List of fishes of the Coral Sea
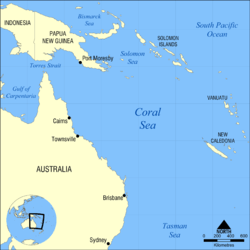
This is a list of fishes recorded from the Coral Sea, bordering Australia, Papua New Guinea, Vanuatu and New Caledonia. This list comprises locally used common names, scientific names with author citation and recorded ranges. Ranges specified may not be the entire known range for the species, but should include the known range within the waters surrounding of the bordering land masses.
List ordering and taxonomy complies where possible with the current usage in Fishbase, and may differ from the cited source, as listed citations are primarily for range or existence of records for the region. Sub-taxa within any given family are arranged alphabetically as a general rule. Details of each species may be available through the relevant internal links. Synonyms may be listed where useful.
Geographical scope
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Coral Sea as follows:[1]
On the North. The South coast of New Guinea from the entrance to the Bensbak River (141°01'E) to Gado-Gadoa Island near its Southeastern extreme (10°38′S 150°34′E / 10.633°S 150.567°E), down this meridian to the 100 fathom line and thence along the Southern edges of Uluma (Suckling) Reef and those extending to the Eastward as far as the Southeast point of Lawik Reef (11°43.5′S 153°56.5′E / 11.7250°S 153.9417°E) off Tagula Island [Vanatinai], thence a line to the Southern extreme of Rennell Island and from its Eastern point to Cape Surville, the Eastern extreme of San Cristobal Island [Makira], Solomons; thence through Nupani, the Northwestern of the Santa Cruz Islands (10°04.5′S 165°40.5′E / 10.0750°S 165.6750°E) to the Northernmost Island of the Duff or Wilson Group (9°48.5′S 167°06′E / 9.8083°S 167.100°E). On the Northeast. From the Northernmost island of the Duff or Wilson Group through these islands to their Southeastern extreme, thence a line to Mera Lava, New Hebrides Islands [Vanuatu] (14°25′S 163°03′E / 14.417°S 163.050°E) and down the Eastern coasts of the islands of this Group to Aneityum Island (20°11′S 169°51′E / 20.183°S 169.850°E) in such a way that all the islands of these Groups, and the straits separating them, are included in the Coral Sea.
On the Southeast. A line from the Southeastern extreme of Aneityum Island to Southeast (Nokanhui) Islets (22°46′S 167°34′E / 22.767°S 167.567°E) off the Southeast extreme of New Caledonia, thence through the East point of Middleton Reef to the Eastern extreme of Elizabeth Reef (29°55′S 159°02′E / 29.917°S 159.033°E) and down this meridian to Latitude 30° South.
On the South. The parallel of 30° South to the Australian coast.
On the West. The eastern limit of the Arafura Sea [The entrance to the Bensbak River (141°01'E), and thence a line to the northwest extreme of York Peninsula, Australia (11°05′S 142°03′E / 11.083°S 142.050°E)] and the East Coast of Australia as far south as Latitude 30° South.
Class Chondrichthyes
Order Hexanchiformes
Family Hexanchidae - Sixgill and sevengill sharks
- Bluntnose sixgill shark Hexanchus griseus (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Worldwide in tropical and tepmperate seas)[2]
Order Heterodontiformes
Family Heterodontidae – Hornsharks, Port Jackson sharks, bullhead sharks.
- Zebra bullhead shark Heterodontus zebra (Gray,1831) (Northern Australia to southern Japan)[2]
Order Orectolobiformes
Family Orectolobidae – Wobbegongs
- Tasselled wobbegong Eucrossorhinus dasypogon Regan, 1908 (Northern Australia and New Guinea)[2]
- Banded wobbegong Orectolobus ornatus (De Vis, 1883) (Northern Australia, New Guinea and southern Japan)[2]
- Northern wobbegong Orectolobus wardi Whitley, 1939 (Northern Australia)[2]
Family Hemiscylliidae - Bamboo sharks
- Brownbanded bamboo shark Chiloscyllium punctatum Mueller and Henle, 1838 (East coast of Indian peninsula to northern Australia and north to Japan)[2]
- Epaulette shark Hemiscyllium ocellatum (Bonnaterre, 1788) (Northern Australia and New Guinea)[2]
- Speckled catshark Hemiscyllium trispeculare Richardson, 1843 (Northern Australia)[2]
Family Stegostomatidae - Leopard sharks
- Leopard shark Stegostoma fasciatum (Hermann, 1783) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Australia and New Caledonia)[2]
Family Ginglymostomatidae - Nurse sharks
- Tawny nurse shark Nebrius ferrugineus (Lesson, 1830) (Indo-West Pacific from East Africa and the Red Sea to the Society Islands)[2]
Family Rhincodontidae - Whale sharks
- Whale shark Rhincodon typus (Smith, 1828) (Circumglobal in warm temperate seas)[2]
Order Lamniformes
Family Odontaspididae - Sand tiger sharks
- Grey nurse shark Carcharias taurus Rafinesque, 1810 syn. Eugomphodus taurus (Around the Australian mainland, also widespread overseas)[3] (Tropical and temperate waters of most seas but absent from eastern and cantral Pacific Ocean)[2]
Family Alopiidae - Thresher sharks
- Small tooth thresher shark Alopias pelagicus Nakamura, 1935 (Circumtropical) [2]
Family Lamnidae – Makos, Mackerel sharks
- Shortfin mako Isurus oxyrinchus Rafinesque, 1809 (Circumglobal in temperate and tropical seas)[2]
Order Carcharhiniformes
Family Scyliorhinidae - Catsharks
- Marbled catshark Atelomycterus macleayi Whitley, 1939 (Northern Australia)[2]
- Reticulated swellshark Cephaloscyllium fasciatum Chen, 1966 (Northern Australia and South China Sea)[2]
Family Carcharhinidae – Whaler sharks, requiem sharks
- Silvertip shark Carcharhinus albimarginatus (Rueppell, 1837) (Tropical Indopacific and eastern Pacific)[2]
- Bignose shark Carcharhinus altimus (Springer, 1950) (Circumglobal in temperate and tropical seas)[2]
- Grey reef shark Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos (Bleeker, 1856) (East Africa and Red Sea east to Hawaii and Pitcairn Island)[2]
- Pigeye shark Carcharhinus amboinensis (Mueller and Henle, 1839) (East Africa to Australia)[2]
- Bronze whaler Carcharhinus brachyurus (Günther,1870) (Jurien Bay, Western Australia to Coffs Harbour, New South Wales, and northern Tasmania)[3] (Along coastal margins in most tropical and temperate seas. Apparently absent in western Atlantic)[2]
- Long nose grey shark Carcharhinus brevipinna (Mueller and Henle, 1839) (Continental margins of all tropical and warm temperate seas except the eastern Pacific)[2]
- Whitecheek shark Carcharhinus dussumieri (Valenciennes, 1839) (Continental margins from the Persian Gulf to northern Australia and north to Japan)[2]
- Silky shark Carcharhinus falciformis (Bibron, 1839) (Circumtropical, oceanic and coastal)[2]
- Bull shark Carcharhinus leucas (Valenciennes, 1839) (Continental coasts of all tropical and subtropical seas, sometimes far up rivers)[2]
- Blacktip shark Carcharhinus limbatus (Valenciennes, 1839) [2]
- Oceanic whitetip shark Carcharhinus longimanus (Poey, 1861) (Circumtropical, mainly oceanic-epipelagic)[2]
- Blacktip reef shark Carcharhinus melanopterus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Ind-west and central Pacific from East Africa and the Red Sea to Hawaii and French Polynesia) [2]
- Black whaler Carcharhinus obscurus (Lesueur, 1815) (Circumglobal in tropical and warm temperate seas, primarily on continental shelves)[2]
- Sandbar shark Carcharhinus plumbeus (Nardo, 1827) (Circumglobal in tropical and warm temperate seas)[2]
- Blackspot shark Carcharhinus sealei (Pietschmann, 1916) (East Africa to Northern Australia)
- Spot-tail shark Carcharhinus sorrah (Valenciennes 1837) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Solomon and Santa Cruz Islands) [2]
- Tiger shark Galeocerdo cuvier (Peron and Lesueur, 1822) (Circumtropical) [2]
- Lemon shark Negaprion acutidens (Rueppell, 1837) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Society Islands)[2]
Family Hemigaleidae - Weasel sharks
- Whitetip reef shark Triaenodon obesus (Rueppell, 1837) (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
Family Sphyrnidae - Hammerhead sharks
- Scalloped hammerhead Sphyrna lewini (Griffith and Smith, 1834) (Worldwide in tropical and warm temperate seas)[2]
- Sphyrna mokarran [2]
- Eusphyra blochii [2]
Order Torpediniformes
Family Hypnidae – Coffin rays, electric rays
- Coffin ray Hypnos monopterygium (Shaw and Nodder, 1795) (Broome, Western Australia to Caloundra, Queensland)[3](Western Australia, South Australia and southeastern Australia, including southern Queensland and adjacent Great Barrier Reef)[2]
Order Rajiformes
Family Rhinobatidae – Guitarfishes
- Common shovelnose ray Glaucostegus typus (Anonymous [Bennett], 1830)[4] syn. Rhinobatos batillum Whitley, 1939 ((as R. batillum)Northern Australia between Shark Bay, Western Australia and the Capricorn Group, occasionally near sand cays on the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
Order Myliobatiformes
Family Dasyatidae – Stingrays
- Kuhl's stingray Dasyatis kuhlii (Mueller and Henle, 1841) (East Africa and Red Sea to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Blue-spotted stingray Taeniura lymma (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa to western Pacific and Great Barrier Reef) [2]
- Black-blotched stingray Taeniura meyeni Mueller an Henle, 1841 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Thorny ray Urogymnus africanus (Bloch and Schneider 1801) (East Africa to northern Australia and the Marshall Islands)[2]
Family Myliobatidae – Eagle rays
- Spotted eagle ray Aetobatus narinari (Euphrasen, 1790) (Cosmopolitan in tropical to warm temperate seas)[2]
Family Mobulidae - Mantas and devil rays
- Manta Manta birostris (Donndorff, 1798) (Circumtropical)[2]
- Devil ray Mobula tarapacana (Philippi, 1892) (Indo-Pacific and eastern Atlantic, possibly circumtropical)[2]
Class Osteichthyes
Order Albuliformes
Family Albulidae - Bonefishes
- Pacific bonefish Albula argentea (Forster and Bloch in Schneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Order Anguilliformes
Family Moringuidae - Worm eels
- Slender worm-eel Moringua ferruginea (Bliss, 1883) (East Africa to Easter Island and north to Ryukyu Islands)[2]
Family Chlopsidae - False morays
- Grey reef eel Kaupichthys diodontus Schultz, 1943 (East Africa to Society and Hawaiian islands)[2]
Family Muraenidae – Moray eels
- Seychelles moray Anarchias seychellensis Smith, 1962 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Starry moray Echidna nebulosa (Ahl, 1879) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Ringed moray Echidna polyzona (Richardson, 1844) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bayer's moray Enchelycore bayeri (Schulz, 1953) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Viper moray Enchelynassa canina (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824)(Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Zebra moray Gymnomuraena zebra (Shaw 1797) (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Latticetail moray Gymnothorax buroensis (Bleeker, 1857) (Indo-Pacific and Galapagos Islands)[2]
- Lipspot moray Gymnothorax chilospilus Bleeker, 1865 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Australian moray Gymnothorax cribroris Whitley, 1932 (Great Barrier Reef and Western Australia)[2]
- Stout moray Gymnothorax eurostus (Abbott, 1860) (Indo-Pacific, antitropical. Only in southern part of Great Barrier Reef.)[2]
- Blackspotted moray Gymnothorax favagineus Bloch and Scneider, 1801 (Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Darkspotted moray Gymnothorax fimbriatus (Bennett, 1832) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Yellowmargin moray Gymnothorax flavimarginatus (Rueppell, 1830) (Indo-Pacific and tropical east Pacific)[2]
- Freckled moray Gymnothorax fuscomaculatus (Schultz, 1953) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Slendertail moray Gymnothorax gracilicauda Jenkins, 1903 (Islands and reefs of Oceania to the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Giant moray Gymnothorax javanicus (Bleeker, 1859) (Indo-Pacific to Hawaii)[2]
- Blackpearl moray Gymnothorax margaritophorus Bleeker, 1864 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Dwarf moray Gymnothorax melatremus Schultz, 1953 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Whitemouth moray Gymnothorax meleagris (Shaw and Nodder, 1795) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Yellowmouth moray Gymnothorax nudivomer (Playfair and Guenther, 1867) (Hawaii and western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Highfin moray Gymnothorax pseudothyrsoideus (Bleeker, 1852) (Western Pacific to India and Oman)[2]
- Banded moray Gymnothorax rueppelliae (McClelland, 1845) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Greyface moray Gymnothorax thyrsoideus (Richardson, 1845)[5] syn. Siderea thyrsoidea (Richardson, 1845) ((as S. Thyrsoidea)Central and western Pacific)[2]
- Undulated moray Gymnothorax undulatus (Lacepede, 1803) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Barredfin moray Gymnothorax zonipectis Seale, 1906 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Ribbon eel Rhinomuraena quaesita Garman, 1888 (Central and western Pacific to islands of the western Indian Ocean)[2]
- Longtail moray Strophidon sathete (Hamilton, 1822) (Western Pacific to East Africa and the Red Sea)[2]
- Peppered moray Siderea picta (Ahl, 1789) (Indo-Pacific and islands of the tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Marbled moray Uropterygius marmoratus (Lacepede, 1803) (Central and western Pacific)[2]
Family Ophichthidae – Snake eels, worm eels
- Sharpsnout snake eel Apterichtus klazingai (Weber, 1913) (East Africa to the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Stargazer snake eel Brachysomophis cirrocheilos (Bleeker, 1857) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Crocoddile snake eel Brachysomophis crocodilinus (Bennett, 1831) (Indo-Pcific and Eastern Pacific) [2]
- Black striped snake eel Callechelys catostoma (Forster in Blich and Schneider, 1801) (Indonesia to Society Islands)[2]
- Marbled snake eel Callechelys marmorata (Bleeker, 1853) (East Africa to Society Islands) [2]
- Culverin Leiuranus semicinctus (Lay and Bennett, 1839) (East Africa to Polynesia) [2]
- Slender snake eel Muraenichthys macropterus Bleeker 1857 (East Africa to the Society Islands) [2]
- Harlequin snake eel Myrichthys colubrinus (Boddaert, 1781) (Red Sea to the Society Islands)[2]
- Spotted snake eel Myrichthys maculosus (Cuvier, 1817) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Johnston snake eel Schultzidia johnstonensis (Schultz and Woods, 1949) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Family Congridae – Conger eels
- Speckled garden eel Gorgasia sp. (Western Pacific including Coral Sea, Guam and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Black edged conger Conger cinereus Rueppell, 1830 (East Africa and Red Sea to Easter Island)[2]
- Spotted garden eel Heteroconger hassi (Klausewitz and Eibl-Ebesfeldt, 1959) (Red Sea to Samoa and Line Islands, north to Ryukyu Islands)[2]
Order Clupeiformes
Family Clupeidae – Herrings, pilchards, sardines
- Fourspot herring Herklotsichthys quadrimaculatus (Rueppell, 1837) (East Africa to Samoa and Marshall Islands, Hawaii)[2]
- Blue-backed sprat Spratelloides delicatulus (Bennett, 1831) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Society Islands)[2]
Order Gonorhynchiformes
Family Chanidae - Milkfish
- Milkfish Chanos chanos (Forskal, 1775) (East Africa to Polynesia)[2]
Order Siluriformes
Family Plotosidae - Eeltail catfishes
- White-lipped catfish Paraplotosus albilabris (Valenciennes, 1840) (Indonesia, Melanesia and northern Australia)[2]
- Striped catfish Plotosus lineatus (Thunberg, 1787) (East Africa and Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
Order Aulopiformes
Family Synodontidae – Lizardfishes
- Slender lizardfish Saurida gracilis (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Two-spot lizardfish Synodus binotatus Schultz, 1953 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Clearfin lizardfish Synodus dermatogenys Fowler, 1912 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Arrowtooth lizardfish Synodus doaki Russell and Cressey, 1979 (Hawaii, New Zealand, eastern Australia, Japan and East Africa)[2]
- Javelinfish Synodus jaculum Russell and Cressey, 1979 (Scattered records from the Line Islands in the central Pacific to Natal and the Comoro Islands)[2]
- Redmarbled lizardfish Synodus rubromarmoratus Russell and Cressey, 1979 (Only known from Taiwan, Philippines and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Reef lizardfish, variegated lizardfish Synodus variegatus (Lacepede, 1803) (Tropical Australia south to Jutten Bay, Western Australia and Merimbula, New South Wales. Also Lord Howe Island and widespread in the Indo-Pacific region)[3] (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Snakefish Trachinocephalus myops (Forster in Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific and Atlantic, tropical to warm temperate)[2]
Order Ophidiiformes
Family Ophidiidae – Cusk eels (?), lings, brotulas
- Bearded brotula Brotula multibarbata Temminck and Schlegel, 1846 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Family Carapidae - Pearlfishes
- Fowler's pearlfish Onuxodon fowleri (Smith, 1955) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
Family Bythitidae - Cuskeels
- Slimy cuskeel Brosmophyciops pautzkei Schultz, 1960 (Red Sea to Samoa and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Yellow cuskeel Dinematichthys sp. (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Order Batrachoidiformes
