InfiLaw System
| Private | |
| Industry | Educational services |
| Founded | July 28, 2006, Wilmington, Delaware |
| Headquarters | Naples, Florida, United States |
Area served | United States |
Key people |
|
| Website |
www |
The InfiLaw System is a for-profit consortium of three, ABA-accredited independent law schools in the United States, consisting of Arizona Summit Law School in Phoenix, Arizona, Charlotte School of Law (currently on probation by the ABA), and Florida Coastal School of Law in Jacksonville, Florida. It is owned by Sterling Partners, a Chicago-based private equity firm,[1] and is headquartered in Naples, Florida.[2]
History
Founding and initial growth
Sterling Partners purchased Florida Coastal School of Law in 2004 and founded the InfiLaw System in concurrence with the purchase. InfiLaw then established the Phoenix School of Law later in 2004 and the Charlotte School of Law in 2006.[1] In November 2013, the Phoenix School of Law officially changed its name to "Arizona Summit School of Law."[3] The InfiLaw mission is to establish the benchmark of inclusive excellence in professional education for the 21st Century, the mission being grounded in three pillars that include serving the underserved, providing a student outcome centered education, and graduating students who are practice-ready. Both Arizona Summit Law School and Charlotte School of Law were awarded full ABA accreditation at the earliest time permitted by the ABA; Arizona Summit Law School in June, 2010, and Charlotte School of Law in June, 2011.
Enrollment at each of the three schools increased dramatically in the early years of InfiLaw ownership. For instance, Florida Coastal School of Law (the only previously established school in the InfiLaw System), increased from 904 students in 2004 to 1,741 students in 2010. The Arizona Summit School of Law had 336 students in 2008, which increased to around 700 by 2010 and necessitated a new, larger downtown Phoenix campus. Also, campus moves to downtown locations of both Arizona Summit Law School (Phoenix) and Charlotte School of Law (Charlotte) allowed students to be closer to the courts, the legal community and the government centers.[4] The Charlotte School of Law's first class in 2007 received 1,010 applicants, of which around 420 were accepted. The initial 1L class size at the Charlotte school was only around 85 students.[2] By 2009, the number for all three classes had grown to 481, and, in 2011, it increased again to 1,151.[5]
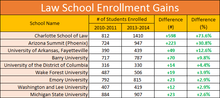
As part of the law school reform movement that occurred in and around 2010 and 2011, the American Bar Association began amending its Section of Legal Education and Admissions to increase transparency at ABA-accredited schools. Among these reforms was the requirement that law schools provide more detailed and complete information about employment outcomes for graduates. This reform, along with an overall economic downturn during the same period, led to a decline in law school applications that also affected the schools in the InfiLaw System. From 2010 to 2014, law school applications dropped from 88,000 to 55,000 across the pantheon of ABA-accredited schools. InfiLaw's schools saw a similar decline in that time period from 12,754 applications in 2010 to 8,066 applications in 2013.[6]
Attempted purchase of Charleston School of Law
In August 2013, two of the three owners of the for-profit Charleston School of Law announced they were selling the school to InfiLaw. Faculty, students, and alumni voiced objections to the sale citing concerns that InfiLaw would lower admissions standards to boost enrollment, resulting in lower bar passage and employment rates, which would, in turn, damage the school's reputation.[7] Despite the opposition, others have pointed out that InfiLaw's schools have produced statistics similar to the Charleston School of Law in regard to tuition, loan default rates, employment outcomes, salaries, and passage of the bar. Two Charleston alumni wrote an op-ed in support of the sale of the school to InfiLaw, stating that InfiLaw gave the school a better chance to "thrive" and avoid struggles. In May 2014, however, a committee of the South Carolina Commission on Higher Education recommended in a 3-to-1 vote that the state's higher education regulator reject the sale.[8]
In May of this year, InfiLaw spokeswoman, Kathy Heldman, has said the company now has no plans to refile an application for a license to operate in South Carolina with the state's Commission on Higher Education. [9]
Operation and statistics
Admissions selectivity
From the outset, InfiLaw has had a social mission of adding diversity to occupations that have an underrepresentation of diverse professionals. The legal profession is one of the least diverse in America, with the American Bar Association (ABA) estimating that just over 12 percent of all lawyers are lawyers of color, in a nation that is 38 percent racially diverse.[10]
In 2007, Florida Coastal School of Law was the only law school in the nation in which students from a minority group outperformed students in non-minority groups on the bar exam.[2] InfiLaw also attracts individuals who do not have high enough LSAT scores and GPAs to be admitted into higher-tier law schools.[1] InfiLaw officials and others have stated that the LSAT "is not the best determinant of success as a lawyer and clearly has racial bias."[11]
In addition, each of the InfiLaw schools has been able to exceed enrollment of diverse students as confirmed by recent data. Diversity enrollment for Fall, 2015 was: Florida Coastal School of Law 52,4%; Charlotte School of Law 58.5% and Arizona Summit Law School 49.7%.
