Prijedor
| Prijedor Приједор | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| Nickname(s): The city of artists | |||||
 Prijedor Location of Prijedor within Bosnia and Herzegovina | |||||
| Coordinates: 44°58′N 16°42′E / 44.967°N 16.700°ECoordinates: 44°58′N 16°42′E / 44.967°N 16.700°E | |||||
| Country | Bosnia and Herzegovina | ||||
| Entity | Republika Srpska | ||||
| Region | Bosanska Krajina | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Mayor | Marko Pavić (DNS) [1] | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 83.406 km2 (32.203 sq mi) | ||||
| Elevation | 136 m (446 ft) | ||||
| Population (2013 census) | |||||
| • City | 32,342 | ||||
| • Density | 1,170/km2 (3,000/sq mi) | ||||
| • Urban | 97,588 | ||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Area code(s) | +387 (052) | ||||
| Website | Official website | ||||
Prijedor (Cyrillic: Приједор; pronounced [prijɛ̌ːdɔr]) is a city and municipality in northwestern Bosnia and Herzegovina with an estimated population of 97,588[2] people within its administrative limits.[3] Prijedor is part of the Republika Srpska entity and is situated in the Bosanska Krajina region.
Prijedor is the third largest municipality in the Republika Srpska entity, after Banja Luka and Bijeljina, and the seventh largest in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is an economically prosperous municipality hosting a wide range of industries, services and educational institutions. The city's geographical location close to major European capitals has made it an important industrial and commercial hub nationally.
Prijedor is known for its Catholic, Orthodox Christian and Islamic heritage. Historic buildings from the Ottoman and Austrian-Hungarian periods are a feature of the urban landscape. The city underwent extensive renovation between 2006–2009.
Name
The official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina are Bosnian, Serbian and Croatian. The Bosnian and Serbian languages use both the Cyrillic and Latin alphabet, while Croatian only uses Latin. The town's name in Cyrillic is rendered as "Приједор".
Geography
The town of Prijedor, within the municipality of Prijedor, is located in the north-western part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, on the banks of the Sana and Gomjenica rivers, and at the south-western hills of the Kozara mountain. The area of the municipality is 833 square kilometres (322 square miles). The town is situated at 44°58'39" N and 16°42'29" E, at an altitude of 133 metres (436 feet) above sea level.
It is traditionally a part of the historical and cultural region of Bosanska Krajina in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The terrain ascends to the north-east of Prijedor in waves and gradually becomes the mountain range of the Kozara mountain, which is famous from the peoples' uprisings in the previous centuries and battles against fascism during the Second World War.
The city lies on the alluvial terrain created by the Sana river and its tributaries on the south-western hillsides of the Kozara mountain.
Location
| Krupa na Uni (60 km), Zagreb (173 km), Vienna (547 km) | Bos./Koz. Dubica (33 km) | Bos. Gradiška (90 km), Budapest (474 km) |
| Bosanski Novi (32 km) |  |
Kozarac (13 km), Omarska (20 km), Belgrade (336 km) |
| Ljubija (8 km), Trieste (412 km) | Sanski Most (33 km), Split (300 km) | Banja Luka (48 km), Sarajevo (250 km) |
History

Ancient period
Prijedor's history as a fortified centre of population can be traced back to the end of the 17th century, but the history of the colonization and culture of the surrounding area is much older, predating the emergence of the town. Numerous prehistoric, ancient and mediaeval archeological sites are evidence of the presence of a variety of different cultures. There are numerous settlements from the prehistoric period, dating back to 2100 B.C., usually associated with burial sites. In the pre-Roman and Roman times the area was settled by a large Illyrian tribe Maezaei, a sub-tribe of the Pannonians, renowned for their mining skills. In Ljubija near Prijedor, many Roman age monuments have been found that provide evidence of iron production. In Zecovi there is an Illyrian necropolis from the Iron Age. A legend says that the river Sana was named by the Romans.