Family Batrachoididae – Frogfishes, toadfishes
- Banded toadfish Halophryne diemensis (Lesueur, 1824) (Northern Australia from Shark Bay, Western Australia to Heron Island, Queensland and throughout the Indo-Malayan Archipelago)[2]
Order Lophiiformes
Family Antennariidae – Anglerfishes
- Freckled anglerfish Antennarius coccineus (Cuvier in Lesson, 1831) (Indo-Pacific eastward to the Americas)[2]
- White-finger anglerfish Antennarius nummifer (Cuvier, 1817) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Society Islans, and north to Japan)[2]
- Painted anglerfish Antennarius pictus (Shaw and Nodder, 1794) (East Africa to the Society and Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Striate anglerfish, striped anglerfish Antennarius striatus (Shaw and Nodder 1794) (Tropical Australia south to Wollagong, New South Wales and Geraldton Western Australia)[3]
- Tuberculated anglerfish Antennarius tuberosus (Cuvier, 1817) (East Africa to Samoa and the Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Sargassum fish Histrio histrio (Linnaeus, 1758) (Indo-West Pacific and tropical Atlantic)[2]
Order Gobiesociformes
Family Gobiesocidae – Clingfishes, shore eels
- Urchin clingfish Diademichthys lineatus (Sauvage, 1883) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- One stripe clingfish Discotrema sp. (Indo-Pacific) [2]
Order Beloniformes
Family Exocoetidae - Flying fishes
- Sutton's flying fish Cypselurus suttoni (Whitley and Colefax, 1938) (Central and western Oceania)[2]
Family Hemiramphidae - Garfishes, halfbeaks
- Barred garfish Hemiramphus far (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Dussumier's garfish Hyporhamphus dussumieri (Valenciennes, 1846) (Seychelles to the Tuamotu Archipelago)[2]
Family Belonidae - Longtoms or needlefishes
- Flat tailed longtom Platybelone argalus platyura (Bennett, 1832) (Circumtropical)[2]
- Slender longtom Strongylura leiura (Bleeker, 1851) (East Africa to Fiji)[2]
- Crocodile longtom Tylosurus crocodilus crocodilus (Peron and Lesueur, 1821) (Tropical Atlantic and Indo-Pacific)[2]
Order Atheriniformes
Family Atherinidae – Hardyheads, silversides
- Robust hardyhead Atherinomorus lacunosus (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Barnes' hardyhead Hypoatherina barnesi Schultz, 1953 (Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
Order Beryciformes
Family Monocentridae – Pineapplefishes
- Australian pineapplefish, knightfish Cleidopus gloriamaris De Vis, 1882 (Shark Bay, Western Australia to Great Australian Bight, Western Australia and Eden, New South Wales to Capricorn Group, Queensland.)[3] (East and west coasts of Australia)[2]
Family Holocentridae - Squirrelfishes and soldierfishes
- Shadowfin soldierfish Myripristis adusta Bleeker, 1851 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bigscale soldierfish Myripristis berndti Jordan and Evermann, 1903 (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Yellowfin soldierfish Myripristis chryseres Jordan and Evermann, 1903 (Scattered records from Natal to Hawaii)[2]
- Doubletooth soldierfish Myripristis hexagona (Lacepede, 1802) (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Epaulette soldierfish Myripristis kuntee (Cuvier, 1831) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blotcheye soldierfish Myripristis murdjan (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Scarlet soldierfish Myripristis pralinia Cuvier, 1829 (Society Islands to Islands of west Indian Ocean)[2]
- Lattice soldierfish Myripristis violacea Bleeker, 1851 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Whitetip soldierfish Myripristis vittata Valenciennes, 1831 (Western Indian Ocean to the islands of Oceania)[2]
- Yellowstriped squirrelfish Neoniphon aurolineatus (Lienard, 1839) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blackfin squirrelfish Neoniphon opercularis(Valenciennes, 1831) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Spotfin squirrelfish Neoniphon sammara (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Rough scale soldierfish Plectrypops lima (Valenciennes, 1831) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tailspot squirrelfish Sargocentron caudimaculatum (Rueppell, 1838) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Threespot squirrelfish Sargocentrum cornutum (Bleeker, 1853) (Indonesia, Philippines, Solomon Islands and Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Crown squirrelfish Sargocentron diadema (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Samurai squirrelfish Sargocentron ittodai (Jordan and Fowler, 1903) (Scattered localities in the Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blackspot squirrelfish Sargocentron melanospilos (Bleeker, 1858) (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Smallmouth squirrelfish Sargocentron microstoma (Guenther, 1859) (Islands of the western Indian Ocean to Oceania excepting Hawaii)[2]
- Peppered squirrelfish Sargocentron punctatissimum (Cuvier, 1839) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Redcoat Sargocentron rubrum (Forsskal, 1775) (Red Sea and East Africa to the western Pacific but absent from oceanic islands)[2]
- Sabre squirrelfish Sargocentron spiniferum (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tahitian squirrelfish Sargocentron tiere (Cuvier, 1829) (Insular Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Pink squirrelfish Sargocentron tiereoides (Bleeker, 1853) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Violet squirrelfish Sargocentrum violaceum (Bleeker, 1853) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Order Syngnathiformes
Family Aulostomidae - Trumpetfishes
- Trumpetfish Aulostomus chinensis (Linnaeus, 1758) (Indo-Pacific and eastern Pacific)[2]
Family Fistulariidae - Flutemouths
- Smooth flutemouth Fistularia commersonii Rueppell, 1838 (Circumtropical)[2]
Family Centriscidae - Razorfishes and shrimpfishes
- Razorfish Aeoliscus strigatus (Guenther, 1860) (Northern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
Family Solenostomidae - Ghost pipefishes
- Ghost pipefish Solenostomus cyanopterus Bleeker, 1852 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Harlequin ghost pipefish Solenostomus paradoxus (Pallas, 1870)[2]
Family Syngnathidae – Pipefishes, pipehorses, seahorses, seadragons
- Sculptured pipefish Choeroichthys sculptus (Guenther, 1870) (East Africa to Polynesia)[2]
- Brown banded pipefish Corythoichthys amplexus Dawson and Randall, 1975 (Western Indian Ocean to Samoa, and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Banded pipefish Corythoichthys intestinalis (Ramsay, 1881) (Philippines to northern Australia, eastward to Samoa and Tonga)[2]
- Schultz's pipefish Corythoichthys schultzi Herald, 1953 (Red Sea to Society Islands)[2]
- Ringed pipefish Doryrhamphus dactyliophorus (Bleeker, 1853) (East Africa and Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Bluestripe pipefish Doryrhamphus excisus excisus Kaup, 1856 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Janss's pipefish Doryrhamphus janssi (Herald and Randall, 1972) (Northern Australia and Solomon Islands north to Philppines and South China Sea)[2]
- Brock's pipefish Halicampus brocki (Herald, 1953) (Western Pacific from northern Australia to the Ryukyu Islands and eastward to the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Ornate pipefish Halicampus macrorhynchus Bamber, 1915 (Red Sea to northern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Glittering pipefish Halicampus nitidus (Guenther, 1873) (Northern Australia to the Ryukyu Islands and eastwards to Fiji)[2]
- Spotted seahorse Hippocampus kuda Bleeker, 1852 (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Hawaiian and Society Islands)[2]
- Shortnose pipefish Micrognathus andersonii (Bleeker, 1858) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Short tailed pipefish Trachyrhamphus bicoarctatus (Bleeker, 1857) (East Africa and the Red Sea to New Caledonia and north to Japan)[2]
Order Scorpaeniformes
Family Dactylopteridae - Helmet gurnards
- Helmet gurnard Dactyloptena orientalis (Cuvier, 1829) (East Africa to Polynesia)[2]
Family Scorpaenidae – Scorpionfishes
- Cockatoo waspfish Ablabys taenianotus (Cuvier, 1829) (Andaman sea to Fiji and north to Japan)[2]
- Dwarf lionfish Dendrochirus brachypterus (Cuvier, 1829) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and Tonga and north to the Philippines)[2]
- Zebra lionfish Dendrochirus zebra (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) ( East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Caledonian stinger Inimicus caledonicus (Sauvage, 1878) (Andaman sea to Australia and New Caledonia)[2]
- Mozambique scorpionfish Parascorpaena mossambica (Peters, 1855) (East Africa to Society Islands)[2]
- Ragged-finned firefish Pterois antennata (Bloch, 1787) (East Africa to southeastern Polynesia)[2]
- Red firefish, turkeyfish Pterois volitans (Linnaeus, 1758) (Western Australia and Malaysia to southeastern Polynesia and north to Japan)[2]
- Whiteface waspfish Richardsonichthys leucogaster (Richardson, 1848) (India to northern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Weedy scorpionfish Rhinopias aphanes Eschmeyer, 1973 (Northeastern Australia, New Caledonis, New Guinea and north to Japan)[2]
- Longfingered scorpionfish Scorpaenodes albaiensis (Evermann and Seale, 1907) (Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Guam scorpionfish Scorpaenodes guamensis (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Pitcairn Group)[2]
- Hairy scorpionfish Scorpaenodes hirsutus (Smith, 1957) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Shortfinned scorpionfish Scorpaenodes parvipinnis (Garrett, 1864) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Shore scorpionfish Scorpaenodes littoralis (Tanaka, 1917) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blotchfin scorpionfish Scorpaenodes varipinnis Smith, 1957 (East Africa to Micronesia)[2]
- False stonefish Scorpaenopsis diabolus Cuvier, 1829 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Smallscale scorpionfish Scorpaenopsis oxycephala (Bleeker, 1849) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the central Pacific)[2]
- Raggy scorpionfish Scorpaenopsis venosa (Cuvier, 1829) (East Africa to central Pacific)[2]
- Yellow-spotted scorpionfish Sebastapistes cyanostigma (Bleeker, 1856) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Barchin scorpionfish Sebastapistes strongia (Cuvier, 1829) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Society Islands)[2]
- Estuarine stonefish Synanceia horrida (Linnaeus, 1766) (India to Australia and north to China)[2]
- Reef stonefish Synanceia verrucosa Bloch and Schneider, 1801 (East Africa and the Red Sea to southeastern Polynesia)[2]
- Leaf scorpionfish Taenianotus triacanthus Lacepede, 1802 (East Africa to the Galapagos)[2]
Family Caracanthidae - Crouchers, orbicular velvetfishes
- Spotted croucher Caracanthus maculatus (Gray, 1831) (East Indies and Australia to southeastern Polynesia, and north to Japan)[2]
- Coral croucher Caracanthus unipinna (Gray, 1831) (East Africa to the Taumotus, and north to Japan)[2]
Family Aploactinidae – Velvetfishes
- Threefin velvetfish Neoaploactis tridorsalis Eschmeyer and Allen, 1978 (Known only from Rottnest Island and Shark Bay in Western Australia and One Tree Island in the Capricorn Group of the southern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
Family Platycephalidae – Flatheads
- Dwarf flathead Onigocia oligolepis (Regan, 1908) (Indo-West Pacific)[2]
- Sand flathead Thysanophrys arenicola Schultz, 1966 (East Africa to the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Longsnout flathead Thysanophrys chiltonae Schultz, 1966 (East Africa to Marquesas Islands)[2]
- Fringelip flathead Sunagocia otaitensis (Cuvier, 1829) syn. Thysanophrys otaitensis (East Africa to the Taumotus)[2]
Order Perciformes
Family Centropomidae - Barramundi
- Sand bass, glasseye perch Psammoperca waigiensis (Cuvier, 1829) (East Indies and northern Australia to China)[2]
Family Serranidae – Rockcods, seaperches, groupers
Subfamily Anthiinae - Anthias
- Waite's splitfin Luzonichthys waitei (Fowler, 1931) (Philippines, Indonesia and Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Longfin perchlet Plectranthias longimanus (Weber, 1913) (Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Dwarf perchlet Plectranthias nanus Randall, 1980 (Islands of Oceania to Christmas and Cocos-Keeling Islands in the eastern Indian Ocean)[2]
- Redblotch perchlet Plectranthias winniensis (Tyler, 1966) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bicolour anthias Pseudanthias bicolor (Randall, 1979) (Hawaii and New Caledonia to the islands of the western Indian Ocean)[2]
- Silverstreak anthias Pseudanthias cooperi (Regan, 1902) (Line Islands and Samoa west to East Africa)[2]
- Redfin anthias Pseudanthias dispar (Herre, 1955) (Western Pacific to Samoa and the Line Islands)[2]
- Barrier Reef anthias Pseudanthias engelhardi (Allen and Starck, 1983) (Known only from Escape Reef, Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Striped anthias Pseudanthias fasciatus (Kamohara, 1954) (Southern Japan to the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Threadfin anthias Pseudanthias huchtii (Bleeker, 1857) (Philippines to Vanuatu and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Stocky anthias Pseudanthias hypselosoma Bleeker, 1878 (Samoa to Maldives)[2]
- Lori's anthias Pseudanthias lori (Lubbock and Randall, 1976) (French Polynesia to Christmas Island, Indian Ocean)[2]
- Yellowlined anthias Pseudanthias luzonensis (Katayama and Masuda, 1983) (Philippines, Indonesia and the northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Amethyst anthias Pseudanthias pascalus (Jordan and Tanaka, 1927) (French Polynesia to Australia, and in the north Pacific from the Marshall Islands to southern Japan) [2]
- Painted anthias Pseudanthias pictilis (Randall and Allen, 1978) (New Caledonia, Lord Howe Island and the southern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Squarespot anthias Pseudanthias pleurotaenia (Bleeker, 1857) (Philippines south to northern Great Barrier Reef and east to the Marshall Islands and Samoa)[2]
- Redbar anthias Pseudanthias rubrizonatus (Randall, 1983) (Philippines, New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Fiji and Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Princess anthia Pseudanthias smithvanizi (Randall and Lubbock, 1981) (Marshall Islands to Christmas and Keeling-Cocos Islands in the eastern Indian Ocean)[2]
- Scalefin anthias Pseudanthias squamipinnis (Peters, 1855) (Western Pacific to East Africa and the Red Sea) [2]
- Purple anthias Pseudanthias tuka (Herre and Montalban, 1927) (Philippines to northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Longfin anthias Pseudanthias ventralis (Randall, 1979) (Great Barrier Reef north to southern Japan, East to the islands of Oceania except Hawaii)[2]
- Hawk anthias Serranocirrhitus latus (Watanabe, 1949) (Southern Japan, Indonesia, Palau, Vanuatu, New Caledonia and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
Subfamily Epinephelinae - Rockcods
- Redmouth rockcod Aethaloperca rogaa (Forsskal, 1775) (Red Sea and coast of East Africa to Kiribati) [2]
- White-lined rockcod Anyperodon leucogrammicus (Valenciennes, 1828) (Red Sea and East Africa to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Peacock rockcod Cephalopholis argus Bloch and Schneider, 1801 (Indo-Pacific and Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Brown-barred rockcod Cephalopholis boenak (Bloch, 1790) (Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Blue-spotted rockcod Cephalopholis cyanostigma (Valenciennes, 1828) (Philippines to Queensland, west to Thailand and Western Australia)[2]
- Blue-lined rockcod Cephalopholis formosa (Shaw, 1804) (Western Pacific to Western India)[2]
- Leopard rockcod Cephalopholis leopardus (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Dothead rockcod Cephalopholis microprion (Bleeker, 1852) (Western Pacific to Andaman Sea)[2]
- Coral cod Cephalopholis miniata (Forsskal, 1775) (Line Islands in the central Pacific to East Africa and the Red Sea)[2]
- Sixspot rockcod Cephalopholis sexmaculata (Rueppell, 1830) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tomato rockcod Cephalopholis sonnerati (Valenciennes, 1828) (Line Islands and Kiribati in central Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Strawberry rockcod Cephalopholis spiloparaea (Valenciennes, 1828) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Flagtail rockcod Cephalopholis urodeta (Bloch and Scneider, 1801) (Central and western Pacific)[2]
- Barramundi cod Cromileptes altivelis (Valenciennes, 1828) (Western Pacific to Nicobar Islands)[2]
- Areolate rockcod Epinephelus areolatus (Forsskal, 1775) (Western Pacific to East Africa and the Red Sea)[2]
- White-spotted rockcod Epinephelus caerulopunctatus (Bloch, 1790) (Kiribati and Caroline Islands to East Africa)[2]
- Estuary cod Epinephelus coioides (Hamilton, 1822) (Western Pacific to western Indian Ocean)[2]
- Coral rockcod Epinephelus corallicola (Valenciennes, 1828) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Blue Maori Epinephelus cyanopodus (Richardson, 1846) (Western Pacific to Marshall Islands and Kiribati)[2]
