Mochnant
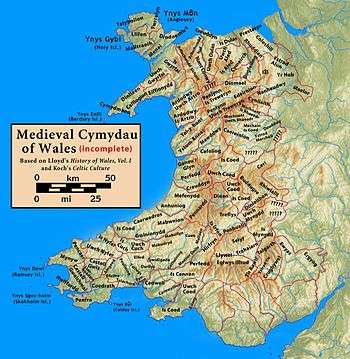
Mochnant (English: Promontory[1]) was a medieval cantref or commote (cwmwd) (sources disagree) in the Kingdom of Powys.[2][3]
In the 12th century it was divided into the commotes of Mochnant Is Rhaeadr (in the north) and Mochnant Uwch Rhaeadr (in the south) (Is signifying 'below' and Uwch 'above' the River Rhaeadr).[3]
Its north-west border was with the cantref of Penllyn which was originally in Powys but became part of the Kingdom of Gwynedd during the time of Owain Brogyntyn. It bordered the cantrefi of Caereinion and Mechain to the south, and Maelor to the north-east.[4] The administrative centre was Llanrhaeadr-ym-Mochnant in Mochnant Is Rhaeadr.[5]
After the death of Madog ap Maredudd and his eldest son and heir in 1160, the kingdom was divided up between his surviving sons Gruffydd Maelor, Owain Fychan and Owain Brogyntyn, his nephew Owain Cyfeiliog and his half-brother Iorwerth Goch. The northern part of Powys, including Mochnant Is Rhaeadr, later became Powys Fadog; the southern part including Mochnant Uwch Rhaeadr became Powys Wenwynwyn. Following Edward I's conquest of Wales (1282-1283), Mochnant Is Rhaeadr become part of the Marcher Lordship of Chirk, but Mochnant Uwch Rhaeadr remained under Welsh rule.[2] Later, Mochnant Is Rhaeadr was in Denbighshire, while Mochnant Uwch Rhaeadr was in Montgomeryshire.[3]
The name survives in the placename Llanrhaeadr-ym-Mochnant, this village also had the ancient commote's ecclesiastical centre at the church of St Dogfan;[3] ym-Mochant means 'in Mochnant'.

References
- ↑ Jones, John (1824). The History of Wales. London: J Williams. p. 105.
- 1 2 "The Tanat Valley". CPAT.
- 1 2 3 4 Lloyd, John Edward (1912). A History of Wales from the Earliest Times to the Edwardian Conquest. Longmans, Green, and Co. p. 246. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
- ↑ Rees, William (1951). An Historical Atlas of Wales from Early to Modern Times. Faber & Faber.
- ↑ "Llanrhaeadr-ym-mochnant, Powys". CPAT.