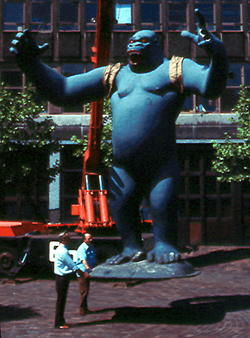
King Kong statue
|
The statue, in its original colours, being temporarily exhibited at Aston University, Gosta Green in Birmingham | |
| Artist | Nicholas Monro |
|---|---|
| Year | 1972 |
| Type | Statue |
| Medium | Fibreglass |
| Subject | King Kong |
| Dimensions | 550 cm (220 in) |
| Weight | 890 kg (1,960 lb) |
| Location | Leeds |
| 53°48′00″N 1°32′51″W / 53.7999301°N 1.5475642°WCoordinates: 53°48′00″N 1°32′51″W / 53.7999301°N 1.5475642°W | |
| Owner | Lesley Maby |
A statue of King Kong by Nicholas Monro was commissioned in 1972 for display in Manzoni Gardens in The Bull Ring, in the centre of Birmingham, England.[1] It was later displayed elsewhere in Birmingham, then at markets in Edinburgh, Penrith (where it was subsequently stored), and now at the Henry Moore Institute in Leeds.
The Arnolfini Gallery in Bristol had a maquette.[1] That is now in the collection of Wolverhampton Art Gallery.
Birmingham
Modelled on the fictional giant gorilla King Kong, the 550 cm (18 ft)-tall,[1] 890 kg (1,960 lb)[2] fibreglass[1] statue was commissioned[1] for display in Birmingham from March to November 1972,[3] by the Peter Stuyvesant Foundation[1] for the Sculpture for Public Places Scheme[4] "City Sculpture",[5] in partnership with the Arts Council of Great Britain.[1]
It was constructed at the artist's studio at Hungerford.[6] Munro's brief was to make something "city orientated" and he chose King Kong because of his association with New York City and "for my own petty reasons".[6]
The statue was displayed in Manzoni Gardens (now the site of the Bullring shopping mall). On 14 July 1972 it was "occupied" by two flying pickets, who were protesting about low wages in the building industry as art of the national builders' strike. They sat on its shoulders and hung from its neck a banner reading "King King says nothing less than £30 for 35 hours and up your T.P.I."[7]
After the statue had been on display for six months, Birmingham City Council was offered the opportunity to purchase the work,[6] but decided not to retain it,[1] and so later in 1972, it was sold for £3,000[8] to a local used-car dealer,[1] Mike Shanley,[9] who changed the name of his dealership to King Kong Car Co.[10] and displayed the statue at his sales lot[1] on the A34 Stratford Road, next to the former Holy Trinity church in the Camp Hill area of the city.[9] While there, it was dressed up as Father Christmas in season. It is likely that a subsequent owner of the statue and lot was a Mr Racey.[9]
By 1976, the King Kong statue had moved to a new location on Ladypool Road, Sparkbrook, close to the Clifton Road junction. It stood at the rear face of the Clifton public house. It was still being used to advertise a King Kong cars dealership at this location [11]
Edinburgh

In 1976, it was sold for £12,700 to Nigel Maby's Scottish company Spook Erection Ltd[12] and displayed at Ingliston Market in Edinburgh.[1] During that period, it was falsely reported destroyed,[1] and repainted several times, including once in tartan,[12] and, in 2001, in shocking pink.[2] Before removal from Edinburgh on the closure of that market in 2005,[13] the statue suffered damage by vandals to its back, and a broken arm, requiring repair.[2]
Penrith
.jpg)

It was subsequently displayed at Skirsgill Auction Mart, a market site in Penrith,[13] and was still there in January 2011[12] albeit lying down,[13] in a car park near its former position. There were calls for it to be returned to Birmingham,[12] but the owner, Lesley Maby[13] (wife of the late Nigel[13]), refused to sell it.[12]
Leeds