- Black-tipped rockcod Epinephalus fasciatus (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Flowery cod Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (Forsskal, 1775) (Marshall Islands and Phoenix Islands to East Africa and the Red Sea)[2]
- Hexagon rockcod Epinephelus hexagonatus (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blacksaddle rockcod Epinephalus howlandi (Guenther, 1873) (Western Pacific from Ryukyu Islands to Great Barrier Reef and east to the Marshalls and Samoa)[2]
- Queensland grouper Epinephelus lanceolatus (Bloch, 1790) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Snubnose rockcod Epinephelus macrospilos (Bleeker, 1855) (Central western Pacific to Nicobar Islands)[2]
- Trout cod Epinephelus maculatus (Bloch, 1790) (Western Pacific to Marshall Islands and Samoa)[2]
- Malabar grouper Epinephelus malabaricus (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Western Pacific to East Africa and Red Sea)[2]
- Dwarf spotted rockcod Epinephelus merra Bloch, 1793 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Speckled-fin rockcod Epinephelus ongus (Bloch, 1790) (Caroline Islands and Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Camouflage rockcod Epinephelus polyphekadion (Bleeker, 1856) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Longfin rockcod Epinephelus quoyanus (Valenciennes, 1830) (Western Pacific to southwest coast of Thailand)[2]
- Chinaman rockcod Epinephelus rivulatus (Valenciennes, 1830) (Western Pacific and Indian Ocean)[2]
- Sixbar rockcod Epinephelus sexfasciatus (Valenciennes, 1828) (Indo-Malayan region)[2]
- Four-saddle rockcod Epinephelus spilotoceps Schultz, 1953 (Line Islands in the central Pacific to East Africa)[2]
- Greasy rockcod Epinephelus tauvina (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Potato cod Epinephelus tukula Morgans, 1959 (Western Pacific to East Africa and the Red Sea)[2]
- Maori cod Epinephelus undulatostriatus (Peters, 1866) (Southern Great Barrier Reef to New South Wales)[2]
- Thinspine rockcod Gracila albomarginata (Fowler and Bean, 1930) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Squaretail coral trout Plectropomus areolatus (Rueppell, 1830) (Marshall Islands and Samoa to the Maldives and Red Sea)[2]
- Chinese footballer Plectropomus laevis (Lacepede, 1802) (Indo-Pacific except Red Sea)[2]
- Coral trout Plectropomus leopardus (Lacepede, 1802) (Fiji and Caroline Islands to Western Australia)[2]
- Barred-cheek coral trout Plectropomus maculatus (Bloch, 1790) (Philippines, southeast Asia, Indonesia and Australia)[2]
- Highfin coral trout Plectropomus oligacanthus (Bleeker, 1854) (Philippines, Indonesia, New Guinea, Solomons and north Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Lyretail trout Variola albimarginata Baissac, 1953 (Western Pacific to western Indian Ocean)[2]
- Coronation trout Variola louti (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Subfamily Grammistinae
Tribe Liopropomini
- Headband perch Liopropoma mitratum Lubbock and Randall, 1978 (Scattered through Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Manyline perch Liopropoma multilineatum Randall and Taylor, 1988 (Philippines to the Coral Sea and Fiji)[2]
- Meteor perch Liopropoma susumi (Jordan and Seale, 1906) (Line Islands and Samoa to East Africa)[2]
- Flathead perch Rainfordia opercularis McCulloch, 1923 (Queensland to Western Australia)[2]
Tribe Diploprioni
- Arrowhead soapfish Belonoperca chabanaudi Fowler and Bean, 1930 (Samoa and Marshall Islands to East Africa)[2]
- Barred soapfish, yellow emperor Diploprion bifasciatum Cuvier, 1828 (Western Pacific to India)[2]
Tribe Grammistini
- Sixline soapfish Grammistes sexlineatus (Thunberg, 1792) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Tribe Pseudogrammini
- Ocellated podge Grammistops ocellatus Schultz, 1958 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Poreless podge Aporops bilinearis Schultz, 1943 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Palespotted podge Pseudogramma polyacantha (Bleeker, 1856) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Family Pseudochromidae – Dottybacks and eel blennies
Subfamily Congrogadinae
- Carpet eel blenny Congrogadus subducens (Richardson, 1843) (Malay Peninsula and Philippine Islands to Australia)[2]
Subfamily Pseudochromidae
- Oblique-lined dottyback Cypho purpurascens (De Vis, 1884) (Southwestern Pacific)[2]
- Fine-scaled dottyback Lubbockichthys multisquamatus (Allen, 1987) syn. Pseudoplesiops multisquamatus (Eastern Indian Ocean to central Pacific) [2]
- Multicoloured dottyback Ogilbyina novaehollandiae (Steindachner, 1880) (Southern Great Barrier Reef) [2]
- Queensland dottyback Ogilbyina queenslandiae (Saville-Kent, 1893) (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Sailfin dottyback Ogilbyina velifera (Lubbock, 1980) (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Double-striped dottyback Pseudochromis bitaeniatus (Fowler, 1931) (Indonesia, Philippines, Solomon Islands and the northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Blue-barred dottyback Pseudochromis cyanotaenia Bleeker, 1857 (Eastern Indian Ocean to central Pacific)[2]
- Brown dottyback Pseudochromis fuscus Mueller and Troschel, 1849 (Central Indian Ocean to western Pacific)[2]
- Firetail dottyback Pseudochromis flammicauda Lubbock and Goldman, 1976 (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Spot-tailed dottyback Pseudochromis jamesi Schultz, 1943 (South-western Pacific)[2]
- Royal dottyback Pseudochromis paccagnellae Axelrod, 1973 (Indonesia to Melanesia and Australia)[2]
- Midnight dottyback Pseudochromis paranox Lubbock and Goldman, 1976 (Southwestern Pacific)[2]
- Spotted dottyback Pseudochromis quinquedentatus McCulloch, 1926 (Northern Australia)[2]
- Yellowfin dottyback Pseudochromis wilsoni (Whitley, 1929) (Northern Australia)[2]
- Bug-eyed dottyback Pseudoplesiops knighti Allen, 1987 (Indonesia, Melanesia and northern Australia) [2]
- Large-scaled dottyback Pseudoplesiops rosae Schultz, 1943 (Eastern Indian Ocean to central Pacific)[2]
- Bearded dottyback Pseudoplesiops sp. (Central Indian Ocean to western Pacific)[2]
- Ring-eyed dottyback Pseudoplesiops typus Bleeker, 1858 (Eastern Indian Ocean to central Pacific)[2]
Family Plesiopidae – Prettyfins, blue devilfishes, hulafishes, longfins
- Yellow devilfish Assessor flavissimus Allen and Kuiter, 1976 (Northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Blue devilfish Assessor macneilli Whitley, 1935 (Great Barrier Reef and New Caledonia)[2]
- Comet Calloplesiops altivelis (Steindachner, 1903) (East Africa and Red Sea to Tonga and the Line Islands)[2]
- Blue-tip longfin Paraplesiops poweri Ogilby, 1908 (Central and southern Queensland and adjacent Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Red-tipped longfin Plesiops coeruleolineatus Rueppell, 1835 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Australia and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Coral Sea longfin Plesiops insularis Mooi and Randall, 1991 (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Plesiops genaricus Mooi and Randall (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
Subfamily Acanthoclininae
- Banded spiny basslet Belonepterygion fasciolatum (Ogilby, 1889) (West and east coasts of Australia in tropical and subtropical seas, and Lord Howe Island)[2]
Family Teraponidae - Grunters
- Crescent grunter Terapon jarbua (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
Family Kuhliidae - Flagtails
- Fiveband flagtail Kuhlia mugil (Forster in Bloch and Scneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
Family Priacanthidae - Bigeyes
- Glasseye Heteropriacanthus cruentatus (Lacepede, 1801) (Circumglobal in tropical and subtropical seas)[2]
- Bloch's bigeye Priacanthus blochii Bleeker,1853 (Samoa to Gulf of Aden)[2]
- Crescent tail bigeye Priacanthus hamrur (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Family Apogonidae – Cardinalfishes
- Ring-tailed cardinalfish Apogon aureus (Lacepede, 1802) (East Africa to western Pacific)[2]
- Ruby cardinalfish Apogon crassiceps Garman, 1903 (Western Pacific to islands of Oceania except Hawaii) [2]
- Split-banded cardinalfish Apogon compressus (Smith and Radcliffe, 1911) (East Indies to Solomon Islands and North to Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Yellow-striped cardinalfish Apogon cyanosoma Bleeker, 1853 (East Africa and Red Sea to Australia and the Marshall Islands) [2]
- Doederlein’s cardinalfish Apogon doederleini Jordan and Snyder, 1901 (Western Pacific antitropical: Southern Japan to Taiwan in the north, subtropical Australia to New Caledonia and the Kermadec Islands in the south) [2]
- Fragile cardinalfish Apogon fragilis Smith, 1961 (East Africa to Samoa) [2]
- Frostfin cardunalfish Apogon hoeveni Bleeker, 1854 (East Indies and northern Australia to Japan) [2]
- Longspine cardinalfish Apogon leptacanthus Bleeker, 1856 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa) [2]
- Moluccan cardinalfish Apogon moluccensis Valenciennes, 1832 (East Indies and northern Australia) [2]
- Blackstripe cardinalfish Apogon nigrofasciatus Lachner, 1953 (Red Sea to the Taumotus) [2]
- Spotnape cardinalfish Apogon notatus (Houttuyn, 1782) (Coral Sea to southern Japan) [2]
- Sangi cardinalfish Apogon sangiensis Bleeker, 1857 (East Indies to Vanuatu and north to Japan) [2]
- Oblique banded cardinalfish Apogon semiornatus Peters, 1876 (East Africa to northern Australia and north to Japan) [2]
- Three-spot cardinalfish Apogon trimaculatus Cuvier, 1828 (East Indies to Samoa, north to the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Three saddle cardinalfish Apogon sp. (French Polynesia and Marshall Islands to northern Indian Ocean) [2]
- Timor cardinalfish Apogonichthyoides timorensis (Bleeker, 1854)[6] syn. Apogon timorensis ((as A. timorensis) East Africa and the Red Sea to northern Australia and north to Japan) [2]
- Ocellated cardinalfish Apogonichthys ocellatus (Weber,1913) (East Africa to the Marquesas and Taumotus) [2]
- Narrow-lined cardinalfish Archamia fucata (Cantor, 1850) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa) [2]
- Lea’s cardinalfish Archamia leai Waite, 1916 (Coral Sea and southern Great Barrier Reef) [2]
- Two-spot cardinalfish Archamia biguttata Lachner, 1951 (Northern Australia and New Guinea) [2]
- Girdled cardinalfish Archamia zosterophora (Bleeker, 1856) (Indonesia and Philippines to New Caledonia and north to the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Tiger cardinalfish Cheilodipterus macrodon (Lacepede, 1802) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Wolf cardinalfish Cheilodipterus artus Smith, 1961 (East Africa to the Taumotu Archipelago, In the western Pacific from Ryukyu Islands to the Great Barrier Reef) [2]
- Five-lined cardinalfish Cheilodipterus quinquelineatus Cuvier, 1828 (East Africa and the Red Sea to southeastern Polynesia) [2]
- Mimic cardinalfish Cheilodipterus parazonatus Gon, 1993 (Indonesia, Phlippines, New Guinea and Queensland) [2]
- Weed cardinalfish Foa brachygramma (Jenkins, 1903) (East Africa to Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Dwarf cardinalfish Fowleria vaiulae (Jordan and Seale, 1906) (Red Sea to western Pacific) [2]
- Aurita cardinalfish Fowleria aurita (Valenciennes, 1831) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the western Pacific) [2]
- Eared cardinalfish Fowleria marmorata (Alleyne and Macleay, 1877) (Red Sea to southeastern Polynesia) [2]
- Peppered cardinalfish Fowleria punctulata (Rueppell, 1838) ( Red Sea to central and south Pacific) [2]
- Variegated cardinalfish Fowleria variegata (Valenciennes, 1832) (Red Sea to Samoa and north to Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Eightspine cardinalfish Neamia octospina Smith and Radcliffe, 1912 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Australia and Philippine Islands) [2]
- Guam cardinalfish Nectamia fusca (Quoy & Gaimard, 1825)[7] syn. Apogon guamensis Valenciennes, 1832 ((as A. guamensis) East Africa and Red Sea to Samoa) [2]
- Samoan cardinalfish Nectamia savayensis (Günther, 1872) syn. Apogon savayensis ((as A. savayensis)Indo-Pacific from East Africa to French Polynesia) [2]
- Striped cardinalfish Ostorhinchus angustatus (Smith & Radcliffe, 1911) syn. Apogon angustatus ((as A. angustatus)East Africa and the Red Sea to Melanesia and Micronesia)[2]
- Goldbelly cardinalfish Ostorhinchus apogonoides (Bleeker, 1856) syn. Apogon apogonides ((as A. apogonides) East Africa to East Indies and Australia)[2]
- Cook’s cardinalfish Ostorhinchus cookii (MacLeay, 1881) syn. Apogon cookii ((as A. cookii)East Africa to Australia, north to Japan) [2]
- Rifle cardinalfish Ostorhinchus kiensis (Jordan & Snyder, 1901) syn. Apogon kiensis ((as A. kiensis)East Africa and Red Sea north to Japan) [2]
- Nine-banded cardinalfish Ostorhinchus novemfasciatus (Cuvier, 1828)[8] syn. Apogon novemfasciatus ((as A. novemfasciatus) Cocos-Keeling Islands to Samoa and north to the Izu Islands) [2]
- Coral cardinalfish Ostorhinchus properuptus (Whitley, 1964)[9] syn. Apogon properupta ((as A. properupta) Queensland and the northern section of the Great Barrier Reef south to Montague Island, New South Wales) [2]
- Reef-flat cardinalfish Ostorhinchus taeniophorus (Regan, 1908)[10] syn. Apogon taeniophorus ((as A. taeniophorus) Mauritius to Polynesia) [2]
- Flame cardinalfish Ostorhinchus talboti (Smith, 1961)[11] syn. Apogon talboti Smith, 1961 ((as A. talboti)Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Narrowstripe cardinalfish Pristiapogon exostigma (Jordan & Starks, 1906) syn. Apogon exostigma ((as A. exostigma)Red Sea to south-eastern Polynesia) [2]
- Spur-cheek cardinalfish Pristiapogon fraenatus (Valenciennes, 1832) syn. Apogon fraenatus ((as A. fraenatus)East Africa and Red Sea to the Line Islands and Taumotu Archipelago) [2]
- Iridescent cardinalfish Pristiapogon kallopterus (Bleeker, 1856)[12] syn.Apogon kallopterus Bleeker, 1856 ((as A. kallopterus) East Africa and Red Sea to Polynesia) [2]
- Gelatinous cardinalfish Pseudamia gelatinosa Smith, 1954 (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Society Islands and north to Japan) [2]
- Slender cardinalfish Rhabdamia gracilis (Bleeker, 1856) (East Africa to the Marshall Islands) [2]
- Striped siphonfish Siphamia majimai Matsubara and Iwai, 1958 (Northern Australia to Japan) [2]
- Threadfin cardinalfish Sphaeramia nematoptera (Bleeker, 1856) (East Indies and northern Australia to Micronesia and north to Japan) [2]
Family Malacanthidae - Sand tilefishes
- Grey tilefish Hoplolatilus cuniculus Randall and Dooley, 1974 (Mauritius to the Society Islands) [2]
- Blue tilefish Hoplolatilus starcki Randall and Dooley, 1974 (Indonesia to Australia, Melanesia and Micronesia) [2]
- Flagtail banquillo Malacanthus brevirostris Guichenot, 1848 (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Blue blanquilillo Malacanthus latovittatus (Lacepede, 1801) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Cook Islands, north to Japan) [2]
Family Echeneidae - Remoras, suckerfish
- Slender suckerfish Echeneis naucrates Linnaeus, 1758 (Circumtropical) [2]
Family Carangidae – Trevallies
- Pennantfish Alectis ciliaris (Bloch, 1788) (Worldwide in tropical seas) [2]
- Diamond trevally Alectis indicus (Rueppell, 1830) (East Africa to Australia and the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Fringe-finned trevally Pantolabus radiatus (MacLeay, 1881)[13] syn. Absalom radiatus (Macleay, 1881) ((as A. radiatus)Indonesia and northern Australia) [2]
- Small mouth scad Alepes sp. (Indonesia and northern Australia) [2]
- Yellowtail scad Atule mate (Cuvier, 1833) (Indo-West Pacific to Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Onion trevally Carangoides caeruleopinnatus (Rueppell, 1830) (East Africa to Japan and Australia) [2]
- Club-nosed trevally Carangoides chrysophrys (Cuvier, 1833) (East Africa to Japan and Australia) [2]
- Whitefin trevally Carangoides equula (Temminck and Schlegel, 1844) (East Africa, Gulf of Oman, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, Hawaii and Easter Island) [2]
- Blue trevally Carangoides ferdau (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific east to Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Gold-spotted trevally Carangoides fulvoguttatus (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Bludger trevally Carangoides gymnostethus (Cuvier, 1833) (Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Bump-nosed trevally Carangoides hedlandensis (Whitley, 1934) (East Africa to Samoa and north to Japan) [2]
- Epaulet trevally Carangoides humerosus (McCulloch, 1915) (Indonesia, New Guinea and northern Australia) [2]
- Malabar trevally Carangoides malabaricus (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Tropical coastal waters of Indo-Pacific) [2]
- Thicklip trevally Carangoides orthogrammus (Jordan and Gilbert, 1881) (Indo-Pacific and eastern Pacific) [2]
- White-tongued trevally Carangoides talamparoides Bleeker, 1852 (Gulf of Oman to northern Australia) [2]
- Japanese trevally Carangoides uii Wakiya, 1924 (East Africa to Australia and Japan) [2]
- Blue-spotted trevally Caranx bucculentus Alleyne and Macleay, 1877 (Northern Australia and New Guinea) [2]
- Giant trevally Caranx ignobilis (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-West Pacific from East Africa to the Hawaiian and Marquesas Islands) [2]
- Black trevally Caranx lugubris Poey, 1860 (Circumtropical) [2]
