Inferior gluteal nerve
| Inferior gluteal nerve | |
|---|---|
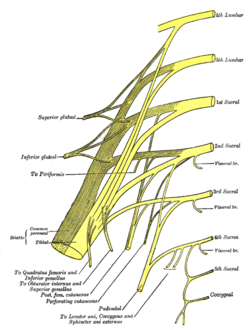 Plan of sacral and pudendal plexuses (inferior gluteal nerve labeled at middle left) | |
|
The gluteus medius and nearby muscles | |
| Details | |
| From | Sacral plexus (L5–S2) |
| Innervates | Gluteus maximus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus gluteus inferior |
| TA | A14.2.07.032 |
| FMA | 16511 |
The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this nerve is rare but often occurs as a complication of posterior approach to the hip during hip replacement. When damaged, one would develop gluteus maximus lurch, which is a gait abnormality which causes the individual to 'lurch' backwards to compensate lack in hip extension.
Anatomy
The largest muscle of the posterior hip, gluteus maximus, is innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve.[1] It branches out and then enters the deep surface of the gluteus maximus, the principal extensor of the thigh, and supplies it.
Origin
The muscle is supplied by the inferior gluteal nerve which arises from the dorsal branches of the ventral rami of the fifth (L5), the first (S1) and second (S2) sacral nerves.[2]
The lumbosacral trunk, which is made up of L5 and a small branch of L4, effectively connects the lumbar and sacral plexuses.[3] The lower branches of the L4 and the L5 nerves enter the sacral plexus.
The sacral plexus is formed by the lumbosacral trunk, the first to third sacral ventral rami, and part of the fourth, the remainder of the last joining the coccygeal plexus. The sacral plexus is formed in the pelvis in front of the piriformis muscle.[3]
The sacral plexus is formed anterior to the piriformis muscle and gives rise to the sciatic nerve, the superior and inferior gluteal nerves, and the pudendal and posterior femoral cutaneous nerves.[3]
However, most of the sacral plexus nerves are scarcely recognizable, because they leave the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. From the pelvis, the anterior primary branches of the nerves entering the plexus (the first sacral nerve being a particularly large one) and a mass of nerves on the piriformis can be recognized.[4]
Course
The inferior gluteal nerve leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen and runs underneath the piriformis muscle. It the divides into muscular branches to supply the gluteus maximus that pass posteriorly into the deep surface of the gluteus maximus muscle.[5]
The inferior gluteal nerve is superficial to the sciatic nerve. It has been described as having multiple branches with subsequent innervation of the overlying gluteus maximus.[1]
The inferior gluteal nerve entered the deep surface of gluteus maximus very inferiorly. At the lower border of the piriformis muscle, the nerve turns backward and divides into upward and downward diverging branches, which enter the gluteus maximus. The nerve may also send a branch to the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve.[3]
The inferior gluteal nerve reliably emerged inferior to the piriformis muscle. The branching characteristics of the nerve falls into two broad categories.One category is short stalks which came under the piriformis and then gave rise to all of the terminal branches of the nerve which spanned the muscle of the gluteus maximus. The number of branches from the stalk ranged from four to six.[1] The second category occurs as a partial split of the stalk that occurred proximal to the coverage of the piriformis. There were two to three divisions of the inferior gluteal nerve under the piriformis that would further divide close to the insertion of the nerve into the actual muscle belly.[1]
The nerve was always seen close to and medial to the sciatic nerve when it left the sacral plexus inferior to the piriformis. In all specimens, the nerve entered the deep surface of gluteus maximus approximately 5 cm from the tip of the greater trochanter of the femur and entered the deep surface of gluteus maximus over the inferior one-third of the muscle belly.[2]
The inferior gluteal nerve is accompanied by the inferior gluteal artery, a branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.[2]
However thee relationship between the inferior gluteal nerve and artery was found to be unpredictable.[1] No consistent relationship between the inferior gluteal artery and the inferior gluteal nerve was observed in current studies.