In November 2016 the statue, which had been repainted in its original colours, was moved to the Henry Moore Institute in Leeds, to be exhibited at the City Sculpture Projects 1972 exhibition, commemorating the original "City Sculpture" programme, to be held 24 November 2016 – 19 February 2017, and where Monro is scheduled to speak on 23 November.[3][14]
The statue's maquette, on loan from Wolverhampton Art Gallery, will also be part of the exhibition.[3]
Locations
| Point | Coordinates (links to map & photo sources) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Aston University, Gosta Green, Birmingham | 52°29′15″N 1°53′19″W / 52.48751°N 1.88862°W | Estimated coordinates |
| Manzoni Gardens | 52°28′40″N 1°53′42″W / 52.477682°N 1.895131°W | |
| King Kong Car Co. (Camp Hill) | 52°28′17″N 1°52′40″W / 52.471475°N 1.877836°W | |
| King Kong Car Co. (Ladypool Road, Sparkbrook) | 52°27′18″N 1°52′39″W / 52.454989°N 1.877578°W | |
| Ingliston Market | 55°56′33″N 3°22′59″W / 55.942555°N 3.382936°W | |
| Skirsgill Auction Mart, Penrith | 54°39′13″N 2°45′59″W / 54.653538°N 2.766318°W | standing location |
| Skirsgill Auction Mart, Penrith | 54°39′07″N 2°46′01″W / 54.651820°N 2.766822°W | recumbent location |
| Henry Moore Institute, Leeds | 53°48′00″N 1°32′51″W / 53.7999301°N 1.5475642°W | current location |
As of August 2011, the statue was visible on the Google Maps' satellite view of both its Edinburgh[15] and Penrith[16] sites.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Noszlopy, George T. (1998). Public Sculpture of Birmingham including Sutton Coldfield. Public Sculpture of Britain. 2. Liverpool University Press. p. 170. ISBN 0-85323-682-8.
- 1 2 3 Anon (4 October 2005). "-". Edinburgh Evening News.
- 1 2 3 "City Sculpture Projects 1972". Henry Moore Foundation. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ↑ "University of Warwick Art Collection - Artists - Nicholas Monro". University of Warwick. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ↑ Peter Stuyvesant Foundation, City Sculpture Project 1972 Staff (1972). "City Sculpture (A Special Issue)". Studio International. Warehouse Publishing Ltd. 184 (946). ISBN 0-902063-09-X.
- 1 2 3 Radio Birmingham interview with Munro, 11 May 1972, transcribed in part in Towers, Alan (July–August 1972). "Birmingham: Nicholas Munro". Studio International. 184 (946): 18.
- ↑ "The Two Building Workers Staging Their Sit Down Demonstration On The Stock Photo, Royalty Free Image: 20204860 - Alamy". Almay. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- ↑ Varma, Anuji (23 January 2011). "We reveal what happened to Birmingham's iconic King Kong statue". Birmingham Mail.
- 1 2 3 "Birmingham garage owner buys King Kong statue". ATV Today. 18 September 1972. ATV Midlands. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- ↑ "Nicholas Monro". Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ↑ King Kong at this location can been seen in the second episode of the first series of the BBC TV series 'Gangsters'. 21 minutes into this episode, one of the characters is shown walking down Ladypool Road passing King Kong Kars Ko and the statue of King Kong
- 1 2 3 4 5 "King Kong statue could be heading back to Birmingham". Birmingham Mail. 25 January 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "King Kong sculpture soon to tower over Cumbrian Saturday market". Cumberland News. 28 January 2011. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ↑ "Gallery discussion - City Sculpture Projects 1972". Henry Moore Foundation. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ↑ "Google Maps satellite view - Ingliston Market". Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ↑ "Google Maps satellite view - Skirsgill Auction Mart". Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to King Kong statue. |
- Film interview with Monro filmed by ATV in Manzoni Gardens, Birmingham, in 1972
- Birmingham mail article with photos
- Flickr group for pictures of the statue