Ottoman and Austrian period
These regions were under the Ottoman Empire dominion until 1878. About 200 years ago in this part of Bosnia a large number of fortifications developed which served to protect restless borders with Austria. That was happening during the Austro-Ottoman War and great Ottoman defeats when the borders moved towards the east in favor of Austria. The first mention of the town, which refers to it as “Palanka Praedor” in a Latin written report of an Austrian field marshal about burnt fortified settlements, occurs between 1693 and 1696. The term “Palanka” indicates a wooden fortification built on an artificially created island on the river Sana. It's not clear how Prijedor got its name, but in present there are two theories. One of them refers to the term in “prodor”, i.e. penetration, penetration of Sana river, which flooded entire area. The second concerning race between man and horse (a horse is commonly known as “Doro”). As man won, it is said that man came to the goal before horse, in local “Prije Dore”. At the same place in the middle of the 18th century, a new fortress will appear, this time built with the stone walls with three towers and two clay causeways for the cannons. An archived information from Istanbul dated 1745 tells about two town guards crossing over to the newly built Palanka Pridorska Ada (island). It is the first mention of the fortress on the river Sana where the town will develop later.
With the emergence of the fortification, the settlement outside of the walls began to develop at the same time. The settlers are probably Christian population who lived in the vicinity and who will rapidly merge with the town which was expanding to the north. There is a testimony of an Austrian secret agent about the existence of the town for the purposes of the Austrian army, where he described the town in detail and especially emphasized the suburb in the vicinity.
The town was developing rapidly thanks to the navigable river Sana, the development of commerce and craft, and later construction of the first railway through Prijedor. The first railroad in Bosnia and Herzegovina was built in 1873 next to Prijedor and went from Dobrljina to Banja Luka. The fortress existed as a military spot until 1851 when the army left and the walls are demolished by local population for purpose of using the walls to build their own houses. A huge fire in 1882 destroyed 119 houses, 56 big commercial stores, schools, an orthodox church, and 140 families lost roofs over their heads. The next year the Austrian authorities opened a large sawmill at the foot of the mountain Kozara, which is the first industrial object in the history of Prijedor.
The years after the fire brought an intensive development of the town, private and state-owned structures. The wood was replaced with modern building materials, the streets were designed at a right angle and the first town plan was created. New buildings were built – the Serbian elementary school, the Catholic Church, the Orthodox Church, and a hotel. First cultural associations appeared in the town as well as the libraries, reading rooms and a printing house. The end of the First World War will bring a new state – the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, with Bosnia-Herzegovina as a part of it. Prijedor will have an important place as the trade and craft center of the whole region. The opening of the iron ore mine in Ljubija near Prijedor in 1916, which employed about 4,000 workers, will strengthen the economy of the town. During that period, the mine was one of the biggest and most modern iron ore mines in Europe.
From 1929 to 1941, Prijedor was part of the Vrbas Banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
World War II
The memorial center Mrakovica at Kozara, the work of the academic artist Dušan Džamonja, is dedicated to this region's Yugoslav partisans resistance victims during WWII.
Some villages around Prijedor and Kozara Mountain suffered the deaths of tremendous amounts of civilians, who were killed by the Ustaše and taken to concentration camps; the most notorious of these was the Jastrebarsko Concentration Camp, where Serb children were imprisoned. No one was ever punished for these crimes although some families (mostly Serbian) and villages were destroyed.
Bosnian war
During the Bosnian war (1992–1995), the area near Prijedor housed the infamous Omarska camp, Keraterm camp, and Trnopolje camp established in 1992 by Radovan Karadžić's Serb authorities for Bosniak and Croat population.[4][5][6]
Demographics
1910
According to the data from the 1910 Austro-Hungarian population census the Prijedor district had a 59.08% Orthodox Serb majority. A portion of the Bosniak population left during the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which increased the proportion of the Serb and Croat population.
1971-1981-1991
According to data from the census, the municipality of Prijedor had:
| Year | total | Bosniaks | Serbs | Croats | Yugoslavs | others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~1971~ | 97.921 | 39.190 (40,02%) | 46.487 (47,47%) | 8.845 (9,03%) | 1.458 (1,48%) | 1.941 (2,00%) |
| ~1981~ | 108.868 | 42.129 (38,69%) | 45.279 (41,59%) | 7.297 (6,70%) | 10.556 (9,69%) | 3.607 (3,33%) |
| ~1991~ | 112.543 | 49.351 (43,85%) | 47.581 (42,27%) | 6.316 (5,61%) | 6.459 (5,73%) | 2.836 (2,54%) |
Prijedor was the sixth largest municipality in Bosnia and Herzegovina with 112.543 inhabitants in 1991.
