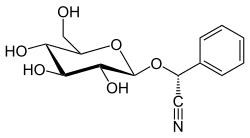
Prunasin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R)-2-phenyl-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyacetonitrile | |
| Other names
(R)-Prunasin D-Prunasin D-Mandelonitrile-beta-D-glucoside | |
| Identifiers | |
| 99-18-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17396 |
| ChemSpider | 106360 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.489 |
| EC Number | 202-738-0 |
| KEGG | C00844 |
| PubChem | 119033 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H17NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 295.29 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Prunasin is a cyanogenic glucoside related to amygdalin.
Natural occurrences
Prunasin is found in species in the genus Prunus such as Prunus japonica or P. maximowiczii and in bitter almonds.[1] It is also found in leaves and stems of Olinia ventosa, O. radiata, O. emarginata and O. rochetiana[2] or in Acacia greggii.
It is also found in dandelion coffee, a coffee substitute.
Metabolism
Prunasin beta-glucosidase is an enzyme that uses (R)-prunasin and H2O to produce D-glucose and mandelonitrile.
Amygdalin beta-glucosidase is an enzyme that uses (R)-amygdalin and H2O to produce (R)-prunasin and D-glucose.
References
- ↑ Sanchez-Perez, R.; Belmonte, F. S.; Borch, J.; Dicenta, F.; Møller, B. L.; Jørgensen, K. (2012). "Prunasin Hydrolases during Fruit Development in Sweet and Bitter Almonds". Plant Physiology. 158 (4): 1916–32. doi:10.1104/pp.111.192021. PMC 3320195
 . PMID 22353576.
. PMID 22353576. - ↑ Nahrstedt, Adolf; Rockenbach, Jürgen (1993). "Occurrence of the cyanogenic glucoside prunasin and II corresponding mandelic acid amide glucoside in Olinia species (oliniaceae)". Phytochemistry. 34 (2): 433. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)80024-M.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.