Politics of Wallonia
The Politics of Wallonia concern the government of Wallonia, that is the southern Region of Belgium.
The capital is Namur, where are the seats of the Government of Wallonia, the Parliament of Wallonia and the Public Service of Wallonia.
Structures
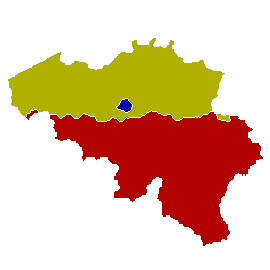
Brussels-Capital (blue)
Wallonia (red)
Flemish Region(yellow)
Since 23 April 1993, Belgium has been a federal state, divided into three geographical regions and three linguistic communities. The Walloon Region is one of the three regions, almost totally French-speaking. The other two geographical regions are the Flemish Region, a mainly Dutch-speaking region in the north and west, and the Brussels-Capital, bilingual French-Dutch administering the city of Brussels. Some governmental competencies are exercised by the linguistic communities, of which the French community of Belgium is the largest in Wallonia, while the German-speaking community of Belgium's responsibilities are for an area within Wallonia.
The Parliament of Wallonia is a unicameral legislature of 75 members elected to serve five-year terms. It is based in the former Hospice Saint-Gilles at Namur.
The Government of Wallonia is responsible to the Parliament. Excepting cultural and education matters, which are controlled by the linguistic communities, the Walloon Region's competences include local administration, housing, transport, training, employment, health and social policy. The region administers a number of companies, including those responsible for the provision of water and public transport.
The constitutional system of Belgium grants the Walloon Region its own legislative and executive powers in the fields for which it is competent:
- agriculture and rural renewal
- development of the territory and town planning
- economy and foreign trade
- employment and vocational training
- the environment, water and nature conservation
- housing
- local authorities, subsidized works and sports infrastructures
- scientific research, new technologies and energy
- international relations
- health and social affairs
- tourism and heritage
- regional transport, mobility and public works.

Parliament

The directly elected Walloon Parliament was created in June 1995, replacing the Conseil régional wallon (Regional Council of Wallonia). This first sat on 15 October 1980 and was composed of members of the Belgian Chamber of People's Representatives and the Belgian Senate elected from Wallonia.
The parliament exercises several functions:
- It discusses and passes decrees, and they can take initiatives to draw them up. After this, decrees are sanctioned and promulgated by the Walloon Government.
- It controls the Walloon Government. Control is exercised via the vote.
- It ratifies the international treaties linked to its powers.
The composition of the parliament for the 2004-2009 legislature was as follows:
- Parti Socialiste (PS) : 34
- Mouvement réformateur (MR) : 20
- Centre démocrate humaniste (CDh) : 14
- Front national (FN) : 4
- Ecolo : 3
The president of the parliament was José Happart (PS), the Vice-Presidents were Véronique Cornet (MR), Michel Lebrun (CDh) and Charles Janssens (PS).
The composition of the parliament for the 2009-2014 legislature is as follows:
- Parti Socialiste (PS) : 29
- Mouvement réformateur (MR) : 19
- Ecolo : 14
- Centre démocrate humaniste (CDh) : 13
The president of the parliament is Emily Hoyos.
The new coalition government is gathering the PS, the CDH and Ecolo and has the same minister-president.
The 75 members of the parliament (except German-speaking members, who are substituted by French-speaking members from the same party), together with 19 French-speaking members elected by the Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region, form the Parliament of the French Community. Since 1999 elections have been held together with those for the European Parliament.
Government

The Walloon Government is the executive body of the Walloon Region. Following the 25 May 2014 election, PS (30 seats) and CDH (13 seats) parties formed a coalition.
| Walloon Government - Magnette | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Name | Function | |
| PS | Paul Magnette | Minister-President | |
| CDH | Maxime Prévot | Vice-Minister-President; Minister of Public Works, Traffic Safety, Health, Childcare Benefits, Equal Chances, Economic Zones of Activity and Patrimony | |
| PS | Jean-Claude Marcourt | Vice-Minister-President; Minister of Economy, Industry, Innovation and Digitalisation | |
| PS | Paul Furlan | Minister of Local Government, Energy, Housing and City Policy | |
| PS | Christophe Lacroix | Minister of Budget, Public Office and Administrative Simplification | |
| PS | Éliane Tillieux | Minister of Employment and Formation/Training | |
| CDH | Carlo Di Antonio | Minister of Environment, Animal Welfare, Spatial Planning, Mobility and Airports | |
| CDH | René Collin | Minister of Agriculture, Nature, Rural Affairs, Tourism and Sports Infrastucture | |
The Government of the French Community and the Government of the German-speaking Community are the executive bodies of respectively the French and German-speaking Communities.
References
See also
External links
- Wallonia Portal
- (French) Government of Wallonia
- (French) Parliament of Wallonia
- (French) Parliament of the French-Speaking Community