Henry Dearborn
| Henry Dearborn | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 5th United States Secretary of War | |
|
In office March 5, 1801 – March 4, 1809 | |
| President | Thomas Jefferson |
| Preceded by | Samuel Dexter |
| Succeeded by | William Eustis |
| United States Minister to Portugal | |
|
In office August 16, 1822 – June 30, 1824 | |
| President | James Monroe |
| Preceded by | John Appleton |
| Succeeded by | Thomas Brent (Acting) |
| 10th Senior Officer of the United States Army | |
|
In office January 27, 1812 – June 15, 1815 | |
| President | James Madison |
| Preceded by | James Wilkinson |
| Succeeded by | Jacob Brown |
| Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Massachusetts's 12th district | |
|
In office March 4, 1795 – March 4, 1797 | |
| Preceded by | Constituency established |
| Succeeded by | Isaac Parker |
| Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Massachusetts's 4th district | |
|
In office March 4, 1793 – March 4, 1795 Serving with Peleg Wadsworth and George Thatcher (General ticket) | |
| Preceded by | Theodore Sedgwick |
| Succeeded by | Dwight Foster |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
February 23, 1751 North Hampton, New Hampshire, British America |
| Died |
June 6, 1829 (aged 78) Roxbury, Massachusetts, U.S. |
| Political party |
Anti-Administration (Before 1792) Democratic-Republican (1792–1829) |
| Signature |
|
| Military service | |
| Allegiance |
|
| Service/branch |
|
| Years of service |
1775–1783 1812–1815 |
| Rank |
|
| Battles/wars |
American Revolutionary War War of 1812 |
Henry Dearborn (February 23, 1751 – June 6, 1829) was an American soldier and statesman. In the Revolutionary War, he served under Benedict Arnold in the expedition to Quebec, of which his journal provides an important record. After being captured and exchanged, he served in George Washington’s Continental Army, and was present at the British surrender at Yorktown. Dearborn served on General Washington's staff in Virginia. He was US Secretary of War serving under President Thomas Jefferson from 1801 to 1809, and served as a commanding general in the War of 1812. In later life his criticism of General Israel Putnam's performance at the Battle of Bunker Hill caused a major controversy. Fort Dearborn and the city of Dearborn, Michigan were named in his honor.[1][2]
Background
Henry Dearborn was born February 23, 1751, to Simon Dearborn and Sarah Marston in North Hampton, New Hampshire, He was descended from Godfrey Dearborn, from Exeter, England, who came to Massachusetts colony in 1639 and settled at Exeter, New Hampshire and then soon after at Hampton, where four successive generations of his descendants lived. He spent much of his youth in Epping, where he attended public schools. He grew up as an athletic boy, notably strong and a champion wrestler.[3] He studied medicine under Dr. Hall Jackson of Portsmouth and opened a practice on the square in Nottingham in 1772.[4]
Dearborn was married three times: to Mary Bartlett in 1771, to Dorcas (Osgood) Marble in 1780, and to Sarah Bowdoin, widow of James Bowdoin, in 1813. Henry Alexander Scammell Dearborn was his son by his second wife.[1]
Revolutionary War service
When fighting in the American Revolutionary War began, Dearborn fought with the Continental Army as a captain in the 1st and 3rd New Hampshire Regiments and soon rose to the rank of Lieutenant Colonel. He was appointed Deputy Quartermaster General in July 1781 and served on George Washington's staff while in Virginia.[5] At age 23 he organized and led a local militia troop of 60 men to the Boston area where he joined up with and fought at the Battle of Bunker Hill as a captain in Colonel John Stark’s 1st New Hampshire Regiment on June 17, 1775.[6][7] During the battle Dearborn observed that "Not an officer or soldier of the continental troops engaged was in uniform, but were in the plain and ordinary dress of citizens; nor was there an officer on horseback."[8][lower-alpha 1] Dearborn years later would accuse Israel Putnam of failing his duty during that battle, resulting in a major controversy.[9]
Dearborn volunteered to serve under Colonel Benedict Arnold in September, 1775, during the difficult American expedition to Quebec. Later Dearborn would record in his Revolutionary War journal their overall situation and condition: "We were small indeed to think of entering a place like Quebec. But being now almost out of provisions we were sure to die if we attempted to return back and we could be in no worse situation if we proceeded on our rout."[10]
On the final leg of the march he was taken seriously ill with fever, forcing him to remain behind in a cottage on the Chaudiere River. Later he rejoined the combined forces of Arnold and Gen. Richard Montgomery in time to take part in the assault on Quebec.[lower-alpha 2][4] Dearborn's journal is an important record for that campaign. During the march he and Aaron Burr became companions.[11] Along with a number of other officers, Dearborn was captured on December 31, 1775, during the Battle of Quebec in Lower Canada and detained for a year.[12][13] He was released on parole in May 1776, but he was not exchanged until March 1777.[1]
After fighting at Ticonderoga in July 1777, Dearborn was appointed Major in the regiment commanded by Alexander Scammell.
