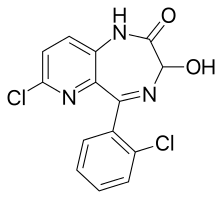
Lopirazepam
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 42863-81-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 68672 |
| ChemSpider | 61926 |
| UNII |
8PDI6DY6GV |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.868 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H9Cl2N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 322.146 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
Lopirazepam (INN)[1] is a short-acting benzodiazepine analog of the pyridodiazepine type (specifically, the pyridodiazepine analog of lorazepam) with anxiolytic and hypnotic properties.[2][3] It has never been marketed.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ US Patent 4008223
- ↑ Saletu M, Saletu B, Grünberger J, Mader R, Karobath M (1983). "Clinical symptomatology and computer analyzed EEG before, during and after anxiolytic therapy of alcohol withdrawal patients". Neuropsychobiology. 9 (2–3): 119–34. doi:10.1159/000117949. PMID 6353268.
- ↑ Fabian A, Röhmel R, Kubicki S (September 1984). "[Changes in the length of sleep cycles during administration of flurazepam and lopirazepam]". EEG EMG Z Elektroenzephalogr Elektromyogr Verwandte Geb (in German). 15 (3): 151–8. PMID 6435999.
- ↑ David J. Triggle; C. R. Ganellin; F. MacDonald (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. 2. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. p. 1232. ISBN 0-412-46630-9. Retrieved on December 31, 2008 through Google Book Search.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.