There is a relationship between the common stalk of the inferior gluteal nerve and external anatomic landmarks. The targeted region should be aimed inferior to the most prominent aspect of the greater trochanter, and medial to the landmark of the ischial tuberosity, at the depth of the posterior border of the proximal femur. Triangulating using these three coordinates, one can reliably reach the source of the inferior gluteal nerve. This will result in maximal stimulation of the gluteus maximus musculature when using electrical stimulation for the purpose of prevention of pressure ulcers.[1]
The sciatic nerve (L4 to S3), the largest nerve of the body, immediately leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, below the piriformis. The superior gluteal nerve passes backward through the greater sciatic foramen, above the piriformis: the inferior gluteal nerve also passes backward through the greater sciatic foramen but below the piriformis."[4]
Function
The major function of the gluteus maximus is to extend the flexed thigh and bring it inline with the trunk. It may prevent the forward momentum of the trunk from producing flexion at the supporting hip during bipedal gait. It is intermittently active in the walking cycle and in climbing stairs and continuously active in strong lateral rotation and abduction of the thigh and also stabilizes the femur on the tibia when the knee extensors are relaxed. In addition to this, the gluteus maximus has an important role during some activities like running or standing up.[5]
The gluteus maximus, a large muscle with numerous attachments, is a powerful extensor of the thigh or of the trunk lower limbs are in a fixed position. The gluteus maximus is also a strong hip stabilzer. It extends thigh at the hip, assists in laterally rotating the thigh.[6] It contracts at heel-strike, slowing forward motion of trunk by arresting flexion of the hip and initiating extension. This movement prevents trunk from falling forward.[6][7]
Surprisingly, however, the gluteus maximus is not important posturally, is relaxed when one is standing, and is little used in walking. It is employed in running, climbing, and rising from a sitting or stooped position. It also controls flexion at the hip upon sitting down.[6]
Injury
From hip replacement
Inferior gluteal entrapment neuropathy is rarely reported but is recognized as a complication of the posterior approach to hip arthroplasty. Injuries to the peripheral nerves occur in 0.5% to 8% of patients undergoing total hip displacement.[2]
The posterior approach has been assessed most widely and is perhaps the most frequently used, but it is also the one most likely to be associated with damage to the inferior gluteal nerve since this structure is not usually seen. Direct abnormalities of the nerve may be difficult to detect due to the small size of the nerve, although signal intensity alterations in the gluteus maximus may be encountered[3]
Diagnostic imaging of peripheral nerves about the hip is a challenging task due to the complex regional anatomy, the small size and intricate course of many nerves. There are also a variety of clinical situations leading to local disturbances in the nerve function the positioning of the inferior gluteal nerve makes it vulnerable to iagtrogenic injury during posterior and posterior approaches to the hip[8]
It is subject to injury by compression and ischemia in sedentary individuals, resulting in difficulty in rising from a sitting position and difficulty climbing stairs.[9]
The incidence of damage to the inferior gluteal nerve after replacement of the hip is still uncertain. Peripheral nerve injury may occur during operations on the hip as a result of operative trauma associated with stretching and retraction of the nerve. Few studies have focused on damage to the inferior gluteal nerve during hip replacement.[5]
In ten other patients who had a posterior approach, nine had abnormal electromyographic findings in inferior gluteal innervated muscles and eight of the ten also had abnormalities in superior gluteal innervated muscles. They suggested that abnormalities of gait after the operation may be due to injury to these nerves.[5]
The reduction in walking speed and persistently abnormal gait, sometimes seen in patients one year after total hip replacement, were associated with a decrease in the extensor moment with a resultant decrease in the range of extension of the hip and a reduction in the abductor moment.[10]
When a muscle-splitting incision is made across gluteus maximus as part of the classical posterior approach and the muscle parted by hand-held or self-retaining retractors, the likelihood of damage to the inferior gluteal nerve is high. The nerve enters the deep surface of the muscle and is not easily visualised and differentiated from other structures running with it, such as the blood vessels. Parting the muscle damages the nerve further by stretching or even rupturing its branches which run superiorly on its deep surface.[2]
Entrapment neuropathy is an underrecognized cause of pain and functional impairment caused by acute or chronic injury to peripheral nerves.[8]
Although nerves may be injured anywhere along their course, they are more prone to compression, entrapment, or stretching as they traverse anatomically vulnerable regions, such as superficial or geographically constrained spaces. Subclinical electromyographic abnormalities of both the superior and inferior gluteal nerves have been described in up to 77% of patients after total hip replacement, regardless of the surgical approach.[8]
The posterior approach is the most common and practical of those used to expose the hip joint. The posterior approaches allow excellent visualization of the femoral shaft, thus are popular for revision joint replacement surgery in cases in which the femoral component needs to be replaced. The likelihood of damage to the inferior gluteal nerve is reported to be high when a muscle-splitting incision is made across the gluteus maximus as a part of the classical posterior approach to the hip.[5]
This may cause selective denervation of the gluteus maximus since the inferior gluteal nerve courses along the deep surface of the muscle and is not easily visualized and differentiated from other structures running with it, such as blood vessels.[3]
Gluteus maximus lurch
Injury to this nerve leads to a gluteus maximus lurch. When gluteus maximus is weak/injured, trunk extends (lean back) on heel-strike on weakened side. This compensates for weakness of hip extension.