In September, 1777, Dearborn was transferred to the 1st New Hampshire Regiment, under Colonel Joseph Cilley. He took part in the Saratoga campaign against Burgoyne at Freeman's Farm. The first battle was largely fought by troops from New Hampshire, Dearborn's home state. The New Hampshire brigade under General Poor and a detachment of infantry under Major Dearborn, numbering about three hundred, along with detachments of other militia, and Whitcomb's Rangers, co-operated with Morgan in the re pulse of Fraser's attack.[14] The cautious General Horatio Gates reluctantly ordered a reconnaissance force consisting of Daniel Morgan's Provisional Rifle Corps and Dearborn's light infantry to scout out the Bemis Heights area.[12] Gates later noted Dearborn's marked ability as a soldier and officer in his report. Thereafter Dearborn joined General George Washington's main Continental Army at Valley Forge, Pennsylvania as a lieutenant colonel where he spent the winter of 1777–1778.[4]
Dearborn also fought at the Battle of Monmouth in New Jersey, in 1778 following the British evacuation of Philadelphia to retreat to concentrate at New York City, in the final major battle of the Northern Theatre, and in the summer of 1779, he accompanied Major General John Sullivan on the Sullivan Expedition against the Iroquois in upstate New York.[12] and in the Battle of Wyoming against the Six Nations, thereafter laying waste to the Genesee Valley and the various regions around the Finger Lakes.[4]
During the winter of 1778-1779, he was encamped at what is now Putnam Memorial State Park in Redding, Connecticut. Dearborn rejoined General Washington’s staff in 1781 as deputy quartermaster general and commanded the 1st New Hampshire at the Battle of Yorktown with the rank of colonel[15] and was present when Cornwallis surrendered after the in Virginia in October 1781.[12]
In June 1783, Dearborn received his discharge from the Continental Arm and settled in Gardiner, Maine where he became Major General of the Maine militia. Washington appointed him Marshall of the District of Maine. Dearborn served in the U.S. House of Representatives from the District, 1793 to 1797.[12] [lower-alpha 3] He was an original member of the New Hampshire Society of the Cincinnati.[16]
Revolutionary War journals
During the American Revolution Dearborn maintained six separate journals where he recorded the various campaigns, battles and other notable events from his point of experience. His Revolutionary War journals of Henry Dearborn, 1775-1783, has provided historians of early American history with valuable first hand information from the perspective of an officer who was engaged in the various battles and surrounding events. His journals were first published in 1939 by the Caxton Club of Chicago and were edited from the original manuscripts by historians Lloyd A. Brown and Howard Henry Peckham; the publication includes a biographical essay of Dearborn by Hermon D. Smith. The six journals are enumerated as follows:
Journal II. The Burgoyne Campaign
Journal III. Operations in the Middle Colonies
Journal IV. Sullivan's Indian Expedition
Journal V. The Yorktown Campaign
Journal VI. Peace Negotiations[17]
Dearborn also wrote a short account of the Battle of Bunker Hill, entitled An Account of the Battle of Bunker Hill. Various scholars have cited the work as being culturally important, and greatly contributes to the knowledge base of early American civilization as we know it.[18]
Post-Revolution
Dearborn was commissioned as a brigadier general in the Massachusetts Militia in 1787 and was promoted to major general in 1789. The same year he was appointed as the first U.S. Marshal for the District of Maine under the new Constitution of 1787 by first President Washington. He represented this district as a Democratic-Republican in the Third and Fourth Congresses from 1793 to 1797.