- Bluefin trevally Caranx melampygus Cuvier, 1833 (Tropical Indo-Pacific to the Americas) [2]
- Brassy trevally Caranx papuensis Alleyne and Macleay, 1877 (Indo-Pacific eastward to the Marquesas) [2]
- Banded scad Alepes kleinii (Bloch, 1793) (East Africa to northern Australia and north to Japan) [2]
- Bigeye trevally Caranx sexfasciatus Quoy and Gaimard, 1824 (Tropical Indo-Pacific from East Africa to the Americas) [2]
- Tille trevally Caranx tille Cuvier, 1833 (East Africa, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Okinawa to Australia and Fiji) [2]
- Redtail scad Decapterus kurroides Bleeker, 1855 (East Africa to Australia and Japan) [2]
- Mackerel scad Decapterus macarellus (Cuvier, 1833) (Circumtropical) [2]
- Long-bodied scad Decapterus macrosoma Bleeker, 1851 (Indo-Pacific and eastern Pacific) [2]
- Russell’s mackerel scad Decapterus russelli (Rueppell, 1830) (East Africa to Japan and Australia) [2]
- Rough-ear scad Decapterys tabl Berry, 1968 (Indo-Pacific east to Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Rainbow runner Elagatis bipinnulata (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) (Circumtropical) [2]
- Golden trevally Gnathanodon speciosus (Forsskal, 1775) (Tropical Indo-Pacific eastwards to the Americas) [2]
- Finny scad Megalaspis cordyla (Linnaeus, 1758) (Indo-Pacific to Japan and Australia) [2]
- Pilotfish Naucrates ductor (Linnaeus, 1758) (Circumtropical) [2]
- Black pomfret Parastromateus niger (Bloch, 1795) (East Africa to Southern Japan and Australia) [2]
- Silver trevally Pseudocaranx dentex (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Antitropical, both sides of the Atlantic, Mediterranean and Indo-Pacific eastwards to the Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Talang queenfish Scomberoides commersonnianus Lacepede, 1801 (East Africa to Taiwan and Australia) [2]
- Double-spotted queenfish Scomberoides lysan (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific eastwards to Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Barred queenfish Scomberoides tala (Cuvier, 1832) (Sri Lanka and east coast of India to Australia and the Solomon Islands) [2]
- Needleskin queenfish Scomberoides tol (Cuvier, 1832) (Indian Ocean to Japan and Australia, eastwards to Fiji) [2]
- Oxeye scad Selar boops (Cuvier, 1833) (Tropical Indo-Pacific and eastern Atlantic) [2]
- Purse-eye scad Selar crumenophthalmus (Bloch, 1793) (Worldwide in tropical and subtropical waters) [2]
- Smooth tailed trevally Selaroides leptolepis (Cuvier, 1833) (Persian Gulf eastwards to Australia and Japan) [2]
- Amberjack Seriola dumerili (Risso, 1810) (Tropical Indo-Pacific and Atlantic) [2]
- Yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi Valenciennes, 1833 (Perth, Western Australia, to Capricorn Group, Queensland, and northern Tasmania.)[3] (Circumglobal restricted to subtropical and temperate waters) [2]
- Almaco jack Seriola rivoliana Valenciennes, 1833 (Circumtropical, entering temperate waters in some areas) [2]
- Black-banded kingfish Seriolina nigrofasciata (Rueppell, 1829) (East Africa to Japan and Australia) [2]
- Black-spotted dart Trachinotus baillonii (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-West Pacific from East Africa to the Marshall and Line Islands) [2]
- Snub-nosed dart Trachinotus blochii (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-Pacific from East Africa to the Marshall Islands) [2]
- Common dart Trachinotus botla (Shaw, 1803) (East Africa to Australia) [2]
Family Coryphaenidae – Dolphinfishes
- Common dolphinfish Coryphaena hippurus Linnaeus, 1758 (Circumtropical) [2]
Family Lutjanidae – Snappers
- Small-toothed jobfish Aphareus furca (Lacepede, 1802) (East Africa to Polynesia) [2]
- Green jobfish Aprion virescens Valenciennes, 1830 (East Africa and the Red sea to Polynesia) [2]
- Hussar Lutjanus adetii Castelnau, 1873 (Eastern Australia and the Coral Sea) [2]
- Mangrove jack Lutjanus argentimaculatus (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa. Introduced to eastern Mditerranean) [2]
- Red bass Lutjanus bohar (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Marquesas and Line Islands) [2]
- Spanish flag Lutjanus carponotatus (Richardson, 1842) (Andaman sea to northern Australia) [2]
- Checkered seaperch Lutjanus decussatus (Cuvier, 1828) (Andaman Sea to Northern Australia) [2]
- Black spot snapper Lutjanus fulviflamma (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa) [2]
- Yellow margined seaperch Lutjanus fulvus (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (East Africa and the Red Sea to eastern Oceania. Introduced in the Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Paddletail Lutjanus gibbus (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to southeastern Oceania) [2]
- Bluestripe seaperch Lutjanus kasmira (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa to Polynesia. Introduced in Hawaiian Islands) [2]
- Dark-tailed seaperch Lutjanus lemniscatus (Valenciennes,1828) (Sri Lanka to northern Australia) [2]
- Bigeye seaperch Lutjanus lutjanus (Bloch, 1790) (East Africa to Australia, Melanesia and Mariana Islands) [2]
- Onespot seaperch Lutjanus monostigma (Cuvier, 1828) (East Africa and Red Sea to the Marquesa and Line Islands) [2]
- Five-lined seaperch Lutjanus quinquelineatus (Bloch, 1790) (Persian Gulf to Fiji) [2]
- Maori seaperch Lutjanus rivulatus (Cuvier, 1828) (East Africa and Red Sea to Society Islans and north to Japan) [2]
- Moses perch Lutjanus russelli (Bleeker, 1849) (East Africa to Fiji) [2]
- Red emperor Lutjanus sebae (Cuvier, 1828) (East Africa to western Pacific) [2]
- Black banded seaperch Lutjanus semicinctus Quoy and Gaimard, 1824 (Indonesia to Fiji) [2]
- Brownstripe seaperch Lutjanus vitta (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Seychelles to western Pacific) [2]
- Midnight seaperch Macolor macularis Fowler, 1931 (East Indies and northern Australia to Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Black and white seaperch Macolor niger (Forsskal 1775) (East Africa to Samoa) [2]
- Sailfin snapper Symphorichthys spilurus (Guenther, 1874) (Western Pacific from northern Australia to Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Chinamanfish Symphorus nematophorus (Bleeker, 1860) (Western Pacific from northern Australia to Ryukyu Islands) [2]
Family Caesionidae – Fusiliers
- Scissortail fusilier Caesio caerulaurea Lacepede, 1801 (East Africa to Samoa) [2]
- Red-bellied fusilier Caesio cuning (Bloch, 1791) (Sri Lanka to New Caledonia, north to the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Lunar fusilier Caesio lunaris Cuvier, 1830 (East Africa to Melanesia) [2]
- Blue and gold fusilier Caesio teres Seale, 1906 (East Africa to the Line Islands and north to Japan) [2]
- Marr’s fusilier Pterocaesio marri Schultz, 1953 (East Africa to the Marquesas and north to Japan) [2]
- Neon fusilier Pterocaesio tile (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa to southeastern Oceania and north to Japan) [2]
- Three lined fusilier Pterocaesio trilineata Carpenter, 1987 (Western and Central Pacific) [2]
Family Lobotidae - Tripletails
- Tripletail Lobotes surinamensis (Bloch, 1790) (Tropical and subtropical seas around the world) [2]
Family Gerreidae – Silverbiddies, silverbellies
- Oceanic silver biddy Gerres longirostris (Lacepède, 1801)[14] syn. Gerres acinaces Bleeker, 1854 ((as G. acinaces)East Africa and Red Sea to Samoa) [2]
Family Haemulidae – Sweetlips, grunts, grunter breams
- Painted sweetlips Diagramma pictum (Thunberg,1792) (East Africa and the Red Sea to New Caledonia, and north to Japan) [2]
- Goldstriped sweetlips Plectorhinchus chrysotaenia (Bleeker,1855) (Indonesi to New Caledonis and north to the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Many-spotted sweetlips Plectorhinchus chaetodonoides (Lacepède, 1800) (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Samoa) [2]
- Striped sweetlips Plectorhinchus lessonii (Cuvier, 1830) (Malaysia to Melanesia and north to Japan) [2]
- Goldspotted sweetlips, netted sweetlips, netted morwong Plectorhinchus flavomaculatus (Ehrenberg, 1830) (Tropical Australia south to Geographe Bay, Western Australia, and to Moruya, New South Wales. Also widespread in the Indo-West Pacific region.)[3] (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa and the Red Sea to western Pacific) [2]
- Brown sweetlips, blubber-lip bream Plectorhinchus gibbosus (Lacepède, 1802) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa, and north to the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Diagonal banded sweetlips Plectorhinchus lineatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Western Pacific from Australia to the Ryukyu Islands) [2]
- Giant sweetlips Plectorhinchus albovittatus (Rueppell, 1838) (Red Sea to Fiji) [2]
- Dotted sweetlips Plectorhinchus picus (Cuvier, 1830) (Seychelles to society Islands and north to Japan) [2]
- Somber sweetlips Plectorhinchus unicolor (Macleay, 1883) (Papua New Guinea to Queensland and the Great Barrier Reef) [2]
Family Sparidae – Breams
- Yellowfin bream, bream, silver bream Acanthopagrus australis (Owen, 1853) (Lakes Entrance, Victoria, to Townsville, Queensland.)[3]
- Tarwhine Rhabdosargus sarba (Forsskål, 1775) (Coral Bay to Albany, Western Australia, and Lakes Entrance, Victoria, to Queensland. Also widespread overseas.)[3]
- Snapper, cockney bream, red bream, squire, old man Pagrus auratus (Schneider, 1801) (Barrow Island, Western Australia, to Hinchinbrook Island, Queensland, and northern Tasmania. Also New Zealand, Japan and the Indo-Malayan region.)[3](Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (New Zealand and southern Australia north to the Capricorns) [2]
Family Lethrinidae – Emperors
- Gold-lined sea bream Gnathodentex aureolineatus (Lacepède, 1802) (East Africa to the Taumotus) [2]
- Collared sea bream Gymnocranius audleyi Ogilby, 1916 (Southern Queensland including southern part of the Great Barrier Reef) [2]
- Japanese sea bream Gymnocranius euanus Guenther, 1879 (Queensland to Tonga and north to Japan) [2]
- Robinson’s sea bream Gymnocranius grandoculis (Valenciennes,1830) (East Africa and the Red Sea to southeastern Oceania) [2]
- Spotted sea bream Gymnocranius sp. (Great Barrier Reef, Coral sea, New Caledonia, New Guinea and southern Japan) [2]
- Yellow tailed emperor Lethrinus atkinsoni Seale, 1909 (Indonesia to Taumotus, north to Japan) [2]
- Bi-eye bream Monotaxis grandoculis (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to southeastern Oceania and Hawaiian Islands)[2]
Family Nemipteridae – Coral breams
- Japanese butterfish Pentapodus nagasakiensis (Tanaka, 1915) (Western Pacific from Japan to northern Australia. Reported from Lizard Island and Lihou Reef)[2]
- Paradise butterfish Pentapodus paradiseus (Guenther, 1859) (Northeastern Australia to the Arafura sea)[2]
- Blue butterfish Pentapodus sp. (Northeastern Australia to Fiji)[2]
- Pale monocle bream Scolopsis affinis Peters, 1877 (Indonesia and Philippines to Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Bridled monocle bream Scolopsis bilineata (Bloch, 1793) (Andaman Sea to Fiji and north to Japan)[2]
- Lined monocle bream Scolopsis lineata Quoy and Gaimard, 1824[15] syn. Scolopsis cancellatus (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Polynesia)[2]
- Pearly monocle bream Scolopsis margaritifera (Cuvier, 1830)[16] (Malay Peninsula to Melanesia and northern Australia)[2]
- Monocle bream Scolopsis monogramma (Cuvier, 1830) (Andaman Sea to New Caledonia and north to Taiwan)[2]
- Threelined monocle bream Scolopsis trilineata Kner, 1868[17] (Western Pacific to Samoa)[2]
Family Mullidae – Goatfishes, red mullet
- Yellowstripe goatfish Mulloidichthys flavolineatus (Lacepede, 1801) syn. M. samoensis (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Yellowfin goatfish Mulloidichthys vanicolensis (Valenciennes, 1831) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bicolour goatfish Parupeneus barberinoides (Bleeker, 1852) (Western Pacific east to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Dash-dot goatfish Parupeneus barberinus (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Doublebar goatfish Parupeneus trifasciatus (Lacepède, 1801)[18] syn. Parupeneus bifasciatus (Lacepede, 1801) ((as P. bifasciatus)Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Cardinal goatfish Parupeneus ciliatus (Lacepede, 1801) syn. P. fraterculus, P. pleurotaenia (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Goldsaddle goatfish Parupeneus cyclostomus (Lacepede, 1801) syn. P. chryserydros, P. luteus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Cinnabar goatfish Parupeneus heptacanthus (Lacepede 1801) syn. P. cinnabarensis, P. Pleurospilos (East Africa to the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Indian goatfish Parupeneus indicus (Shaw, 1803) (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Manybar goatfish Parupeneus multifasciatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) (Central and western Pacific)[2]
- Sidespot goatfish Parupeneus pleurostigma (Bennett, 1830) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blacksaddle goatfish, blackspot goatfish Parupeneus spilurus (Bleeker, 1854) syn. P. signatus (Tropical Australia south to Geographe Bay, Western Australia, and to Mallacoota, Victoria. Also Lord Howe Island, New Zealand and New Guinea.)[3] (Northern New Zealand and New Caledonia to Western Australia)[2]
- Bartail goatfish, freckled goatfish Upeneus tragula Richardson, 1846 (Tropical Australia south to Perth, Western Australia, and to Merimbula, New South Wales.)[3] (Western Pacific to East Africa)[2]
Family Pempheridae – Bullseyes, sweepers
- Golden sweeper Parapriacanthus ransonneti Steindachner, 1870 (Western Pacific east to New Caledonia and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Bronze sweeper Pempheris analis Waite, 1910 (Kermadec Islands, Lord Howe Island, southern Great Barrier Reef and Western Australia)[2]
- Copper sweeper Pempheris otaitensis Lesson, 1830 (Islands of Oceania and western Pacific to Western Australia and Christmas Island in the Indian Ocean)[2]
- Silver sweeper Pempheris schwenkii Bleeker, 1855 (Fiji and Vanuatu through Australia and Indonesia to East Africa)[2]
Family Kyphosidae – Drummers, rudderfishes
- Topsail drummer Kyphosus cinerascens Forsskal, 1775 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Long finned drummer Kyphosis vaigiensis (Quoy and Gaimard 1825) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Stripey Microcanthus strigatus (Cuvier, 1831) (Antiequatorial, Isolated populations in western and eastern Australia, and in the Hawaiian Island and Taiwan to Japan)[2]
Family Ephippidae - Batfishes
- Hump-headed batfish Platax batavianus Cuvier, 1831 (Malay Peninsula to northern Australia)[2]
- Orbicular batfish Platax orbicularis (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Taumotus)[2]
- Pinnate batfish Platax pinnatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Western Pacific from the Ryukyu Islands to Australia)[2]
- Teira batfish Platax teira (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Melanesia)[2]
- Short-finned batfish Zabidius novemaculeatus (McCulloch, 1916)[19] syn. Platax novemaculatus ((as P. novemaculatus)Northern Australia and southern New Guinea)[2]
Family Chaetodontidae – Butterflyfishes
- Bennett's butterflyfish Chaetodon bennetti Cuvier, 1831 (East Africa to the Pitcairn Islands, and north to Japan)[2]
- Speckled butterflyfish Chaetodon citrinellus Cuvier, 1831 (East Africa to the Hawaiian Islands and Tuamotu archipelago)[2]
- Saddled butterflyfish Chaetodon ephippium Cuvier, 1831 (Cocos-Keeling Islands to the Hawaiian Islands and Tuamotu Archipelago)[2]
- Dusky butterflyfish Chaetodon flavirostris Guenther, 1873 (Great Barrier Reef to Pitcairn Islands)[2]
- Gunther’s butterflyfish Chaetodon guentheri Ahl, 1913 (Merimbula, New South Wales, to Capricorn Group, Queensland.)[3] (Antiequatorial. Lord How Island and New South Wales, also Japan. Sighted at Lizard Island)[2]
- Klein's butterflyfish Chaetodon kleinii Bloch, 1790 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Hawaiian Islands and Samoa)[2]
- Lined butterflyfish Chaetodon lineolatus Cuvier, 1831 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Raccoon butterflyfish Chaetodon lunula (Lacepede, 1802) (East Africa to Polynesia)[2]
- Blackback butterflyfish Chaetodon melannotus Bloch and Schneider, 1801 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Merten's butterflyfish Chaetodon mertensii Cuvier, 1831 (Lord Howe Island and the Great Barrier Reef to the Ryukyu Islands and east to the Tuamotu Archipelago)[2]
- Meyer's butterflyfish Chaetodon meyeri Bloch and Schneider, 1801 (East Africa to the Line Islands)[2]
- Spot-tail butterflyfish Chaetodon ocellicaudus Cuvier, 1831 (East Indies, Philippines and northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Ornate butterflyfish Chaetodon ornatissimus Cuvier, 1831 (Sri Lanka to Polynesia)[2]
- Spotnape butterflyfish Chaetodon oxycephalus Bleeker, 1851 (Sri Lanka to Queensland and north to the Philippines)[2]
- Dot and dash butterflyfish Chaetodon pelewensis Kner, 1868 (Southern Oceania from Queensland to the Tuamotus)[2]
- Bluespot butterflyfish Chaetodon plebeius Cuvier, 1831 (Andaman sea to Fiji and north to Japan)[2]