The city centre of Prijedor itself in 1991 had a population of 34,635, including:
- 13,927 (40,21%) Serbs
- 13,388 (38,65%) Bosniaks
- 4,282 (12,36%) Yugoslavs
- 1,757 (5,07%) Croats
- 1,281 (3,69%) others
Current population
According to the official strategy rapport made for 2008–2013 by the Prijedor assembly the municipality hosted around 100,000 innhabitants. Prijedor municipality falls into one of the municipalities with the largest number of returnees. Namely, the total number of returnees in Prijedor municipality is 25,000 (24,997), of which 22,809 Bosniaks and 2,188 Croats according to the assembly rapport.[7]
According to this data there are over 100.000 inhabitants of which 48% belong to the urban population while 52% to the rural population.
This gives the estimated numbers:[7]
Some sources claim that the current population of Prijedor is higher than estimated, they claim that the number is close to 130,000 with almost 70% belonging to the urban population. Because of increased economical activity, large scale building and educational offers, both Bosniaks and Serbs are moving to the city to find themselves opportunities. Prijedor has around 1,300 enrolled students and many of them come from other municipalities in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[8] Also a slightly increase of Bosniaks moving back to Prijedor contributes to the population growth.
Education
The first forms of organized education can be tracked back in the first half of the 19th century. In 1834 Prijedor had the "Serbian elementary school" that later with so-called "Communal school" was transformed into "State school" in 1919. One of the first most important school institutions was the Prijedor Gymnasium founded in 1923.[9]
Elementary and High schools
Nowadays, there are 11 elementary schools with circa 8,000 students and 6 high schools attended by 4,000 students. A music school and a special school for mentally dysfunctioned persons are also part of the municipal educational system.
Colleges and Universities
Over the last several years, important steps were taken, aimed at establishing colleges. As a result, Prijedor now has a University college of Economics and Informatics,[10] a University College of Medicine,[11] and a mining geology branch department of the University of Banja Luka. In the northwestern part of the city in the neighborhood of Pećani a Law and Economics faculty is under construction, this are the first steps to establish an independent University center in Prijedor. Today Prijedor has around 1300 enrolled students.[8]
Economy
Prijedor is a large service and industrial center and hosts some of the largest companies in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
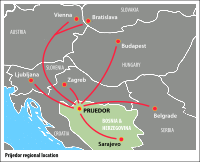
It has a developed financial sector; 11 international banks are represented in the city, as well as 5 microcredit organizations and a foundation for development. The city's huge economic potential lies in its strategic geographical location, as it is close to Zagreb, Belgrade, Budapest and Vienna, giving it one of the best climates for economic expansion in Bosnia-Herzegovina.
The agricultural land around the city, raw minerals in the municipality and growth of high educated population in the city proper gives it a unique combination of both being able to produce sophisticated industrial products, food and service branches.
Companies

The city today hosts the Bosnian headquarters of the ArcelorMittal Steel Company, which is the world's largest steel company, with over 320,000 employees in more than 60 countries. Prijedor also contains companies specialized in the chemical industry such as Ferrox A.D., producing iron oxides-pigments. BosnaMontaza A.D., one of Bosnia and Herzegovina's most specialized steel manufacturers, manufactures steel, pipelines, reservoirs, technological equipment, cranes and energy plants. Other companies such as the Croatian food company Kraš has one of its biggest facilities in Bosnia and Herzegovina in Prijedor, producing confectionery products under the brand names MIRA and Kraš. Brand names such as "Prijedorčanka" are one of the leading producers of the alcoholic beverage Rakija in Bosnia and Herzegovina, placing its products in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Croatia. Celpak Prijedor is also a big enterprise producing cellulose and paper for export.
Agricultural sector
Among fish production, Prijedor has a fruit growing industry, gardening industry, crop farming industry, mill and bakery industries, stock farming industry, processing industries, as well as a milk industry.
Lake Saničani, near Prijedor, is one of the biggest commercial fish farming lakes in the southern Europe.
Prijedor municipality takes up 834.06 hectares (58.450, 00 private property and 24.956,00 state property). Plowed fields and gardens take up 34.026,00 hectares, orchards 2.386 hectares and vineyards 5 hectares. All cultivate soil takes up 40.206,00 hectares.