In 1801, third President Thomas Jefferson appointed Dearborn Secretary of War, a post he held for eight years until March 7, 1809. Dearborn advised Jefferson in matters of military personnel when the latter was formulating the Military Peace Establishment Act in 1800-01, which outlined a new set of laws and limits for the military and also led to the founding of a national military academy at West Point.[19] In April 1801, Dearborn asked George Baron, an Englishman who was Dearborn's friend from Maine, to be the mathematics instructor at the academy. Dearborn also offered the superintendency of the school to Jonathan Williams,[lower-alpha 4] who had translated into English some European treatises on artillery and fortification.[20]
During the 1801 and 1802 period, Dearborn and Jefferson corresponded frequently, discussing various political and military matters. Notable among them was Dearborn's report of 12 May 1801 on the War Department,[20] and his recommendation for "designating the boundary line between the United States, and the adjacent British possessions, in such manner as may prevent any disputes in future..."[21]
During his tenure, he helped Jefferson form a policy on Native Americans, whose goal was to establish a western boundary by procuring lands along the Mississippi River.[22]
In 1805 while events in the Burr conspiracy were beginning to unfold, Aaron Burr and Louisiana Territory governor James Wilkinson were allegedly planning War with Mexico with the aim of establishing a secessionist state in the Southwest in the process.[lower-alpha 5] Hoping to incite war with Spain, Wilkinson in a letter to Secretary of War Dearborn urged him to attack Western Spanish-Florida from Baton Rouge. Prompted by prevailing rumors of war, Deaborn ordered him to send three companies of troops to Fort Adams in Western Florida as a precaution.[lower-alpha 6] The prospect of war in turn was used by Wilkinson to justify sending an exploratory military expedition into the Southwest to find a route that would be used to supply a war effort at the U.S.-Spanish-Mexican border.[23][lower-alpha 7] In May Dearborn ordered Wilkinson to the Orleans territory directing his General to "repel any invasion of the United States east of the Sabine River or north or west of the bounds of what has been called West Florida..." Dearborn further maintained that any such movements across these borders would constitute "an actual invasion of our territorial rights". This was the opportunity both Burr and Wilkinson were hoping for, thinking that Spanish officials were on edge over the prospect of confrontation with the U.S. and could easily be provoked into war.[24] When Wilkinson however had asked Dearborn to send an exploratory military expedition into the Southwest, Dearborn replied that, "you, Burr, etc., are becoming too intimate ... keep every suspicious person at arm's length".[lower-alpha 8] At this time Dearborn also warned his top general that "your name has very frequently been mentioned with Burr's". Shortly thereafter Burr was arrested for treason.[26]
Dearborn was appointed collector of the port of Boston by Madison in March 1809,[27] a position he held until January 27, 1812, when he was appointed as the Commanding General of the United States Army.[2]
War of 1812

During the War of 1812, while President James Madison was urging Federalists to join in "united support" against Britain in a war they were given little reason to cooperate in, he gave Henry Dearborn senior command of the northeast sector which ranged from the Niagara River to the New England coast. Dearborn had favor with Madison as a Revolutionary War veteran who rose to the rank of Colonel and for serving as Secretary of War under President Jefferson,[28] and especially for helping Jefferson draft the Military Peace Establishment Act which served to remove many Federalist officers from the ranks of the military. Subsequently, Madison's choice for commanding General of the northeast theater was not well received by most Federalists.[29] [lower-alpha 9] At age 61 however Dearborn was now overweight, slow and insecure, and he found it difficult to inspire confidence among the men under his command. In March he suffered a minor injury from a fall, and it is suggested that Dearborn took his time recovering, and when the war broke out he spent even more time in Boston fearing, as did Vice President Elbridge Gerry, that the Federalists were, once again, plotting a northeastern secession[lower-alpha 10] and ready to install a "Hanoverian" like monarchy in opposition to them.[29]