- Spot-banded butterflyfish Chaetodon punctatofasciatus Cuvier 1831 (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to the Line Islands)[2]
- Latticed butterflyfish Chaetodon rafflesii Bennett, 1830 (Sri Lanka to Taumotus and north to Japan)[2]
- Rainford's Butterflyfish Chaetodon rainfordi McCulloch, 1923 (Great Barrier Reef and inshore areas of the Queensland coast)[2]
- Reticulated butterflyfish Chaetodon reticulatus Cuvier, 1831 (Great Barrier Reef to Taiwan and east to Polynesia)[2]
- Dotted butterflyfish Chaetodon semeion Bleeker, 1855 (Maldive Islands to Tuamotus)[2]
- Ovalspot butterflyfish Chaetodon speculum Cuvier, 1831 (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to Tonga and North to Japan)[2]
- Chevroned butterflyfish Chaetodon trifascialis Quoy and Gaimard, 1825 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Hawaiian and Society Islands)[2]
- Redfin butterflyfish, oval butterflyfish Chaetodon trifasciatus Park, 1797 (East Africa to Hawaiian Islands and Tuamotu Archipelago)[2]
- Pacific double-saddle butterflyfish Chaetodon ulietensis Cuvier 1831 (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Tuamotus and north to Japan)[2]
- Teardrop butterflyfish Chaetodon unimaculatus Bloch, 1787 (East Africa to Polynesia)[2]
- Müller's coralfish Chelmon muelleri (Klunzinger, 1879) (Northern Australia coastal reefs)[2]
- Beaked coralfish Chelmon rostratus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Andaman Sea to Australia and the Great Barrier Reef, north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Highfin coralfish Coradion altivelis McCulloch, 1916 (Western Pacific from Australia north to Japan)[2]
- Orange-banded coralfish Coradion chrysozonus (Cuvier, 1831) (Western Pacific from Australia north to the Ogasawara Islands)[2]
- Forcepsfish Forcipiger flavissimus Jordan and McGregor, 1898 (East Africa to Central America and Mexico)[2]
- Longnose butterflyfish Forcipiger longirostris (Broussonet, 1782) (East Africa to Polynesia)[2]
- Pyramid butterflyfish Hemitaurichthys polylepis (Bleeker, 1857) (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Hawaiian Islands and Pitcairn group)[2]
- Longfin bannerfish Heniochus acuminatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (East Africa and the Persian Gulf to the Society Islands)[2]
- Pennant bannerfish Heniochus chrysostomus Cuvier, 1831 syn. H. permutatus (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Pitcairn Group)[2]
- Schooling bannerfish Heniochus diphreutes Jordan, 1903 (East Africa to the Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Masked bannerfish Heniochus monoceros Cuvier, 1831 (East Africa to the Tuamotus)[2]
- Singular bannerfish Heniochus singularius Smith and Radcliffe, 1911 (Andaman Sea to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Humphead bannerfish Heniochus varius (Cuvier, 1829) (Malay Peninsula to Samoa)[2]
- Ocellated coralfish Parachaetodon ocellatus (Cuvier, 1831) (Australia north to Ogasawara Islands)[2]
Family Pomacanthidae - Angelfishes
- Three-spot angelfish Apolemichthys trimaculatus (Valenciennes, 1831) (East Africa to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Golden angelfish Centropyge aurantia Randall and Wass, 1974[20] (Northern Great Barrier Reef to Samoa)[2]
- Bicolor angelfish Centropyge bicolor (Bloch, 1787) (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Two-spined angelfish Centropyge bispinosus (Guenther, 1860) (East Africa to Tuamotus and north to Izu Islands)[2]
- White-tail angelfish Centropyge flavicauda Fraser-Brunner, 1933 (Queensland and East Indies north to Japan and east to the Tuamotu Archipelago)[2]
- Lemonpeel angelfish Centropyge flavissima (Cuvier, 1831)[21] (Cocos-Leeling Islands to southeastern Oceania and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Herald's angelfish Centropyge heraldi Woods and Schultz, 1953 (Queensland to the Tuamotus and north to Taiwan)[2]
- Flame angelfish Centropyge loricula (Guenther, 1874)[22] syn. C. flammeus (Oceanic coral reefs from Queensland to Samoa and the Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Multi-barred angelfish Centropyge multifasciata (Smith and Radcliffe, 1911)[23] (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Society Islands)[2]
- Midnight angelfish Centropyge nox (Bleeker, 1853) (Queensland and Melanesia north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Keyhole angelfish Centropyge tibicen (Cuvier, 1831) (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to Melanesia and north to Japan)[2]
- Pearl-scaled angelfish Centropyge vrolikii (Bleeker, 1853) (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to Melanesia and Micronesia)[2]
- Conspicuous angelfish Chaetodontoplus conspicillatus (Waite, 1900) (Southern part of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea)[2]
- Scribbled angelfish Chaetodontoplus duboulayi (Guenther, 1867) (Northern Australia and southern New Guinea. Also reported from Japan)[2]
- Queensland yellowtail angelfish Chaetodontoplus meredithi Kuiter, 1990 (Queensland coastal and inner reefs)[2]
- Lamarck's angelfish Genicanthus lamarck (Lacepede, 1802) (East Africa and Indonesia to Queensland and Solomon Islands, and north to Japan. Recorded from Escape Reef on the northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Black-spot angelfish Genicanthus melanospilos (Bleeker, 1857) (Queensland to Fiji and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Watanabe's angelfish Genicanthus watanabei (Yasuda and Tominaga, 1970) (Queensland to Tuamotus and north to Taiwan)[2]
- Emperor angelfish Pomacanthus imperator (Bloch, 1787) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotus and north to Japan)[2]
- Blue-girdled angelfish Pomacanthus navarchus (Cuvier, 1831) (Indonesia and Philippines to northern Queensland)[2]
- Semicircle angelfish Pomacanthus semicirculatus (Cuvier, 1831) (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Six-banded angelfish Pomacanthus sexstriatus (Cuvier, 1831) (Malaysia to Solomon Islands and north to Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Yellowmask angelfish Pomacanthus xanthometopon (Bleeker, 1853) (Maldive Islands to Vanuatu and north to Yaeyama Islands)[2]
- Regal angelfish Pygoplites diacanthus (Boddaert, 1772) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotus and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
Family Pomacentridae – Damselfishes
- Bengal sergeant Abudefduf bengalensis (Bloch, 1787) (Northeastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
- Banded sergeant Abudefduf septemfasciatus (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa to Tuamotu Archipelago and Line Islands)[2]
- Scissor-tail sergeant Abudefduf sexfasciatus (Lacepede, 1802) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotus)[2]
- Blackspot sergeant Abudefduf sordidus (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Polynesia)[2]
- Indo-Pacific sergeant Abudefduf vaigiensis (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Marquesas)[2]
- Whitley's sergeant Abudefduf whitleyi Allen and Robertson, 1974 (Great Barrier Reef, Coral Sea and New Caledonia)[2]
- Spiny chromis Acanthochromis polyacanthus (Bleeker, 1855) (Indonesia and the Philippines to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Golden damsel Amblyglyphidodon aureus (Cuvier, 1830) (Eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
- Staghorn damsel Amblyglyphidodon curacao (Bloch, 1787) (Eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
- White-belly damsel Amblyglyphidodon leucogaster (Bleeker, 1847) (Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Black banded demoiselle Amblypomacentrus breviceps (Schlegel and Mueller, 1839)[2]
- Barrier reef anemonefish Amphiprion akindynos (Allen, 1972) (Southwestern Pacific, including Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea, northern New South Wales, New Caledonia and Loyalty Islands)[2]
- Orange-fin anemonefish Amphiprion chrysopterus Cuvier, 1830 (Queensland and New Guinea to Tuamotus and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Clark's anemone fish Amphiprion clarkii (Bennett, 1830) (Persian Gulf to Vanuatu and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Red and black anemonefish Amphiprion melanopus Bleeker, 1852 (Indonesia to the Society and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Clown anemonefish Amphiprion percula (Lacepede, 1802) (Queensland and Melanesia)[2]
- Pink anemonefish Amphiprion perideraion Bleeker, 1855 (Western Pacific including Melanesia and Micronesia ranging north to Japan)[2]
- Big-lip damsel Cheiloprion labiatus (Day, 1877) (Andaman Sea to northern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Midget chromis Chromis acares Randall and Swerdloff, 1973 (Coral Sea to Society islands and Johnston Island)[2]
- Agile chromis Chromis agilis Smith, 1960 (East Africa to the Hawaiian Islands and Pitcairn group)[2]
- Yellow speckled chromis Chromis alpha Randall, 1988 (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to Society Islands)[2]
- Ambon chromis Chromis amboinensis (Bleeker, 1873) (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Samoa and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Yellow chromis Chromis analis (Cuvier, 1830) (Indonesia to Fiji and Mariana Islands)[2]
- Black-axil chromis Chromis atripectoralis Welander and Schultz, 1951 (Seychelles to Tuamotus)[2]
- Dark-fin chromis Chromis atripes Fowler and Bean, 1928 (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Kiribati)[2]
- Stout body chromis Chromis chrysura (Bliss, 1883) (Three isolated antitropical populations at Southwestern Pacific, Japan to Taiwan and Mauritius to Reunion)[2]
- Deep reef chromis Chromis delta Randall, 1988 (Cocos Keeling Islands to Fiji)[2]
- Twin-spot chromis Chromis elerae Fowler and Bean, 1928 (Maldive Islands to Fiji and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Yellow-spotted chromis Chromis flavomaculata Kamohara, 1960 (Antiequatorial distribution with two isolated populations: Lord Howe Island, Coral Sea New Caledonia and Loyalty Islands, and Japan to Taiwan)[2]
- Half and half chromis Chromis iomelas Jordan and Seale, 1906 (Great Barrier Reef and northern New Guinea to Samoa and the Society Islands)[2]
- Scaly chromis Chromis lepidolepis Bleeker, 1877 (Rast Africa and the Red Sea to Fuji and the Line Islands)[2]
- Bicolour chromis Chromis margaritifer Fowler, 1946 (Cocos-Keeling Islands to the Tuamotus)[2]
- Barrier Reef chromis Chromis nitida (Whitley, 1928) (Southern and central Great Barrier Reef, Rare or absent in other parts of the Coral Sea)[2]
- Black-bar chromis Chromis retrofasciata Weber, 1913 (Indonesia and the Philippines to Fiji)[2]
- Ternate chromis Chromis ternatensis (Bleeker, 1856) (East Africa to Fiji and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Vanderbilt's chromis Chromis vanderbilti (Fowler, 1941) (Scattered localities in the western and central Pacific)[2]
- Blue-green chromis Chromis viridis (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotu Archipelago and Line Islands)[2]
- Weber's chromis Chromis weberi Fowler and Bean, 1928 (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Line Islands and Pitcairn group)[2]
- Yellow-axil chromis Chromis xanthochira (Bleeker, 1851) (Indonesia and Philippines to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Pale-tail chromis Chromis xanthura (Bleeker, 1854) (Cocos-Keeling Islands to southeastern Oceania)[2]
- Two-spot demoiselle Chrysiptera biocellata (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (East Africa to Samoa and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Blueline demoiselle Chrysiptera caeruleolineata (Allen, 1973) (Coral Sea to Samoa and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Blue devil Chrysiptera cyanea (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Indonesia to Vanuatu and Palau and north to the Ryukyu Islands. Fairly common on the Great Barrier Reef but absent from other parts of the Coral Sea)[2]
- Yellowfin damsel Chrysiptera flavipinnis (Allen and Robertson, 1974) (Southwestern Pacific including New Guinea, eastern Australia and the Coral Sea)[2]
- Grey damsel Chrysiptera glauca (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa to the Pitcairn group and Line Islands)[2]
- Surge demoiselle Chrysiptera brownriggii (Bennett, 1828) (East Africa to the Marquesas and Line Islands)[2]
- King demoiselle Chrysiptera rex (Snyder, 1909) (Indonesia and the Philippines to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Rolland's demoiselle Chrysiptera rollandi (Whitley, 1961) (Malay Peninsula to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Starck's demoiselle Chrysiptera starcki (Allen, 1973) (Antiequatorial distribution in the western Pacific: New Caledonia to Queensland, and Taiwan to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Talbot's demoiselle Chrysiptera talboti (Allen, 1975) (Malay Peninsula to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- South seas demoiselle Chrysiptera taupou (Jordan and Seale, 1906) (Southwestern Pacific, including Australia, to Fiji and Samoa)[2]
- Threeband demoiselle Chrysiptera tricincta (Allen and Randall, 1974) (Antiequatorial distribution in western Pacific: Coral Sea to Samoa, and Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Onespot demoiselle Chrysiptera unimaculata (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Fiji)[2]
- Humbug dascyllus Dascyllus aruanus (Linnaeus, 1758) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Line Islands and southeastern Polynesia)[2]
- Black tailed dascyllus Dascyllus melanurus Bleeker, 1854 (Malay Peninsula to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Reticulated dascyllus Dascyllus reticulatus (Richardson, 1846) (Cocos-Keeling Islands to Samoa)[2]
- Three-spot dascyllus Dascyllus trimaculatus (Rueppell, 1828) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Line Islands and Pitcairn group)[2]
- Black vent damsel Dischistodus melanotus (Bleeker, 1853) syn. D. notopthalmus (Indonesia and the Philippines to northern Australia and the Solomon Islands)[2]
- White damsel Dischistodus perspicillatus (Cuvier 1830) (Eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
- Honey-head damsel Dischistodus prosopotaenia (Bleeker, 1852) (Andaman Sea to northern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Monarch damsel Dischistodus pseudochrysopoecilus (Allen and Robertson, 1974) (Philippines to northern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Lagoon damsel Hemiglyphidodon plagiometopon (Bleeker, 1852) (Andaman Sea to Queensland and the Solomon Islands, and north to China. Northern Great barrier Reef, apparently absent from the rest of the Coral Sea)[2]
- Fusilier damsel Lepidozygus tapeinosoma (Bleeker, 1856) (East Africa to the Tuamotus, Marquesas and Line Islands)[2]
- Yellowtail damsel Neopomacentrus azysron (Bleeker, 1877) (East Africa to New Caledonia)[2]
- Chinese demoiselle Neopomacentrus bankieri (Richardson, 1846) (South China Sea and Java Sea to Northeastern Australia)[2]
- Regal demoiselle Neopomacentrus cyanomos (Bleeker, 1856) (East Africa to northern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Black demoiselle Neoglyphidodon melas (Cuvier, 1830) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Vanuatu and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Yellowfin damsel Neoglyphidodon nigroris (Cuvier, 1830) (Andaman Sea to Vanuatu, and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Multispine damselfish Neoglyphidodon polyacanthus (Ogilby, 1889) (Southernmost Great Barrier Reef, Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island and New Caledonia)[2]
- Bigscale scalyfin Parma oligolepis Whitley, 1929 (Sydney, New South Wales, to Cairns, Queensland.)[3] (Northern New South Wales to Cape Tribulation on the Cape Yorke Peninsula)[2]
- Banded scalyfin Parma polylepis Günther, 1862 (Bass Point, New South Wales, to Capricorn Group, Queensland. Also Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island and New Caledonia.)[3] (Southernmost Great Barrier Reef, New South Wales, Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island and New Caledonia)[2]
- Dick's damsel Plectroglyphidodon dickii (Lienard, 1839) (East Africa to the Tuamotus and Line Islands)[2]
- Brighteye damsel Plectroglyphidodon imparipennis (Vaillant and Sauvage, 1875) (East Africa to the Pitcairn group and Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Johnston damsel Plectroglyphidodon johnstonianus Fowler, and Ball, 1924 (East Africa to Pitcairn group and Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Jewel damsel Plectroglyphidodon lacrymatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Society Islands and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Whiteband damsel Plectroglyphidodon leucozonus (Bleeker, 1859) (East Africa to Pitcairn group and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Phoenix damsel Plectroglyphidodon phoenixensis (Schultz, 1943) (East Africa to the Tuamotus and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Ambon damsel Pomacentrus amboinensis Bleeker, 1868 (Andaman Sea to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Australian damsel Pomacentrus australis Allen and Robertson, 1973 (Great Barrier Reef south to Sydney)[2]
- Speckled damsel Pomacentrus bankanensis Bleeker, 1853 (Christmas Island, (Indian Ocean) to Fiji and north to Japan)[2]
