Michaelis–Gutmann bodies
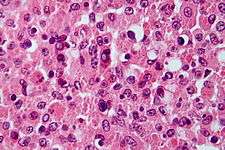
Micrograph showing Michaelis-Gutmann bodies. H&E stain.
Michaelis–Gutmann bodies (M-G bodies) are concentrically layered basophilic inclusions found in the urinary tract. They are 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are thought to represent remnants of phagosomes mineralized by iron and calcium deposits.
M-G bodies are a pathognomonic feature of malakoplakia, an inflammatory condition that affects the genitourinary tract. They were discovered in 1902 by Leonor Michaelis and Carl Gutmann.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.