Needing to present Congress with reports of progress, Secretary of War William Eustis urged Dearborn to promptly embark for Albany and plan and make preparations for an invasion of Montreal in Canada. Dearborn maintained however that he must first get to New England and secure the militia for defending the New England coast, which would free up the regular troops of the region for the coming campaign against Canada, and before the Federalists effected an open revolt there. After disputes with the several New England's Federalist governors, who refused to supply the militia for coastal defense, Dearborn reluctantly left New England for Albany with regular troops in late July, leaving the coast almost defenseless against British coastal attacks.[31][lower-alpha 11]
On August 9, while General William Hull was expecting a diversionary attack by Dearborn in the Niagara area, the latter was still at his headquarters at Greenbush, just outside of Albany, and was having great difficulty amassing troops for the coming offensive in Canada. At this time George Prevost had sent British Colonel Edward Baynes to negotiate a temporary armistice with Dearborn. Dearborn learned that Lord Liverpool was giving the American government time to respond. Lacking the means to adequately engage the British in Canada, Dearborn was not eager for battle, welcomed the delay and rushed news of the armistice to Madison for approval. In the mean time Dearborn gave orders to General Van Rensselaer to avoid any engagements along the Niagara. The truce however was short lived when on August 15 Madison repudiated Dearborn's agreement and orders were issued to renew the offensive.[31][32]
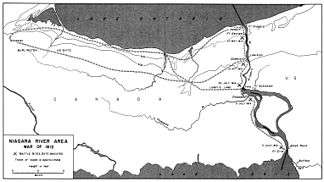
Dearborn prepared plans for simultaneous assaults on Montreal, Kingston, Fort Niagara, and Amherstburg, but the execution was imperfect. Some scholars believe that he did not move quickly enough to provide sufficient troops to defend Detroit. Hull, without firing a shot, surrendered the city to British General Isaac Brock.[lower-alpha 12] Hull was court-martialed and sentenced to death, but the sentence was commuted. Dearborn headed the court martial.[33]
On April 27, American forces on Lake Ontario under Dearborn and Commodore Isaac Chauncey gained success at the Battle of York, occupying the town for several days, capturing many guns and stores. Thereafter the American army was transported across the lake in Chauncey's ships to Fort Niagara. Dearborn assembled 4,500 troops at Fort Niagara and planned to attack Fort George next, and entrusted the attack to Colonel Winfield Scott,[34] but his army required rest and reorganisation. No preparations had been made to accommodate the troops at Fort Niagara, and they suffered considerable shortages and privations for several days.[35]
Although Dearborn had minor successes at the capture of York (now Toronto) on April 27, 1813, and at the capture of Fort George on May 27, 1813, his command was, for the most part, ineffective. He was recalled from the frontier on July 6, 1813, and reassigned to an administrative command in New York City.[36] and married his third wife, Sarah Bowdoin.[1]
Dearborn was honorably discharged from the Army on June 15, 1815.[37]
Later life
Dearborn was elected a member of the American Antiquarian Society in 1816, now the oldest historical society in the United States.[38]
Dearborn ran for governor of Massachusetts in 1818 against incumbent John Brooks. Because Dearborn was a Republican in a predominantly Federalist state, he needed favorable press to help his campaign. Subsequently, Dearborn accepted an offer from Charles Miner, the editor of the The Port Folio, a Philadelphia political magazine, asking him to verify and edit a British soldier’s map depicting the Battle of Bunker Hill, Dearborn saw this as a chance to win public favor and seized the opportunity.[39] However his efforts backfired when he also wrote a "correct account" of the battle in the article, which was reprinted in 1818, accusing Israel Putnam of inaction and cowardly leadership during the battle, which sparked a major and long lasting controversy among veterans of the war and various historians.[9][40]
President James Madison nominated Dearborn for reappointment as Secretary of War, but the Senate rejected the nomination and in the face of fierce criticism over Dearborn's performance during the War of 1812, Madison withdrew the nomination.[2][41] He was later appointed Minister Plenipotentiary to Portugal by President James Monroe and served from May 7, 1822, until June 30, 1824, when, by his own request, he was recalled.[2]
He retired to his home in Roxbury, Massachusetts, where he died 5 years later. He is interred in Forest Hills Cemetery, in Jamaica Plain outside of Boston at the time (later in 1874 Jamaica Plain was annexed to Boston).[1]
Legacy
Lewis and Clark, appointed by Thomas Jefferson, named the Dearborn River in west-central Montana after Dearborn in 1803. Dearborn County, Indiana; Dearborn, Michigan; and Dearborn, Missouri, were also named for him, as was Fort Dearborn in Chicago, which in turn was the namesake for Dearborn Street, a major street in downtown Chicago. There was also a Fort Dearborn in Adams County, Mississippi, in the early 1800s; see Leonard Covington.