- Charcoal damsel Pomacentrus brachialis Cuvier, 1830 (Western Pacific to Fiji and Samoa)[2]
- Whitetail damsel Pomacentrus chrysurus Cuvier 1830 syn. P.rhodonotus, P. flavicauda (Maldive Islands to the Coral Sea. Melanesia and Micronesia)[2]
- Neon damsel Pomacentrus coelestis Jordan and Starks, 1901 (Cocos-Leeling Islands to Tuamotus)[2]
- Bluespot damsel Pomacentrus grammorhynchus Fowler, 1918 (Indonesia and Philippines to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Imitator damsel Pomacentrus imitator (Whitley, 1964) (Rare on Great Barrier Reef, but common in other parts of the Coral sea. Also New Caledonia, Rotuma and Fiji)[2]
- Scaly damsel Pomacentrus lepidogenys Fowler and Ball, 1928 (Malay Peninsula to Fiji)[2]
- Lemon damsel Pomacentrus moluccensis Bleeker, 1853 syn. P. popei (Andaman Sea to Fiji and north to Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Sandy damsel Pomacentrus nagasakiensis Tanaka, 1917 syn. P. arenarius (Indonesia to Coral Sea and Vanuatu, north to Japan)[2]
- Blackmargined damsel Pomacentrus nigromarginatus Allen, 1973 (Indonesia to Coral Sea and Solomon Islands, north to Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Blue damsel, Pomacentrus pavo (Bloch, 1787) (East Africa to the Tuamotus and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Philippine damsel Pomacentrus philippinus Evermann and Seale, 1907 (Maldive Islands to Fiji)[2]
- Reid's damsel Pomacentrus reidi Fowler and Bean, 1928 (Indonesia and Philippines to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Threespot damsel Pomacentrus tripunctatus Cuvier, 1830 (Sri Lanka to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Princess damsel Pomacentrus vaiuli Jordan and Seale, 1906 (Molucca Islands to Samoa and north to Japan)[2]
- Ward's damsel Pomacentrus wardi Whitley, 1927 (Great Barrier Reef and eastern Australian coast south to Sydney)[2]
- Richardson's reef-damsel Pomachromis richardsoni (Snyder, 1909) (Mauritius to Fiji)[2]
- Spine cheek anemonefish Premnas biaculeatus (Bloch, 1790) (Malay peninsula to northeastern Australia and Melanesia)[2]
- Gulf damsel Pristotis obtusirostris (Guenther, 1862) syn. P. jerdoni (Persian Gulf and Red Sea to Australia, north to Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Whitebar gregory Stegastes albifasciatus (Schlegel and Mueller, 1839) (East Africa to the Tuamotus and Line Islands)[2]
- Australian gregory Stegastes apicalis (De Vis, 1885) (Great Barrier Reef and eastern coast of Australia to Sydney)[2]
- Pacific gregory Stegastes fasciolatus (Ogilby, 1889) syn. S. jenkinsi (East Africa to Hawaiian Islands and Easter Island)[2]
- Coral Sea Gregory Stegastes gascoynei (Whitley, 1964) (Coral Sea and northern Tasman Sea)[2]
- Bluntsnout gregory Stegastes lividus (Forster in Bloch and Schneider, 1801)[2]
- Dusky gregory Stegastes nigricans (Lecepede, 1802) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotus, Marquesas and Line Islands)[2]
Family Cirrhitidae – Hawkfishes
- Twinspot hawkfish Amblycirrhitus bimacula Jenkins, 1903 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Threadfin hawkfish, blotched hawkfish Cirrhitichthys aprinus (Cuvier, 1829) (Tropical Australia south to Houtman Abrolhos, Western Australia, and to Merimbula, New South Wales. Also widespread in the Indo-West Pacific region.)[3] (Western Pacific)[2]
- Dwarf hawkfish Cirrhitichthys falco Randall, 1963 (Maldives through western Pacific to Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands and Samoa)[2]
- Pixy hawkfish Cirrhitichthys oxycephalus (Bleeker, 1855) (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Stocky hawkfish Cirrhitus pinnulatus (Schneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Swallowtail hawkfish Cyprinocirrhites polyactis (Bleeker, 1875) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Flame hawkfish Neocirrhites armatus Castelnau, 1873 (Islands of Oceania and western Pacific)[2]
- Longnose hawkfish Oxycirrhites typus Bleeker, 1857 (Indo-Pacific and tropical Eastern Pacific)[2]
- Arc-eye hawkfish Paracirrhites arcatus (Cuvier, 1829) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blackside hawkfish Paracirrhites forsteri (Schneider, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Halfspotted hawkfish Paracirrhites hemistictus (Guenther, 1874) syn. P. polystictus (Islands of Oceania, Great Barrier Reef and Christmas and Cocos-Keeling Islands)[2]
Family Sphyraenidae – Pikes, barracudas
- Great barracuda Sphyraena barracuda (Walbaum, 1792) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Hawaiian Islands and the Tuamotu archipelago)[2]
- Yellowtail barracuda Sphyraena flavicauda Rueppell, 1838 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bigeye barracuda Sphyraena forsteri Cuvier, 1829 (East Africa to the Society Islands)[2]
- Heller's barracuda Sphyraena helleri Jenkins, 1901 (Western Pacific including the Coral Sea to Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Pickhandle barracuda Sphyraena jello Cuvier, 1829 (East Africa and the Red Sea to western Pacific)[2]
- Chevron barracuda Sphyraena qenie Klunzinger, 1870 (East Africa and the Red Sea to western Pacific)[2]
Family Polynemidae - Threadfins
- Six-fingered threadfin Polydactylus sexfilis (Valenciennes, 1831) (India to Hawaiian Islands and Tuamotu archipelago)[2]
Family Labridae - Wrasses
- Bluespotted wrasse Anampses caeruleopunctatus Rueppell, 1829 syn. A. diadematus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Feminine wrasse Anampses femininus Randall, 1972 (Southern subtropical Pacific from Easter Island to New Caledonia and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Geographic wrasse Anampses geographicus Valenciennes, 1840 syn. A. pterophthalmus (Western Australia and western Pacific east to the Caroline Islands and Fiji)[2]
- Spotted wrasse Anampses meleagrides Valenciennes, 1840 syn. A. amboinensis(East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the Caroline Islands)[2]
- New Guinea wrasse Anampses neoguinaicus Bleeker, 1878 (Western Pacific, east to Fiji)[2]
- Yellowbreasted wrasse Anampses twistii Bleeker, 1856 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Lyretail hogfish Bodianus anthioides (Bennett, 1830) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Axilspot hogfish Bodianus axillaris (Bennett, 1831) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Twospot hogfish Bodianus bimaculatus Allen, 1973 (Mauritius and the Maldives to the western Pacific)[2]
- Diana’s pigfish, Diana's hogfish Bodianus diana (Lacépède, 1801) syn. Lepidapolois aldabraensis (Tropical Australia south to Montague Island, New South Wales. Also widespread in the Indo-Pacific region.)[3] (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Blackfin hogfish Bodianus loxozonus (Snyder, 1908) (Western Pacific to French Polynesia)[2]
- Splitlevel hogfish Bodianus mesothorax (Bloch and Scneider, 1801) (Western Pacific to Fiji)[2]
- Goldspot hogfish Bodianus perditio (Quoy and Gaimard, 1834) (Antiequatorial: Southern Africa to islands of southern Oceania, and Taiwan to southern Japan)[2]
- Floral Maori wrasse Cheilinus chlorourus (Bloch, 1791) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Redbreasted Maori wrasse Cheilinus fasciatus (Bloch, 1791) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and Micronesia)[2]
- Snooty Maori wrasse Cheilinus oxycephalus Bleeker, 1853 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tripletail Maori wrasse Cheilinus trilobatus Lacepede, 1801 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Humphead Maori wrasse Cheilinus undulatus Rueppell, 1835 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Cigar wrasse Cheilio inermis (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Anchor tuskfish Choerodon anchorago (Bloch, 1791) (Sri Lanka to Western Pacific)[2]
- Grass Ttuskfish Choerodon cephalotes (Castelnau, 1975) (Indonesia to Queensland)[2]
- Blue tuskfish Choerodon cyanodus (Richardson, 1843) syn. Choerops albigena (Western Australia to Queensland)[2]
- Harlequin tuskfish Choerodon fasciatus (Guenther, 1867) (Antiequatorial; Taiwan to Ryukyu Islands and Queensland to New Caledonia)[2]
- Graphic tuskfish Choerodon graphicus (De Vis, 1885) syn. C. transversalis (Queensland to New Caledonia)[2]
- Blackspot tuskfish Choerodon schoenleinii (Valenciennes, 1839) (Western Australia to western Pacific)[2]
- Venus tuskfish Choerodon venustus (De Vis, 1884) (Northern New South Wales to Queensland)[2]
- Exquisite wrasse Cirrhilabrus exquisitus Smith, 1957 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Magenta streaked wrasse Cirrhilabrus laboutei Randall and Lubbock, 1982 (Great Barrier Reef to New Caledonia and the Loyalty Islands)[2]
- Purplelined wrasse Cirrhilabrus lineatus Randall and Lubbock, 1982 (Great Barrier Reef to New Caledonia and the Loyalty Islands)[2]
- Dotted wrasse Cirrhilabrus punctatus Randall and Kuiter, 1989 (New South Wales to southern New Guinea, and east to Fiji)[2]
- Scott's wrasse Cirrhilabrus scottorum Randall and Pyle, 1989 (South Pacific from the Great Barrier Reef to the Pitcairn group)[2]
- Goldlined coris Coris aurilineata Randall and Kuiter, 1982 (New South Wales to the southern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Clown coris Coris aygula Lacepede, 1801 syn. Coris angulata (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Pale-barred coris Coris dorsomacula Fowler, 1908 syn. Coris dorsomaculata ((as C. dorsomaculata) Western Pacific)[2]
- Yellowtail coris Coris gaimard (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Central and western Pacific)[2]
- Blackspot coris Coris pictoides Randall and Kuiter, 1982 (Known from New South Wales, Great Barrier Reef, Western Australia, Indonesia and the Philippines)[2]
- Batu coris Coris batuensis (Bleeker, 1857) (Western Indian Ocean to the Marshall Islands and Tonga)[2]
- Knifefish Cymolutes praetextatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1834) (Indo-Pacific except Hawaii)[2]
- Collared knifefish Cymolutes torquatus Valenciennes, 1840 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Yellowtail tubelip Diproctacanthus xanthurus (Bleeker, 1856) (Philippines, Palau, Indonesia, New Guinea and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Slingjaw wrasse Epibulus insidiator (Pallas, 1770) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bird wrasse Gomphosus varius Lacepede, 1801 syn. G. tricolor (Oceania and the western Pacific)[2]
- Biocellate wrasse Halichoeres biocellatus Schultz, 1960 (Western Pacific to Samoa and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Pastel-green wrasse Halichoeres chloropterus (Bloch, 1791) syn. H. gymnocephalus (Philippines to Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Golden wrasse Halichoeres chrysus Randall, 1981 (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean), Western Pacific and Micronesia)[2]
- Goldstripe wrasse Halichoeres hartzfeldii (Bleeker, 1852) (Red sea, Persian Gulf and western Indian Ocean to the Western Pacific)[2]
- Checkerboard wrasse Halichoeres hortulanus (Lacepede, 1801) syn. H. centiquadrus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Pink-belly wrasse Halichoeres margaritaceus (Valenciennes, 1839) (Western and central Pacific)[2]
- Dusky wrasse Halichoeres marginatus Rueppell, 1835 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tailspot wrasse Halichoeres melanurus (Bleeker, 1851) (Western Pacific east to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Ocellated wrasse Halichoeres melasmapomus Randall, 1980 (Islands of Oceania except Hawaii and Easter Island, and from the Philippines to the Red Sea. Also recorded from Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) and the Cocos-Keeling Islands)[2]
- Circle-cheek wrasse Halichoeres miniatus (Valenciennes, 1839) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Nebulous wrasse Halichoeres nebulosus (Valenciennes, 1839) (Red Sea and tropical and subtropical Indian Ocean to the western Pacific)[2]
- Ornate wrasse Halichoeres ornatissimus (Garrett, 1863) (Western Pacific and islands of Oceania)[2]
- Twotone wrasse Halichoeres prosopeion (Bleeker, 1853) (Western Pacific to Samoa, and Palau)[2]
- Zigzag wrasse Halichoeres scapularis (Bennett, 1831) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the western Pacific)[2]
- Threespot wrasse Halichoeres trimaculatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1834) (Western Pacific and Islands of Oceania, and Christmas Island (Indian Ocean))[2]
- Barred thicklip Hemigymnus fasciatus (Bloch, 1792) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Blackeye thicklip Hemigymnus melapterus (Bloch, 1791) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Ringwrasse Hologymnosus annulatus (Lacepede, 1801) syn. H. semidiscus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Pastel ringwrasse Hologymnosus doliatus (Lacepede, 1801) (East Africa to Samoa and the Line Islands)[2]
- Sidespot ringwrasse Hologymnosus longipes (Guenther, 1862) (Southern Great Barrier Reef, New Caledonia, Loyalty Islands and Vanuatu)[2]
- Whitepatch razorfish Iniistius aneitensis (Günther, 1862) syn. Xyrichthys aneitensis ((as X. aneitensis) Western and central Pacific)[2]
- Peacock razorfish Iniistius pavo (Valenciennes, 1840) syn. Xyrichtys pavo ((as X. pavo) Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tubelip wrasse Labrichthys unilineatus (Guichenot, 1847) syn. L. cyanotaenia (East Africa to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Bicolor cleaner wrasse Labroides bicolor Fowler and Bean, 1928 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Striped cleaner wrasse Labroides dimidiatus (Valenciennes, 1839) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Breastspot cleaner wrasse Labroides pectoralis Randall and Springer, 1975 (Indonesia and the Geat Barrier Reef to Micronesia and New Caledonia. Also Christmas Island (Indian Ocean))[2]
- Southern tubelip Labropsis australis Randall, 1981 (Great Barrier Reef and Solomon Islands to Fiji and Samoa)[2]
- Yellowback tubelip Labropsis xanthonota Randall, 1981 (East Africa to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Shoulderspot wrasse Leptojulis cyanopleura (Bleeker, 1853) (Gulf of Oman to Philippines and Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Choat's wrasse Macropharyngodon choati Randall, 1978 (Southern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Kuiter's wrasse Macropharyngodon kuiteri Randall, 1978 (New South Wales and southern Great Barrier Reef to New Caledonia)[2]
- Blackspotted wrasse Macropharyngodon meleagris (Valenciennes, 1839) syn. Leptojulis pardalis (Cocos-Keeling Islands to western Pacific and the Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Black wrasse Macropharyngodon negrosensis Herre, 1932 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Rockmover wrasse Novaculichthys taeniourus (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Twospot Maori wrasse Oxycheilinus bimaculatis (Valenciennes, 1840) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Cheeklined Maori wrasse Oxycheilinus digramma (Lacepede, 1801) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Ringtail Maori wrasse Oxycheilinus unifasciatus (Streets, 1877) (Central and western Pacific, Hawaii)[2]
- Disappearing wrasse Pseudocheilinus evanidus Jordan and Evermann, 1903 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Sixstripe wrasse Pseudocheilinus hexataenia (Bleeker, 1857) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Eightstripe wrasse Pseudocheilinus octotaenia Jenkins, 1900 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Redspot wrasse Pseudocoris yamashiroi (Schmidt, 1930) (Western Pacific to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Chiseltooth wrasse Pseudodax moluccanus (Valenciennes, 1839) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Smalltail wrasse Pseudojuloides cerasinus (Snyder, 1904) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Gunther’s wrasse Pseudolabrus guentheri Bleeker, 1862 (Montague Island, New South Wales, to Whitsunday Group, Queensland.)[3] (New South Wales to southern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Redstriped wrasse Pteragogus enneacanthus (Bleeker, 1853) syn. P. amboinensis (Indonesia to the Coral Sea)[2]
- Cryptic wrasse Pteragogus cryptus Randall, 1981 (Red Sea and western Pacific to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Bluelined wrasse Stethojulis bandanensis (Bleeker, 1851) syn. S rubromaculata, S. linearis (Western Pacific and islands of Oceania and the eastern Pacific except Hawaii)[2]
- Cutribbon wrasse Stethojulis interrupta (Bleeker, 1851) syn. S. kalosoma (East Africa to Samoa and the Mariana Islands)[2]
- Stripebelly wrasse Stethojulis strigiventer (Bennett, 1832) syn. S. renardi (East Africa to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Three-ribbon wrasse Stethojulis trilineata (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) syn. S. phekadopleura (Maldives to western Pacific)[2]
- Slender wrasse Suezichthys gracilis (Steindachner and Doederlein, 1887) (Antitropical. Known from southern Japan, Korea and Taiwan in the north and New South Wales and the southern Great Barrier Reef to New Caledonia in the south)[2]
- Bluntheaded wrasse Thalassoma amblycephalum (Bleeker, 1856) syn. T. melanochir(Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Sixbar wrasse Thalassoma hardwicke (Bennett, 1828) syn. T. schwanefeldii (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Jansen's wrasse Thalassoma jansenii (Bleeker, 1856) (Maldives to the western Pacific and Fiji)[2]
