Larsa
Coordinates: 31°17′9″N 45°51′13″E / 31.28583°N 45.85361°E
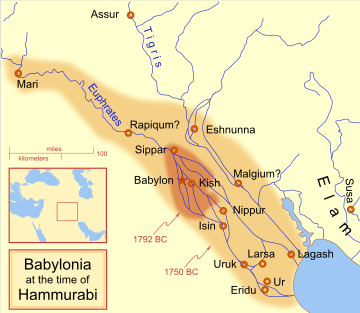

Larsa (Sumerian logogram: UD.UNUGKI,[1] read Larsamki[2]) was an important city of ancient Sumer, the center of the cult of the sun god Utu. It lies some 25 km southeast of Uruk in Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate, near the east bank of the Shatt-en-Nil canal at the site of the modern settlement Tell as-Senkereh or Sankarah.
History
The historical "Larsa" was already in existence as early as the reign of Eannatum of Lagash, who annexed it to his empire.
The city became a political force during the Isin-Larsa period. After the Third Dynasty of Ur collapsed ca. 2000 BC, Ishbi-Erra, an official of Ibbi-Sin, the last king of the Ur III Dynasty, relocated to Isin and set up a government which purported to be the successor to the Ur III dynasty. From there, Ishbi-Erra recaptured Ur as well as the cities of Uruk and Lagash, which Larsa was subject to. Subsequent Isin rulers appointed governors to rule over Lagash; one such governor was an Amorite named Gungunum. He eventually broke with Isin and established an independent dynasty in Larsa. To legitimize his rule and deliver a blow to Isin, Gungunum captured the city of Ur. As the region of Larsa was the main center of trade via the Persian Gulf, Isin lost an enormously profitable trade route, as well as a city with much cultic significance.
Gungunum's two successors, Abisare (ca. 1841 - 1830 BC) and Sumuel (ca. 1830 - 1801 BC), both took steps to cut Isin completely off from access to canals. After this period, Isin quickly lost political and economic force.
Larsa grew powerful, but it never accumulated a large territory. At its peak under king Rim-Sin I (ca. 1758 - 1699 BC), Larsa controlled only about 10-15 other city-states — nowhere near the territory controlled by other dynasties in Mesopotamian history. Nevertheless, huge building projects and agricultural undertakings can be detected archaeologically. After the defeat of Rim-Sin I by Hammurabi of Babylon, Larsa became a minor site, though it has been suggested that it was the home of the 1st Sealand Dynasty of Babylon.[3]
Larsa is thought to be the source of a number of tablets involving Babylonian mathematics, including the Plimpton 322 tablet that contains patterns of Pythagorean triples.[4]
Kings of Larsa
| Ruler | Reigned (short chronology) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Naplanum | ca. 1961—1940 BC | Contemporary of Ibbi-Suen of Ur III |
| Emisum | ca. 1940—1912 BC | |
| Samium | ca. 1912—1877 BC | |
| Zabaia | ca. 1877—1868 BC | Son of Samium, First royal inscription |
| Gungunum | ca. 1868—1841 BC | Gained independence from Lipit-Eshtar of Isin |
| Abisare | ca. 1841—1830 BC | |
| Sumuel | ca. 1830—1801 BC | |
| Nur-Adad | ca. 1801—1785 BC | Contemporary of Sumu-la-El of Babylon |
| Sin-Iddinam | ca. 1785—1778 BC | Son of Nur-Adad |
| Sin-Eribam | ca. 1778—1776 BC | |
| Sin-Iqisham | ca. 1776—1771 BC | Contemporary of Zambiya of Isin, Son of Sin-Eribam |
| Silli-Adad | ca. 1771—1770 BC | |
| Warad-Sin | ca. 1770—1758 BC | Possible co-regency with Kudur-Mabuk his father |
| Rim-Sin I | ca. 1758—1699 BC | Contemporary of Irdanene of Uruk, Defeated by Hammurabi of Babylon, Brother of Warad-Sin |
| Hammurabi of Babylon | ca. 1699—1686 BC | Official Babylonian rule |
| Samsu-iluna of Babylon | ca. 1686—1678 BC | Official Babylonian rule |
| Rim-Sin II | ca. 1678—1674 BC | Killed in revolt against Babylon |
Archaeology
The remains of Larsa cover an oval about 4.5 miles in circumference. The highest point is around 70 feet in height.
