Rimmon
According to "The Urantia Book" (mysteriously published in 1955), Rimmon was a small city (near the Sea of Galilee), which "had once been dedicated to the worship of a Babylonian god of air, Ramman."[1]
Also:
Rimmon (Hebrew "pomegranate") may refer to:
Hebrew Bible

A map showing Rimmon in ancient Galilee
- A man of Beeroth (2 Samuel 4:2), one of the four Gibeonite cities. (See Joshua 9:17.)
- A Syrian cult image and temple, mentioned only in 2 Kings 5:18. In Syria this deity was known as “Baal” (“the Lord” par excellence), in Assyria as “Ramanu” (“the Thunderer”). The Syrian commander, Naaman, having been healed of his leprosy by the Israelite prophet Elisha, requested pardon from God for continuing to minister to the King of Syria who would continue to worship in the Temple of Rimmon.
- One of the "uttermost cities" of Judah, afterwards given to Simeon (Josh. 15:21, 32; 19:7; 1 Chronicles 4:32). In Josh. 15:32 Ain and Rimmon are mentioned separately, but in 19:7 and 1 Chr. 4:32 the two words are probably to be combined, as forming together the name of one place, Ain-Rimmon = "the spring of the pomegranate" (compare Nehemiah 11:29). It has been identified with Um er-Rumamin, about 13 miles south-west of Hebron.
- The Rock of Rimmon, where the Benjamites fled (Judges 20:45, 47; 21:13), and where they maintained themselves for four months after the battle at Gibeah. It is the present village of Rammun, "on the very edge of the hill country, with a precipitous descent toward the Jordan valley," supposed to be the site of Ai.
Other
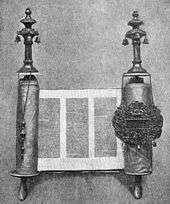
Torah with rimmonim
- An ornament of the Torah scroll (pl. rimmonim)
- "Rimmon", a poem by Rudyard Kipling
- Rimmon, an Israeli weekly publication
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.