Damage to the inferior gluteal nerve causes loss of extension at hip, and causes the buttock to waste.
The normal gluteus maximus gait is when the gluteus maxims begins to contract at moment of heel-strike, slowing forward motion of trunk by arresting flexion of hip and initiating extension. When gluteus maximus is weak, trunk lurches backward (gluteus maximus lurch) at heel-strike on weakened side to interrupt forward motion of the trunk.[11]
There is great difficulty in preventing the flexion of the trunk heel strike so the person may use trunk extension before heel strike to maintain balance causing a backwards lurch.[6] The trunk lurches back on the stance phase side hyperextending. The backwards trunk lurch persists throughout the stance to maintain the gravitational force line behind the hip axis locking the hip into extension. There is an apparent forward protrusion of the affected hip due to exaggerated hip motion and the person may also hold the shoulders backward to keep the center of gravity behind the joint. The hamstring muscles often compensate for the gluteus maximus weakness resulting in a near normal gait pattern but most often theses muscles are affected together.[7]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Skalak, A. F., et al. "Relationship of Inferior Gluteal Nerves and Vessels: Target for Application of Stimulation Devices for the Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in Spinal Cord Injury." Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy 30.1 (2008): 41-45. Print.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Ling, Z. X., and V. P. Kumar. "The Course of the Inferior Gluteal Nerve in the Posterior Approach to the Hip." Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume 88B.12 (2006): 1580-83. Print.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Petchprapa, C. N., et al. "Mr Imaging of Entrapment Neuropathies of the Lower Extremity Part 1. The Pelvis and Hip." Radiographics 30.4 (2010): 983-1000. Print.
- 1 2 Mirilas, P., and J. E. Skandalakis. "Surgical Anatomy of the Retroperitoneal Spaces, Part Iv: Retroperitoneal Nerves." American Surgeon 76.3 (2010): 253-62. Print.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Apaydin, N., et al. "The Course of the Inferior Gluteal Nerve and Surgical Landmarks for Its Localization During Posterior Approaches to Hip." Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy 31.6 (2009): 415-18. Print.
- 1 2 3 4 Delisa, Joel A. (1998). Gait Analysis In The Science Of Rehabilitation. Diane Pub Co. pp. 8, 9. ISBN 0756700213.
- 1 2 Hoppenfeld, Stanley (2000). Treatment and rehabilitation of fractures. Philadelphia [u.a.]: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 39,259,277. ISBN 0781721970.
- 1 2 3 Tagliafico Alberto, et al. "Imaging Of Neuropathies About The Hip." European Journal Of Radiology (n.d.): ScienceDirect. Web. 16 Nov. 2012
- ↑ Dejong, P. J., and T. W. Vanweerden. "Inferior and Superior Gluteal Nerve Paresis and Femur Neck Fracture after Spondylolisthesis and Lysis - a Case-Report." Journal of Neurology 230.4 (1983): 267-70. Print.
- ↑ Mondelli, M., et al. "Mononeuropathies of Inferior and Superior Gluteal Nerves Due to Hypertrophy of Piriformis Muscle in a Basketball Player." Muscle & Nerve 38.6 (2008): 1660-62. Print.
- ↑ Wheeless, Clifford R. "Gait". Retrieved 2012-11-26.
- This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Inferior_gluteal_nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- Gluteus Maximus Lurch / Inferior Gluteal Nerve This video is a demonstration of gluteus maximus lurch caused by damage to the inferior gluteal nerve.