Service sector
The service sector in Prijedor is growing rapidly and this is reflected in the growth of hotels, stores, roads, educational facilities and shoppings centers that are being built in the city, making it a growing commercial hub in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Transport and aviation

Prijedor has a high standard of roads thanks to the Prijedor putevi Company and is planning a highway connection to Banja Luka in the east and Sisak to west to short down the distance to Zagreb from the Bosanska Krajina region. A so-called "brzi put" a semi highway is being prepared to connect Prijedor to the Zagreb-Belgrade highway via Bos./Koz. Dubica i the north.
The city is also connected to the rail system in Bosnia and located on the Zagreb-Sarajevo-Ploče line.
The city has a public transport system with 3 bus lines serving 60 stations in and around the city.
Prijedor also has an airfield in the north-eastern part of the city in the area of Urije. The airfield has a fleet of light aircraft and sailplanes. The airfield also serves as the home of the city's renomated Parachuting club.
Notable people
- Mladen Stojanović, leader of Yugoslav Partisans in western Bosnia and a People's Hero of Yugoslavia
- Nasko Budimlić, musician, drummer in the Bosnian hard rock band Divlje Jagode
- Nebojša Grahovac, professional handballer
- Nermin Alukić Čerkez, musician, vocal and guitarist in the well-known Bosnian Sevdalinka band, "Mostar Sevdah Reunion"
- Sreten Stojanović, sculptor
- Todor Švrakić, painter
- Vehid Gunić, journalist and writer
- Milja Marin, the subject of the iconic photograph Kozarčanka
- Živko Radišić, politician and former chairman of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Zlatan Arnautović, former Yugoslav handball player who competed in the 1980 Summer Olympics and the 1984 Summer Olympics
- Borislav Topić, football player
- Edis Elkasević, shot putter
- Eldin Jakupović, football player
- Dr. Eso Sadiković, well-known doctor of medicine
- Fikret Hodžić, professional bodybuilder
- Halid Muslimović, folk singer
- Idriz Hošić, football player
- Josip Iličić, football player
- Željko Buvač, ex footballer, now assistant manager of Liverpool FC.
- Emil Bakaj,prva motorka zapadne Bosne
Sport
The local football club, FK Rudar Prijedor, plays in the highest ranked football league of Bosnia and Hercegovina The Premier League of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Among the oldest sporting clubs in Prijedor is the football club OFK Prijedor founded in 1919. The tennis club of Prijedor was founded by Mladen Stojanović in 1932, though tennis was first played in the town in 1914.[12]
On Mrakovica, Kozara skiing center is located. All ski lifts are functional and there is a ski path for children on Mrakovica as well. The skiing center is located inside the Kozara national park and there are several possibilities for mountain house rentals. A renovated hotel with various sport facilities lies close to the path.
Other popular sports in Prijedor are Basketball and Handball. The highest ranked teams are ZKK Mladost Prijedor, KK Prijedor (Basketball), and RK Prijedor (Handball).
Culture

Prijedor has a various number of galleries, religious sights, libraries, statues, fountains, national monuments, cinemas and a city theater.
Museums
Prijedor is home of the Museum of Kozara founded in 1953, which has a regional status.
It is also home of the local national hero, Dr. Mladen Stojanovic. His house is today converted into the Stojanovic Memorial House.
At Kozara National Park in the vicinity of Prijedor, there is the Mrakovica war museum. It includes the Second World War history photographs, guns and artillery used during the Battle of Kozara.
Theatre
Pozorište Prijedor was founded in 1953, dough the tradition of theatre in Prijedor can be dated back to the 19th century. The theatre hosts different plays during the year, starring actors from within and outside of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Besides theatrical plays, the theatre hosts local city choirs that perform regularly.
Festivals
The Day of Honey: Locally called "Dani meda". Trade-tourist event where local honey producers from the Prijedor area and farer away gather at the square in the main street to sell and demonstrate their products.
Prijedor summer and river Festival: "Ljeto na sani". Includes a wide music program, sport activities and other happenings along the city river beach.
Writers Gathering: Each year in September, cultural gathering "Writers gathering in Kozara", where works of literal art by local authors are being presented is taking place.