- Moon wrasse Thalassoma lunare (Linnaeus 1758) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Sunset wrasse Thalassoma lutescens (Lay and Bennett, 1839) (Indo-Pacific and Clipperton Island in the eastern Pacific, but apparently absent from the Indo-Malayan region and southern Indian Ocean)[2]
- Surge wrasse Thalassoma purpureum (Forsskal, 1775) syn. T. umbrostygma (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Fivestripe wrasse Thalassoma quinquevittatum (Lay and Bennett, 1839) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Ladder wrasse Thalassoma trilobatum (Lacepede, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Whitebanded sharpnose wrasse Wetmorella albofasciata (Schultz and Marshall, 1954) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Sharpnose wrasse Wetmorella nigropinnata (Seale, 1901) syn. W. philippinus, W. ocellata, W. triocellata (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Fivefinger razorfish Xyrichthys pentadactylus (Linnaeus, 1758) (East Africa and the Red Sea to the western Pacific)[2]
Family Scaridae - Parrotfishes
- Bumphead parrotfish Bolbometopon muricatum (Valenciennes, 1840) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the Line Islands in the central Pacific)[2]
- Stareye parrotfish Calotomus carolinus (Valenciennes, 1840) syn. C. sandwicensis (Indo-Pacific and tropical east Pacific)[2]
- Raggedtooth parrotfish Calotomus spinidens (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (East Africa to Tonga and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Bicolour parrotfish Cetoscarus bicolor (Rueppell, 1829) syn. Scarus pulchellus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bleeker's parrotfish Chlorurus bleekeri (de Beaufort, 1940)[24] syn. S. bleekeri ((as S. bleekeri) Western Pacific to Fiji and the islands of Micronesia)[2]
- Reefcrest parrotfish Chlorurus frontalis (Valenciennes, 1840) (Western Pacific to Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Redtail parrotfish Chlorurus japanensis (Bloch, 1789) syn. Scarus pyrrhurus (Western Pacific to Samoa)[2]
- Steephead parrotfish Chlorurus microrhinos (Bleeker, 1854) (Western Pacific and Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Bullethead parrotfish Chlorurus sordidus (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Pacific longnose parrotfish Hipposcarus longiceps (Valenciennes. 1840) (Western Pacific to French Polynesia)[2]
- Slender parrotfish, marbled parrotfish Leptoscarus vaigiensis (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Scattered localities in the Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Minifin parrotfish Scarus altipinnis (Steindachner, 1879) syn. S. brevifilis (Great Barrier Reef and Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Chameleon parrotfish Scarus chameleon Choat and Randall, 1986 (Western Australia to western Pacific and Fiji)[2]
- Bridled parrotfish Scarus frenatus (Lacepede, 1802) syn. S. sexvittatus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bluebarred parrotfish Scarus ghobban Forsskal, 1775 (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Globehead parrotfish Scarus globiceps Valenciennes, 1840 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Highfin parrotfish Scarus longipinnis Randall and Choat, 1980 (Southern subtropical Pacific from the Great Barrier Reef to Pitcairn Islands)[2]
- Swarthy parrotfish Scarus niger Forsskal, 1775 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Egghead parrotfish Scarus oviceps Valenciennes, 1840 (Western Pacific and Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Whitespot parrotfish, Palenose parrotfish Scarus psittacus Forsskål, 1775[25] syn. Scarus forsteri (Bleeker, 1861) ((as S. forsteri) Western Pacific to Micronesia and Pitcairn Group)[2] ((as S. psittacus) Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Surf parrotfish Scarus rivulatus Valenciennes, 1840 syn. S. fasciatus (Western Pacific to the Caroline Islands and New Caledonia)[2]
- Ember parrotfish Scarus rubroviolaceus Bleeker, 1847 (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Schlegel's parrotfish Scarus schlegeli (Bleeker, 1861) (Western Pacific and Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Greensnout parrotfish Scarus spinus (Kner, 1868) (Western Pacific to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
Family Opistognathidae - Jawfishes, smilers
- Papuan jawfish Opistognathus papuensis (Bleeker, 1868) (Southern New Guinea and northern Queensland)[2]
- Coral sea jawfish Opistognathus sp. (Known only from Lizard Island and Lihou Reef in the Coral Sea)[2]
Family Uranoscopidae – Stargazers
- Whitemargin stargazer Uranoscopus sulphureus Valenciennes, 1831 syn U. fuscomaculatus (Tonga, Fiji, Samoa, Indonesia and the Red Sea)[2]
Family Trichonotidae - Sand-divers
- Spotted sand-diver Trichonotus setiger (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) (Persian Gulf to Queensland and Melanesia)[2]
- Threadfin sand-diver Trichonotus sp. (Coral sea, Marians and Marshall Islands)[2]
Family Creediidae - Sand burrowers
- Sand dart Chalixodytes chameleontoculis Smith, 1957 [2]
- Barred sand burrower Limnichthys fasciatus Waite, 1904 (Western Pacific from Japan to Australia and the Kermadec Islands)[2]
- Limnichthys nitidus Smith, 1958[26] syn. Limnichthys donaldsoni (as L. donaldsoni)[2]
Family Pinguipedidae – Grubfishes, weevers, sandperches
- Latticed sandperch Parapercis clathrata Ogilby, 1911 (Western Pacific to Samoa and the islands of Micronesia)[2]
- Sharpnose sandperch Parapercis cylindrica (Bloch, 1797) (Western Pacific to Fiji and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Speckled sandperch Parapercis hexophtalma (Cuvier, 1829) syn, P. polyophtalma (East Africa and the Red Sea to the western Pacific and Fiji)[2]
- Spotted sandperch Parapercis millepunctata (Guenther, 1860) (Maldives to the islands of Oceania)[2]
- Redbarred sandperch Parapercis multiplicata Randall, 1984 (Ryukyu Islands, Indonesia, New Caledonia, Western Australia and the Coral Sea)[2]
- Barred sandperch Parapercis nebulosa (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) (Western Australia to New South Wales)[2]
- Redspotted sandperch Parapercis schauinslandii (Steindachner, 1900) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- U-mark sandperch Parapercis snyderi Jordan and Starcks, 1905 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Yellowbar sandperch Parapercis xanthozona (Bleeker, 1849) (East Africa to western Pacific and Fiji)[2]
Family Tripterygiidae – Triplefins, threefins
- Highfin triplefin Enneapterygius tutuilae Jordan and Seale, 1906 syn. E. altipinnis (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Saddled triplefin Enneapterygius atrogulare (Guenther, 18??) syn. E. annulatus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Tailbar triplefin Enneapterygius sp. (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Neon triplefin Helcogramma striatum Hansen, 1986 (Sri-lanka to western Pacific and Line Islands)[2]
- Red-finned triplefin Ucla xenogrammus Holleman, 1993 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bigmouth triplefin Ucla sp. (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Family Blenniidae – Blennies
Tribe Nemophini -Sabretooth blennies, fangblennies
- Lance blenny Aspidontus dussumieri (Valenciennes, 1836) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Mimic blenny Aspidontus taeniatus Quoy and Gaimard, 1834 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Yellowtail fangblenny Meiacanthus atrodorsalis (Guenther, 1877) (Western Australia and western Pacific to Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Doublepore fangblenny Meiacanthus ditrema Smith-Vaniz, 1976 (Western Australia and western Pacific to Samoa and Tonga)[2]
- Striped fangblenny Meiacanthus grammistes (Valenciennes, 1836) (Western Australia and western Pacific to Caroline Islands and Santa Cruz Islands)[2]
- Lined fangblenny Meiacanthus lineatus (De Vis, 1884) (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Yellow fangblenny Meiacanthus luteus Smith-Vaniz, 1987 (Western Australia, 20°S to Queensland, 19°S)[2]
Subfamily Blenniinae[27]
- Black blenny Enchelyurus ater (Guenther, 1877) (Southern Oceania from the Coral Sea to the Tuamotu Archipelago, but not the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Krauss's blenny Enchelyurus kraussii (Klunzinger, 171) (Comores, Seychelles and Red Sea to the western Pacific and Mariana Islands)[2]
- Oyster blenny Omobranchus anolius (Valenciennes, 1836) (Spencer gulf, South Australia to the Queensland coast of the Gulf of Carpentaria)[2]
- Hepburn's blenny Parenchelyurus hepburni (Snyder, 1908) (Western Pacific to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Deceiver fangblenny Petroscirtes fallax Smith-Vaniz, 1976 (Great Barrier Reef south of 17°S to New South Wales)[2]
- Wolf fangblenny, Brown sabretooth blenny Petroscirtes lupus (De Vis, 1886) (Queensland, New South Wales, Lord Howe Island and New Caledonia)[2] (Merimbula, New South Wales, to southern Queensland. Also New Caledonia.)[3]
- Highfin fangblenny Petroscirtes mitratus Rueppell, 1830 (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa, Tonga and the islands of Micronesia)[2]
- Variable fangblenny Petroscirtes variabilis Cantor, 1850 (Sri Lanka to the western Pacific)[2]
- Smooth fangblenny Petroscirtes xestus Jordan and Seale, 1906 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bicolour fangblenny Plagiotremus laudandus (Whitley, 1961) (Western Australia and western Pacific to Samoa and the islands of Micronesia)[2]
- Bluestriped fangblenny, blue-lined sabretooth blenny Plagiotremus rhinorhynchos (Bleeker, 1852) (Indo-Pacific except Hawaii)[2] (Tropical Australia south to Walpole, Western Australia, and to Merimbula, New South Wales. Also widespread in the Indo-West Pacific region.)[3]
- Piano fangblenny, hit and run blenny, yellow sabretooth blenny Plagiotremus tapeinosoma (Bleeker, 1857) (Tropical Australia south to Rottnest Island, Western Australia, and to Merimbula, New South Wales. Also widespread in the Indo-West Pacific region.)[3] (Indo-Pacific except Hawaii)[2]
- Hairtail blenny Xiphasia setifer Swainson, 1839 (East Africa and the Red Sea to western Pacific including New Caledonia and Vanuatu)[2]
Subfamily Salariinae[28]
- Brown coral blenny Atrosalarias fuscus (Rueppell, 1835) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- White-dotted blenny Cirripectes alboapicalis (Ogilby, 1899) syn. C. patuki (Southern subtropical Pacific from the southern Great Barrier Reef and Lord Howe Island to Easter Island)[2]
- Chestnut blenny Cirripectes castaneus (Valenciennes, 1836) syn. C. sebae (East Africa and the Red Sea to Tonga and the Caroline Islands)[2]
- Lady Musgrave blenny Cirripectes chelomatus Williams and Maugé, 1983 (Great Barrier Reef and Lord Howe Island to Tonga and Fiji)[2]
- Filamentous blenny Cirripectes filamentosus (Alleyne and Macleay, 1877) (Western Indian Ocean including Persian Gulf and southern Red Sea to western Pacific)[2]
- Barred blenny Cirripectes polyzona (Bleeker, 1868) (East Africa to Samoa and the Line Islands)[2]
- Zebra blenny Cirripectes quagga (Fowler and Ball, 1924) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Reticulated blenny Cirripectes stigmaticus Strasburg and Schultz, 1953[29] (East Africa to Samoa and islands of Micronesia)[2]
- Triplespot blenny Crossosalarias macrospilus Smith-Vaniz and Springer, 1971 (Western Pacific to Tonga)[2]
- Fourline blenny Ecsenius aequalis Springer, 1988 (Great Barrier Reef, Coral Sea, Trobriand Islands, Papua New Guinea)[2]
- Australian blenny Ecsenius australianus Springer, 1988 (Northern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Bicolour blenny Ecsenius bicolor (Day, 1888) (Maldives to the islands of Micronesia and Samoa)[2]
- Queensland blenny Ecsenius mandibularis McCulloch, 1923 (Queensland from Cape Yorke Peninsula at 12°S to the Bunger Group, southern Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Midas blenny Ecsenius midas Starck, 1969 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Great Barrier Reef blenny Ecsenius stictus Springer, 1988 (Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Tiger blenny Ecsenius tigris Springer, 1988 (Osprey, Bougainville and Holmes reefs in the western Coral Sea)[2]
- Wavyline rockskipper Entomacrodus decussatus (Bleeker, 1858) (Western Australia to western and central Pacific)[2]
- Blackspotted rockskipper Entomacrodus striatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1836) syn. E. plurifilis (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Shortbodied blenny Exallias brevis (Kner, 1868) ((Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Goldspotted rockskipper Blenniella chrysospilos (Bleeker, 1857) syn. Salarias coronatus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Dussumier's rockskipper Istiblennius dussumieri (Valenciennes. 1836) (East Africa to western Pacific)[2]
- Rippled rockskipper Istiblennius edentulus (Forster, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Lined rockskipper Istiblennius lineatus (Valenciennes, 1836) (Maldive to Pitcairn group)[2]
- Peacock rockskipper Istiblennius meleagris (Valenciennes, 1836) (Western Australia to Queensland)[2]
- Bullethead rockskipper Blenniella paula (Bryan and Herre, 1903) (Great Barrier Reef and the Islands of Oceania except Hawaii and Easter Island)[2]
- Throatspot blenny Nannosalarias nativitatis (Regan, 1909) (Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) to western Pacific and Tonga)[2]
- Barred-chin blenny Rhabdoblennius nitidus (Günther, 1861) syn. Rhabdoblennius ellipes ((As R. ellipes)Great Barrier Reef and islands of Oceania)[2]
- Jewelled blenny Salarias fasciatus (Bloch, 1786) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the islands of Micronesia)[2]
- Fringelip blenny Salarias sinuosus Snyder, 1908 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Talbot's blenny Stanulus talboti Springer, 1968 (Great Barrier Reef, Lord Howe Island, Ryukyu Islands and Ogasawara Islands)[2]
Family Callionymidae - Dragonets
- Goram dragonet Diplogrammus goramensis (Bleeker, 1858) (Western Pacific from China to Fiji)[2]
- Morrison's dragonet Synchiropus morrisoni Schultz, 1960 (Japan to Australia and east to the Marshall Islands and Fiji)[2]
- Ocellated dragonet Synchiropus ocellatus (Pallas, 1770) (Japan to Australia and east to Pitcairn Island)[2]
- Mandarinfish Synchiropus splendidus (Herre, 1927) (Western Pacific from the Ryukyu Islands to Australia)[2]
Family Eleotridae - Gudgeons, sleepers
- Tailface sleeper Calumia godeffroyi (Guenther, 1877) (East Africa to the Society Islands)[2]
Family Xenisthmidae - Wrigglers
- Bullseye wriggler Xenisthmus polyzonatus (Red Sea to Samoa and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
Family Gobiidae – Gobies
- Spotted shrimp goby Amblyeleotris guttata (Fowler, 1938) (East Indies to Samoa and north to the Ryukyu Islands)[2]
- Blotchy shrimp goby Amblyeleotris periophthalma (Bleeker, 1853) (Western Pacific eastwards to Samoa)[2]
- Steinitz's shrimp goby Amblyeleotris steinitzi (Klausewitz, 1974) (Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Wheeler's shrimp goby Amblyeleotris wheeleri (Polunin and Lubbock, 1977) (East Africa to Australia and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Orange-striped goby Amblygobius decussatus (Bleeker, 1855) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Banded goby Amblygobius phalaena (Valenciennes, 1837) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Old glory Amblygobius rainfordi (Whitley, 1940) (Queensland and Coral Sea to Philippines)[2]
- Sphynx goby Amblygobius sphynx (Valenciennes, 1837) (East Africa to Western Pacific)[2]
- Starry goby Asteropteryx semipunctata Rueppell, 1830[30] (East Africa and the Red Sea to Hawaiian Islands and Tuamotus)[2]
- Common goby Bathygobius fuscus (Rueppell, 1830) (East Africa and Red Sea to Tuamotus and Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Cocos goby Bathygobius cocosensis (Bleeker, 1854) (East Africa to the Hawaiian Islands and Tuamotu Archipelago)[2]
- Large whip goby Bryaninops amplus Larson, 1985 (Madagascar and the Seychelles to the Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Erythrops goby Bryaninops erythrops (Jordan and Seale, 1906) (Chagos Archipelago to Marhall Islands and Samoa)[2]
- Redeye goby Bryaninops natans Larson, 18985 (Red Sea to Micronesia and Cook Islands)[2]
- Black coral goby Bryaninops tigris Larson, 1985 (Chagos Archipelago to Hawaiian Islands)[2]
- Whip goby Bryaninops yongei (Davis and Cohen, 1968) (Australia to Hawaiian Islands and Rapa)[2]
- Ostrich goby Callogobius maculipinnis (Fowler, 1918) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Tripleband goby Callogobius sclateri (Steindachner, 1880) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Yellow shrimp goby Cryptocentrus cinctus (Herre, 1936) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Y-bar shrimp goby Cryptocentrus fasciatus (Playfair and Guenther, 1867) (East Africa to Melanesia and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Saddled shrimp goby Cryptocentrus leucostictus (Guenther, 1871) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Target shrimp goby Cryptocentrus strigilliceps (Jordan and Seale, 1906) (East Africa to the Marshall Islands and Samoa)[2]