In 2015, PreLaw Magazine named Arizona Summit Law School to its Most Diverse Law School list. The magazine honored Summit Law with an A+ rating and was named one of the top ten law schools for diversity nationwide among accredited law schools. [12]
For students with lower LSAT scores, the InfiLaw schools offer students the ability to participate in a 7-week program called AAMPLE, (Alternative Admissions Model Program for Legal Education), that includes two actual law such/content courses and is designed to evaluate the student's ability to handle the rigors of the law school curriculum and achieve success in law school. This program has provided those students who typically have had difficulty with standardized testing the opportunity to prove themselves and to attend law school and earn a law degree. InfiLaw schools are said to provide more "hands-on learning" for individuals who score lower marks on their LSATs, offering around 400 hours of on-the-job training.[1]
Florida Coastal School of Law was named a best law school for providing its students practical training by National Jurist Magazine, a leading news source in legal education. Coastal Law was listed in the top 20 of all law schools listed and received a grade of A+, up from an A- in 2014. Florida Coastal School of Law was named a best law school for providing its students practical training by National Jurist Magazine, a leading news source in legal education.[13]
InfiLaw has received criticism for their admissions standards (sometimes described as "lax"), with suggestions that these admissions standards could lead to fewer students passing the bar exam. By 2015, the predictions came true when only 30.6% of first time bar takers from Arizona Summit passed the July 2015 bar exam.

In 2010, the average LSAT score for all three InfiLaw schools was either 149 or 150, a mark generally considered average. By 2013, the median LSAT score at InfiLaw schools had dropped to 144 (23rd percentile), with 25% of its students achieving marks at or below 141. The median GPA for the class of 2016 at Florida Coastal School of Law is 2.97[14] and is 2.88 for Arizona Summit.[15] At Charlotte, the median GPA is 2.91.[16]
A 2012 report showed that 18% of first-year students at Arizona Summit had transferred to other law schools. This led to a policy in which transfer students were required to meet with an adviser before their transcripts would be released. In 2013, two professors filed a lawsuit against the school, alleging that they had been fired for objecting to a new policy related to student transfers, among other policy changes.[17] InfiLaw disputes that claim, instead noting that the professors simply failed to execute letters of appointment proffered by the school for succeeding academic terms, before the expiration of their last term of employment. United States federal judge, Susan Bolton, dismissed the original complaint, but allowed the complaint to be amended in 2014.[18] The amended complaint was subsequently dismissed by District Court, this time with prejudice.[19] The District Court also ordered plaintiffs to pay most of the defendants' costs incurred to date in connection with the case. The plaintiffs appealed both the granting of the Motion to Dismiss and the Order to pay costs/fees to the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit.
Bar-passage rates
In the summer of 2013, each of the three schools in the InfiLaw system posted bar-passage rates of 58% or above. Charlotte achieved a 58% passage rate while Florida Coastal earned a 67.4% passage rate. A student from Arizona Summit posted the highest score on the Arizona bar exam in 2013.[20] However, in 2015, Arizona Summit's bar passage rate fell to just 31%.[21]
When InfiLaw first took over Florida Coastal, they improved their bar-passage rate from 58.2% to 76.4%.[8] In February 2014, 73% of Florida Coastal students passed the bar but fewer students take the February bar. For graduates who took the exam in July, only 58 % of Florida Coastal students passed, compared to a statewide average of 72%.[22]For February, 2015 bar pass, Florida Coastal School of Law ranked third in the state among all state law schools at a passing rate of 74.5%, compared to 64.3% for all Florida law schools.[23] However in 2016, Coastal Law's bar passage rate fell to just 32.7%.[24]
Employment outcomes
In 2012, a group of former Florida Coastal students filed a lawsuit against the law school, alleging that the school had inflated their post-graduate employment numbers in promotional material. The suit alleged that the school advertised an 80 to 95% employment rate for graduates in the first 9 months after receiving their diplomas. This case was part of a series of class action lawsuits filed by law school students and applicants across the country, a number of which have been dismissed. Continuing this trend of dismissals, in Casey et al. v. Florida Coastal, Judge Brian J. Davis of the United States District Court for the Middle District of Florida, Jacksonville Division, dismissed the entire case with prejudice, accepting United States Magistrate Judge Patricia D. Barksdale’s recommendation of dismissal issued on August 15, 2015 . In a decision supplementing the reasoning of Magistrate Judge Barksdale, Judge Davis concluded that plaintiffs' allegations failed to state a claim and that the defendant's alleged conduct failed to rise to the level of deceptive or unfair trade practices, stating that claim of deceptive trade practice "requires proof that defendant's act would likely mislead the [objective] consumer acting reasonably in the circumstances."'[25]
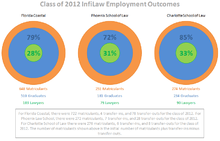
Like all ABA-accredited law schools, Florida Coastal School of Law is required to survey members of its most recent graduating class to ascertain their employment status. In March of each year, law schools report this employment data to the American Bar Association and NALP, a non-profit education association for law schools and legal employers that also conducts an annual employment survey. The data collected reflect the employment status of each law school's graduates as of February 15. Florida Coastal School of Law was able to confirm the employment status of 98.4% (553 of 562) of its program completers who graduated September 1, 2012 through August 31, 2013. The job placement rate for these graduates was 62.1%. This figure was calculated using the NALP formula for calculating job placement rate. Therefore, the 62.1% job placement rate was calculated by adding together all of the employed graduates (349) and then dividing by the total number of graduates (562).
