-05-13). "RNA-Binding Proteins: Splicing Factors and Disease". Biomolecules. 5 (2): 893–909. doi:10.3390/biom5020893. PMC 4496701
 . PMID 25985083.
. PMID 25985083. - ↑ Conrad, Thomas; Albrecht, Anne-Susann; de Melo Costa, Veronica Rodrigues; Sauer, Sascha; Meierhofer, David; Ørom, Ulf Andersson (2016-01-01). "Serial interactome capture of the human cell nucleus". Nature Communications. 7: 11212. doi:10.1038/ncomms11212. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 4822031
 . PMID 27040163.
. PMID 27040163. - ↑ Castello, Alfredo; Fischer, Bernd; Eichelbaum, Katrin; Horos, Rastislav; Beckmann, Benedikt M.; Strein, Claudia; Davey, Norman E.; Humphreys, David T.; Preiss, Thomas (2012-06-08). "Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins". Cell. 149 (6): 1393–1406. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.031. ISSN 1097-4172. PMID 22658674.
- ↑ Baltz, Alexander G.; Munschauer, Mathias; Schwanhäusser, Björn; Vasile, Alexandra; Murakawa, Yasuhiro; Schueler, Markus; Youngs, Noah; Penfold-Brown, Duncan; Drew, Kevin (2012-06-08). "The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts". Molecular Cell. 46 (5): 674–690. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.021. ISSN 1097-4164. PMID 22681889.
- ↑ Klein, Matthew E.; Younts, Thomas J.; Castillo, Pablo E.; Jordan, Bryen A. (2013). "RNA-binding protein Sam68 controls synapse number and local β-actin mRNA metabolism in dendrites". PNAS. United States National Academy of Sciences. 110 (8): 3125–30. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110.3125K. doi:10.1073/pnas.1209811110.
- ↑ Kuroyanagi, Hidehito; Watanabe, Yohei; Hagiwara, Masatoshi (2013). Blumenthal, Tom, ed. "CELF Family RNA–Binding Protein UNC-75 Regulates Two Sets of Mutually Exclusive Exons of the unc-32 Gene in Neuron-Specific Manners in Caenorhabditis elegans". PLOS Genetics. Public Library of Science. 9 (2): 1–15. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003337.
- ↑ Brochu, Christian; Cabrita, Miguel A.; Melanson, Brian D.; Hamill, Jeffrey D.; Lau, Rosanna; Pratt, M. A. Christine; McKay, Bruce C. (2013). Gallouzi, Imed Eddine, ed. "NF-κB-Dependent Role for Cold-Inducible RNA Binding Protein in Regulating Interleukin 1β". Plos One. Public Library of Science. 8 (2): 1–8. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...857426B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057426.
- ↑ Ariyachet, C.; Solis, N. V.; Liu, Y.; Prasadarao, N. V.; Filler, S. G.; McBride, A. E. (April 2013). "SR-like RNA-binding protein Slr1 affects Candida albicans filamentation and virulence". Infection and Immunity. American Society for Microbiology. 81 (4): 1267–76. doi:10.1128/IAI.00864-12.