- Spotfin shrimp goby Ctenogobiops pomastictus Lubbock and Polunin, 1977 (Queensland to Ryukyo Islands, east to Mariana Islands)[2]
- Masted shrimp goby Ctenogobiops tangaroai Lubbock and Polunin, 1977 (Australia to Samoa)[2]
- Spikefin goby Discordipinna griessingeri Hoese and Fourmanoir, 1978 (Red Sea to the Marquesas)
- Doublebar goby Eviota bifasciata Lachner and Karnella, 1989 (Philippines and Indonesia to northern Australia)[2]
- Blackbelly goby Eviota nigriventris Giltay, 1933 (Philippines to Melanesia and eastern Australia)[2]
- Beautiful goby Exyrias belissimus (Smith, 1959) (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Exyrias puntang Bleeker (Queensland)[2]
- Novice goby Fusigobius neophytus (Günther, 1877)[31] syn. Coryphopterus neophytus ((as C. neophytus)East Africa to the Tuamotus)[2]
- Blotched sand goby Coryphopterus sp. (Western Pacific)[2]
- Shoulderspot goby Gnatholepis cauerensis (Bleeker, 1853)[32] syn. Gnatholepis scapulostigma Herre, 1953 ((as G. scapulostigma) Eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
- Fourbar goby Gobiodon citrinus (Rueppell, 1838) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Broad-barred goby Gobiodon histrio (Valenciennes, 1837) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Small-eyed goby Gobiodon micropus (Guenther, 1861) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Okinawa goby Gobiodon okinawae (Sawada, Arai and Abe, 1973) (Western Pacific, Japan to Australia)[2]
- Decorated goby Istigobius decoratus (Herre, 1927) (East Africa and the Red Sea to Samoa)[2]
- Orange-spotted goby Istigobius rigilius (Herre, 1953) (Molucca and Philippine Islands to Australia and east to Fiji and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Whitecap goby Lotilia graciliosa Klausewitz, 1960 (Red Sea to Southern Japan, Marshall Islands and Fiji)[2]
- Wilbur's goby Macrodontogobius wilburi Herre, 1926 (Seychelles to New Caledonia and Line Islands)[2]
- Spinecheek goby Oplopomus oplopomus (Valenciennes, 1837) (East Africa to Society Islands)[2]
- Redhead goby Paragobiodon echinocephalus Rueppell, 1828 (East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotus and Marshall Islands)[2]
- Yellowskin goby Paragobiodon xanthosoma (Bleeker, 1852) (Chagos Archipelago to Samoa)[2]
- Silverlined mudskipper Periophthalmus argentilineatus (Valenciennes, 1837) (Southern Red Sea south to Natal and east to the Marianas and Samoa)[2]
- Coral goby Pleurosicya micheli Fourmanoir, 1971 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Girdled goby Priolepis cincta (Regan, 1908) syn. P. naraharae (East Africa to southeastern Polynesia)[2]
- Trinspot goby Signigobius biocellatus Hoese and Allen, 1977 (Philippines, Indonesia and Palau Islands to Melanesia and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Yellownose shrimp goby Stonogobiops xanthorhinica Hoese and Randall, 1982 Western edge of Pacific from Japan to the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Orange-red goby Trimma okinawae (Aoyagi, 1949) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Stripehead goby Trimma striatum (Herre, 1945) (Philippines to Australia)[2]
- Orange-spotted goby Trimma sp.1 (in Randall 1997) (DFH-9 - Hoese) (Western Pacific)[2]
- Benjamin's goby Trimma benjamini Winterbottom, 1996 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Twostripe goby Valenciennea helsdingenii (Bleeker, 1858) (East Africa to the western Pacific)[2]
- Long finned goby Valenciennea longipinnis (Lay and Bennett, 1839) (Eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific)[2]
- Striped goby Valenciennea muralis (Valenciennes, 1837) (Indonesia to Melanesia and northern Australia)[2]
- Orange-dashed goby Valenciennea puellaris (Tomiyama, 1956) (Red Sea to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Sixspot goby Valenciennea sexguttata (Valenciennes, 1837) (East Africa to Samoa and the Marshall Islands)[2]
- Blueband goby Valenciennea strigata (Broussonet, 1782) (East Africa to Society Islands and Line Islands)[2]
- Parva goby Valenciennea parva Hoese and Larson, 1994 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Elegant goby Valenciennea decora Hoese and Larson, 1994 (Great Barrier Reef to New Caledonia)[2]
- Ambanoro goby Vanderhorstia ambanoro (Fourmanoir, 1957) (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Ocellated goby Vanderhorstia ornatissima Smith, 1959 (East Africa to Samoa)[2]
- Shadow goby Acentrogobius nebulosus (Forsskål, 1775) syn.Yongeichthys nebulosus ((as Y. nebulosus) East Africa to western Pacific)[2]
Family Microdesmidae - Wormfishes, dartfishes
- Curious wormfish Gunnellichthys curiosus Dawson, 1968 (Seychelles, Maldives, Indonesia, Coral Sea, Society Islands and Hawaii)[2]
- Onespot wormfish Gunnellichthys monostigma Smith, 1958[33] syn. Gunnellichthys monostigmata Smith, 1958 ((as G. monostigmata) Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Brownstripe wormfish Gunnellichthys pleurotaenia Bleeker, 1858 (Western Pacific east to Samoa and the Mariana Islands)[2]
- Yellowstripe wormfish Gunnellichthys viridescens (Seychelles, Maldives, Marshall Islands and Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Elegant firefish Nemateleotris decora Randall and Allen, 1973 (Islands of the western Indian Ocean to the Western Pacific)[2]
- Fire dartfish Nemateleotris magnifica Fowler, 1938 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Twotone dartfish Ptereleotris evides (Jordan and Hubbs, 1925) syn. P. tricolor (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Lined dartfish Ptereleotris grammica Randall and Lubbock, 1982 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Threadfin dartfish Ptereleotris hanae (Jordan and Snyder, 1901) (Western Australia to western Pacific and east to Samoa and the Line Islands)[2]
- Spottail dartfish Ptereleotris heteroptera Bleeker, 1855 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Pale dartfish Ptereleotris microlepis (Bleeker, 1856) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Monofin dartfish Ptereleotris monoptera Randall and Hoese, 1985 (Indo-Pacific from scattered localities)[2]
- Bandtail dartfish Ptereleotris uroditaenia Randall and Hoese, 1985 (Indonesia, Solomon Islands and Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Zebra dartfish Ptereleotris zebra Fowler, 1938 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
Family Acanthuridae - Surgeonfishes
Subfamily Acanthurinae
- Whitefin surgeonfish Acanthurus albipectoralis Allen and Ayling, 1987 (Great Barrier Reef and of the Coral Sea to Tonga)[2]
- Orange-socket surgeonfish Acanthurus auranticavus Randall, 1956 (Maldives, Philippines, Indonesia and the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Roundspot surgeonfish Acanthurus bariene Lesson, 1830 syn. A. nummifer (Maldives to the western Pacific)[2]
- Ringtail surgeonfish Acanthurus blochii Valenciennes, 1835 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Eyestripe surgeonfish Acanthurus dussumieri Valenciennes, 1835 (East Africa to the Line Islands and Hawaii)[2]
- Finelined surgeonfish Acanthurus grammoptilus Richardson, 1843 (Philippines to Australia including the Great Barrier Reef)[2]
- Whitespotted surgeonfish Acanthurus guttatus Forster, 1801 (Islands of the western Indian Ocean to Oceania)[2]
- Striped surgeonfish Acanthurus lineatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Indo-Pacific except Red Sea)[2]
- Elongate surgeonfish Acanthurus mata (Cuvier, 1829) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Whitecheek surgeonfish Acanthurus nigricans (Linnaeus, 1758) syn. A. glaucopareius (Islands of the tropical Pacific including eastern Pacific)[2]
- Blackstreak surgeonfish Acanthurus nigricauda Duncker and Mohr, 1929 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Brown surgeonfish Acanthurus nigrofuscus (Forsskal, 1775) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Bluelined surgeonfish Acanthurus nigroris Valenciennes, 1835 (Islands of Oceania)[2]
- Orangeband surgeonfish Acanthurus olivaceus Forster, 1801 (Western Pacific and islands of Oceania)[2]
- Mimic surgeonfish Acanthurus pyroferus Kittlitz, 1834 (Western Pacific to islands of Oceania)[2]
- Thompson's surgeonfish Acanthurus thompsoni (Fowler, 1923) syn. A. philppinus (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Convict surgeonfish Acanthurus triostegus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Yellowfin surgeonfish Acanthurus xanthopterus (Valenciennes, 1835) (Indo-Pacific and tropical eastern Pacific)[2]
- Twospot bristletooth Ctenochaetus binotatus Randall, 1955 (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Lined bristletooth Ctenochaetus striatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Goldring bristletooth Ctenochaetus strigosus (Bennett, 1828) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Palette surgeonfish Paracanthurus hepatus (Linnaeus, 1766) (East Africa to Samoa, Kiribati and Mariana Islands)[2]
- Brushtail tang Zebrasoma scopas (Cuvier, 1829) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Sailfin tang Zebrasoma veliferum (Bloch, 1797) (Western Pacific and islands of Oceania)[2]
Subfamily Nasinae
- Whitemargin unicornfish Naso annulatus (Quoy and Gaimard, 1825) syn. N. herrei (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Humpback unicornfish Naso brachycentron (Valenciennes, 1835) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Spotted unicornfish Naso brevirostris (Valenciennes, 1835) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Sleek unicornfish Naso hexacanthus (Bleeker, 1855) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Orangespine unicornfish Naso lituratus (Forster, 1801) (Indo-Pacific)[2]
- Elongate unicornfish Naso lopezi Herre, 1927 (Western Pacific)[2]
- Grey unicornfish Naso caesius Randall and Bell, 1992 (Antiequatorial in Oceania including New Caledonia and the southern Coral Sea)[2]
Binomials checked to here
Entered to here
End of working area
Family Zanclidae - Moorish idol
Family Siganidae – Rabbitfishes, spinefeet
Family Istiophoridae - Billfishes
Family Scombridae – Mackerels, tunas
- [2]
- Southern bluefin tuna Thunnus maccoyi Castelnau, 1872 (Western Australia to southern Queensland and around Tasmania. Also widespread in the southern hemisphere.)[3]
Order Mugiliformes
Family Mugilidae – Mullets
- Fringelip mullet Crenimugil crenilabis (Forsskal, 1775) (East Africa to Line and Tuamotu Islands)[2]
- Diamond-scale mullet Liza vaigiensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1825)[34] syn. Ellochelon vaigensis ((as E. vaigensis) East Africa and the Red Sea to the Tuamotus)[2]
Order Pleuronectiformes
Family Bothidae - Lefteye flounders
Family Pleuronectidae – Righteye flounders
Order Tetraodontiformes
Family Balistidae
Family Monacanthidae – Leatherjackets, filefishes
- Fanbelly leatherjacket Monacanthus chinensis (Osbeck, 1765) (Tropical Australia south to Geographe Bay, Western Australia, and to Western Port, Victoria. Also widespread in the Indo-West Pacific region.)[3]
Family Ostraciidae – Boxfishes, cowfishes, trunkfishes
- Humpback turretfish Tetrasomus gibbosus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Tropical Australia south to Albany, Western Australia, and to Cape Conran, Victoria. Also widespread in the Indo-West Pacific region.)[3]
Family Tetraodontidae – Toadfishes, pufferfishes
Family Diodontidae – Porcupine fishes
Unallocated species
(Perciformes) Family Chironemidae
- Silver spot Chironemus maculosus (Richardson, 1850) syn. Threpterius maculosus
References
- ↑ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 890 891 892 893 894 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 911 912 913 914 915 916 917 918 919 920 921 922 923 924 925 926 927 928 929 930 931 932 933 934 935 936 937 938 939 940 941 942 943 944 945 946 947 948 949 950 951 952 953 954 955 956 957 958 959 960 961 962 963 964 965 966 967 968 969 970 971 972 973 974 975 976 977 978 979 980 981 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 991 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 1000 1001 1002 1003 1004 1005 1006 Randall, John E.; Allen, Gerald R.; Steene, Roger C. (1997). Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea (second ed.). Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press. ISBN 0 8248 1895 4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Edgar, Graham J. (2008). Australian Marine Life: The plants and animals of temperate waters (Second ed.). Sydney: New Holland. ISBN 9781921517174.
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Glaucostegus typus (Anonymous [Bennett], 1830). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=280875 on 2014-03-10
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Gymnothorax thyrsoideus (Richardson, 1845). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=271889 on 2014-03-10
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Apogonichthyoides timorensis. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=475093 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Nectamia fusca (Quoy & Gaimard, 1825). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=398505 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Ostorhinchus novemfasciatus. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=319881 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Ostorhinchus properuptus (Whitley, 1964). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=712684 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Ostorhinchus taeniophorus (Regan, 1908). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=712689 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Ostorhinchus talboti. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=712690 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Pristiapogon kallopterus (Bleeker, 1856). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=712696 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Pantolabus radiatus (Macleay, 1881). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=281991 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Gerres longirostris (Lacepède, 1801). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=367242 on 2014-03-11
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Scolopsis lineata Quoy & Gaimard, 1824. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=276786 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Scolopsis margaritifera (Cuvier, 1830). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=276787 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Scolopsis trilineata Kner, 1868. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=276791 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Parupeneus trifasciatus (Lacepède, 1801). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=277826 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Zabidius novemaculeatus (McCulloch, 1916). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=283201 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Centropyge aurantia Randall & Wass, 1974. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=278828 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Centropyge flavissima (Cuvier, 1831). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=278836 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Centropyge loricula (Günther, 1874). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=278841 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Paracentropyge multifasciata (Smith & Radcliffe, 1911). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=320012 on 2014-03-12
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Chlorurus bleekeri (de Beaufort, 1940). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=277504 on 2014-03-14
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Scarus psittacus Forsskål, 1775. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=219125 on 2014-03-14
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Limnichthys nitidus. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=219164 on 2014-03-15
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Blenniinae. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=710669 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Salariinae. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=710670 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Cirripectes stigmaticus Strasburg & Schultz, 1953. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=219265 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Asterropteryx semipunctata Rüppell, 1830. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=277497 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Fusigobius neophytus. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=219467 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Gnatholepis cauerensis (Bleeker, 1853). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=219476 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Gunnellichthys monostigma Smith, 1958. In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=219607 on 2014-03-17
- ↑ Bailly, N. (2013). Liza vaigiensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1825). In: Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2013) FishBase. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=218879 on 2014-03-14