Days of the Winter: This tourist event is held at the beginning of February in the mountain Kozara. It lasts three days and its main aim is to promote tourist potentials of the Kozara mountain. Sporting and gastro competitions followed by a rich entertaining programme are an integral part of this event.
International Chorus Festival – Zlatna Vila: This cultural event is held in Prijedor People's Theatre every May and it represents a competition in choral singing. Participants to the festival are choruses from different countries both from ex-Yugoslavia and abroad.
St Peter’s Day Parachuting Cup: Each year, in the month of July, a sporting event, St Peter’s Day Parachuting Cup is held. Parachutists from different countries take part in this event, and competitions are organised in various categories, women, men, juniors and teams.


Religious sites
Prijedor is known for being a multi religious society including a Catholic church, Orthodox churches and Mosques. Due to this Prijedor has a large number of mosques in the city center, one of the oldest dating back to the 16th and 17th century.
The most known is the City mosque "Carsijska dzamija" built in 1750 located the main street. The mosque includes a library and a school. Mostly all of Prijedor municipality's 33 mosques and the catholic cathedral that were damaged and destroyed are now rebuilt and renovated.
Other sights is the orthodox church "Crkva Svete Trojice" built in 1891 which is surrounded with a wall including a small church park. The catholic cathedral "Sv. Josip" built in 1898 is located in the northern part of the city center close to the city theater.
Prijedor used to have a small Jewish population before WWII and the Bosnian war, but today there are no traces of the former Jewish population in the city.[13]
Archeological findings
Evidence that Prijedor was settled dates from 2100 B.C., the traces of life are evident in numerous settlements in the region of the present-day town, with necropolises subjacent to the settlements, as a rule.
Prijedor was settled by the Illyrian tribe Maezaei, a sub-tribe of Pannonians, with a talent for mining. In Ljubija near Prijedor, there are evidence of iron production from the Roman period. In Zecovi close to Prijedor there is an Illyrian necropolis from the Iron Age.
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Prijedor is twinned with:
Partner cities :
Gallery
 Austro-Hungarian architecture
Austro-Hungarian architecture Fountain in centre
Fountain in centre Old city mosque
Old city mosque Prijedor main street buildings
Prijedor main street buildings- Statue of national hero Dr.Mladen Stojanović
 Recreation and sports facilities
Recreation and sports facilities- Old tower/Stara kula
 Urije Airport
Urije Airport Hotel Prijedor
Hotel Prijedor
References
- ↑ "IZBORI 2008". Izbori.ba. Retrieved 2013-11-23.
- ↑ "Saopstenje : First Releases" (PDF). Bhas.ba. Retrieved 2013-11-23.
- ↑ Archived November 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ United Nations – Security Council (28 December 1994). "The Prijedor report". Final report of the United Nations Commission of Experts established pursuant to security council resolution 780 (1992).
- ↑ Simons, Marlise (3 November 2001). "5 Bosnian Serbs Guilty of War Crimes at Infamous Camp". The New York Times.
- ↑ Simons, Marlise (14 November 2001). "3 Ex-Guards at Bosnia Camp Are Sentenced by Hague Panel". The New York Times.
- 1 2 "raport – Google zoeken". Google.com. Retrieved 2013-11-23.
- 1 2 "U prvom roku uglavnom upisan planirani broj studenata | GradPrijedor.com – Prijedor – Portal grada Prijedora". GradPrijedor.com. Retrieved 2013-11-23.
- ↑ Archived January 1, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "University College of Economics and Informatics Prijedor". Koledzprijedor.org. Retrieved 2013-11-23.
- ↑ "University College of Medicine Prijedor". Vmspd.com. Retrieved 2013-11-23.
- ↑ "Istorijat kluba" [History of the Club] (in Serbian). Dr Mladen Stojanović Tennis Club, Prijedor. Archived from the original on 2011-12-05.
- ↑ "Jews of Prijedor". 19 May 2008.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Prijedor. |
External links
- Official Municipality of Prijedor website
- Prijedor travel agency
- Map of the city
- Kozara National Park
- News & information from Prijedor – GradPrijedor.com
- PrijedorCity: City Portal – News & Happenings in Prijedor and Bosnia
- News, information and photos from Prijedor
- Kozarski vjesnik Prijedor
- Map of city center and business register
- Grad Prijedor mobile app (android)