Tuition and costs at Charlotte School of Law initially started out at around $27,000 per student in 2007[2] with similar rates at the other two InfiLaw schools.[8] As of 2014, median tuition costs for all three InfiLaw schools are generally around $40,000.[1][7] According to Harvard Law School, 97% of Arizona Summit's graduates have debt that averages around $162,000. 92% of Florida Coastal graduates incurred an average of $143,000 in debt, while 90% of Charlotte graduates incurred an average of $115,000 in debt. Charlotte's debt statistics are in line with comparable law schools across the nation.[20]
Cohort Default Rate
The InfiLaw schools weighted average cohort default rate for 2011 was 1.6%, as 98.4% of InfiLaw schools graduates are in compliance with the terms of their student loan agreements, well below the national rate of 13.7%.[26]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Warren, Zach (21 October 2013). "For-profit law schools on the rise". Inside Counsel Magazine. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Clary, Ellison (January 2007). "Charlotte's New Legal Beagle". Greater Charlotte Biz. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ Scott, Eugene (3 November 2013). "Phoenix School of Law to adopt new name". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ Gersema, Emily (27 April 2011). "For-profit Phoenix School of Law plans to move downtown". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ http://lsac.org/lsacresources/publications/official-guide-archives
- ↑ http://lsac.org/lsacresources/data/lsac-volume-summary
- 1 2 Jones, Ashby (20 October 2013). "Private-Equity Group's for-Profit Law School Plan Draws Critics". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- 1 2 3 Davidoff Solomon, Steven (3 June 2014). "Potential Sale of Law School Raises Debate Over Who Should Profit". The New York Times. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ http://www.postandcourier.com/article/20150522/PC16/150529765/charlestom-school-of-law-to-enroll-students-for-the-fall
- ↑ http://www.americanbar.org/content/dam/aba/migrated/marketresearch/PublicDocuments/lawyer_demographics_2012_revised.authcheckdam.pdf
- ↑ http://www.unc.edu/edp/pdf/NLBPS.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nxtbook.com/nxtbooks/cypress/prelaw_2015winter/#/32/
- ↑ http://www.nationaljurist.com/content/best-law-schools-practical-training-2015
- ↑ "Florida Coastal School of Law Profile". Law School Transparency. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ↑ "Arizona Summit Law School Profile". Law School Transparency. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ↑ "Charlotte School of Law Profile". Law School Transparency. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ↑ Cassens Weiss, Debra (4 June 2013). "Suit claims law profs were fired after opposing proposals to discourage student transfers". ABA Journal. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ Cassens Weiss, Debra (4 June 2013). "Suit claims law profs were fired after opposing proposals to discourage student transfers". ABA Journal. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ http://azcommonlaw.com/2014/03/12/amended-lawsuit-against-phoenix-school-of-law-by-former-profs/
- 1 2 Reilly, Amanda (3 December 2013). "For-Profit Law Schools: Impacting the Future of Legal Education". The Case Studies Blog at Harvard Law School. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ http://www.globallegalpost.com/big-stories/law-school-which-cut-admissions-standards-sees-31pc-pass-rate-77337780/
- ↑ Pantazi, Andrew (24 September 2014). "Florida Coastal School of Law graduates finish second-to-last in passing the Bar". The Florida Times-Union. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ↑ passers.https://www.floridabarexam.org/__85257bfe0055eb2c.nsf/52286ae9ad5d845185257c07005c3fe1/61848a37f7f3ac9c85257e27005dc978
- ↑ Florida Board of Bar Examiners, February 2016 General Bar Examination. https://www.floridabarexam.org/__85257bfe0055eb2c.nsf/52286ae9ad5d845185257c07005c3fe1/082c539f6245872085257f9200485121
- ↑ Casey et al. v. Florida Coastal School of Law, 3:14-cv-1229-J-39PDB, (M.D.Fla. September 29, 2015)
- ↑ http://www2.ed.gov/offices/OSFAP/defaultmanagement/cdr.html