The site of Tell es-Senkereh, then known as Sinkara, was first excavated by William Loftus in 1850 for less than a month.[5] In those early days of archaeology, the effort was more focused on obtaining museum specimens than scientific data and niceties like site drawings and findspots were not yet in common usage. Loftus recovered building bricks of Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire which enabled the sites identification as the ancient city of Larsa. Much of the effort by Loftus was on the temple of Shamash, rebuilt by Nebuchadnezzar II. Inscriptions of Burna-Buriash II of the Kassite dynasty of Babylon and Hammurabi of the First Babylonian Dynasty were also found. Larsa was also briefly worked by Walter Andrae in 1903. The site was inspected by Edgar James Banks in 1905. He found that widespread looting by the local population was occurring there.[6]
The first modern, scientific, excavation of Senkereh occurred in 1933, with the work of Andre Parrot.[7][8] Parrot worked at the location again in 1967.[9] In 1969 and 1970, Larsa was excavated by Jean-Claude Margueron.[10][11] Between 1976 and 1991, an expedition of the Delegation Archaeologic Francaise en Irak led by J-L. Huot excavated at Tell es-Senereh for 13 seasons.[12][13][14][15]
Notes
- ↑ ETCSL. The Lament for Nibru. Accessed 19 Dec 2010.
- ↑ ETCSL. The Temple Hymns. Accessed 19 Dec 2010.
- ↑ W. G. Lambert, The Home of the First Sealand Dynasty, Journal of Cuneiform Studies, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 208-210, 1974
- ↑ Robson, Eleanor (2002). "Words and pictures: new light on Plimpton 322" (PDF). American Mathematical Monthly. Mathematical Association of America. pp. 105–120. doi:10.2307/2695324. JSTOR 2695324. MR 1903149..
- ↑ WIlliam Loftus, Travels and researches in Chaldæa and Susiana; with an account of excavations at Warka, the Erech of Nimrod, and Shúsh, Shushan the Palace of Esther, in 1849-52, J. Nisbet and Co., 1857
- ↑ Edgar James Banks, Senkereh, the Ruins of Ancient Larsa, The Biblical World, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 389-392, 1905
- ↑ Andre Parrot, Villes enfouies. Trois campagnes de fouilles en Mésopotamie, 1935
- ↑ A. Parrot, Les fouilles de Tello et de. Senkereh-Larsa, campagne 1932-1933, Revue d'Assyriologie, vol. 30, pp.169-182, 1933
- ↑ André Parrot, Les fouilles de Larsa, Syria, vol. 45, iss. 3-4, pp. 205-239, 1968
- ↑ Jean-Claude Margueron, Larsa, rapport preliminaire sur la quatrieme campagne, Syria, vol. 47, pp. 271-287, 1970
- ↑ Jean-Claude Margueron, Larsa, rapport preliminaire sur la cinquieme campagne, Syria, vol. 48, pp. 271-287, 1971
- ↑ J-L. Huot, Larsa, rapport preliminaire sur la septieme campagne Larsa et la premiere campagne Tell el 'Oueili (1976), Syria, vol. 55, pp. 183-223, 1978
- ↑ J-L. Huot, Larsa et 'Oueili, travaux de 1978-1981. Vol. 26, Memoire, Editions Recherche sur les civilisations, 1983, ISBN 2-86538-066-1
- ↑ J.-L. Huot, Larsa (10e campagne, 1983) et Oueili: Rapport preliminaire, Editions Recherche sur les civilisations, 1987, ISBN 2-86538-174-9
- ↑ J-L. Huot, Larsa, Travaux de 1985, Editions Recherche sur les civilisations, 1989, ISBN 2-86538-198-6
See also
References
- Ettalene M. Grice, Clarence E. Keiser, Morris Jastrow, Chronology of the Larsa Dynasty, AMS Press, 1979, ISBN 0-404-60274-6
- The Rulers of Larsa, M. Fitzgerald, Yale University Dissertation, 2002
- Larsa Year Names, Marcel Segrist, Andrews University Press, 1990, ISBN 0-943872-54-5
- Judith K. Bjorkman, The Larsa Goldsmith's Hoards-New Interpretations, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 1–23, 1993
- T. Breckwoldt, Management of grain storage in Old Babylonian Larsa, Archiv für Orientforschung, no. 42-43, pp. 64–88, 1995–1996
- D. Arnaud, French Archaeological Mission in Iraq. A Catalogue of the Cuneiform Tablets and Inscribed Objects Found during the 6th Season in Tell Senkereh/Larsa, Sumer, vol. 34, no. 1-2, pp. 165–176, 1978
- EJ Brill, Legal and economic records from the Kingdom of Larsa, Leemans, 1954, ISBN 90-6258-120-X
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Larsa. |
![]() Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Larsa". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Larsa". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