Augusta, Maine was so renamed after Henry's daughter, Augusta Dearborn, in August, 1797.
A U.S. military armory, initially named Mount Dearborn, was planned in the early 1800s to be built on an island near the confluence of the Catawba and Wateree Rivers, adjacent to Great Falls, SC. The facility was never constructed, but the island name stuck and after the town was founded in 1905, its main thoroughfare was named Dearborn Street.
During World War II, a Fort Dearborn was established in Henry Dearborn's home state of New Hampshire.
His son, Henry A. S. Dearborn, was a Massachusetts Congressman in 1831–1833.
See also
Notes
- ↑ In 1822 Dearborn wrote an anonymous plea in the Boston Patriot to urge the purchase the site of the Bunker Hill battlefield which was currently listed for sale.[9]
- ↑ During the battle Montgomery was killed and Arnold seriously wounded.
- ↑ Then being a part of the Massachusetts.
- ↑ A grandnephew of Benjamin Franklin; John Adams appointed Williams a major in the Corps of Artillerists and Engineers in February 1801. President Thomas Jefferson appointed him the Army's Inspector of Fortifications.
- ↑ Both Burr and Wilkinson, with large land holding and other interests in the Louisiana Territory, claimed that most Louisiana residents, who were recently ruled by France, preferred to be separate from the United States.
- ↑ Present day southern Louisiana
- ↑ Burr and Wilkinson, with the support of General Andrew Jackson, were earnestly promoting the idea (e.g.via newspapers) in the Southwest that war with Spain was imminent and that he would use "Mexican treasure" to entice the Western states along the Mississippi and Ohio rivers into secession.[23]
- ↑ This is when Wilkinson realized that knowledge of his plotting with Burr was becoming common place, confirming similar reports coming out of New Orleans.[25]
- ↑ The Federalists viewed the war as a political plot against them, moreover, the Republicans portrayed the Federalsists as traitors for their concerted efforts to oppose the war effort.[29]
- ↑ Timothy Pickering and the Federalists once attempted a northeastern secession during Jefferson's first term.[30]
- ↑ No British coastal attacks occurred for the first year of the war -- presumably a favor from the British for New England's open opposition to the war.[31]
- ↑ While governor, Hull's repeated requests to build a naval fleet on Lake Erie to properly defend Detroit, Fort Mackinac, and Fort Dearborn were ignored by Dearborn, which contributed to Hull's overall unpreparedness.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 U.S. Army Center of Military History
- 1 2 3 4 U.S. Biographical Directory
- ↑ Dearborn, Smith, 1939, p.4
- 1 2 3 4 Malone, Allan, 1930, p. 174
- ↑ N.Y. Public library: Archives division
- ↑ Willey, 1903, p. 161
- ↑ Philbrick, 2013, chap.10
- ↑ Dearborn, Peckham, 2009, p. 5
- 1 2 3 Cray, 2001
- ↑ Dearborn, Smith, 1939, p.50
- ↑ Dearborn, Smith, 1939, p.19
- 1 2 3 4 5 Willey, 1903, p. 162
- ↑ Dearborn, Peckham, 2009, pp. 36-37
- ↑ Willey, 1903, p. 9
- ↑ Willey, 1903, p. 13
- ↑ Proceedings of the General Society of the Cincinnati, 1784-, Volume 1 (1887), p. 98
- ↑ Dearborn, Peckham, 2009, pp. i - vii5
- ↑ Dearborn, 2016
- ↑ Thomas Jefferson to the Senate, 25 March 1802
- 1 2 Henry Dearborn’s Report on the War Department, 12 May 1801
- ↑ Dearborn's 5 December 1801 letter to Jefferson
- ↑ Thomas Jefferson Foundation: Henry Dearborn (Physiognotrace)
- 1 2 Wheelan, 2005, p. 128
- ↑ Stewart, 2011 pp. 148-149
- ↑ Stewart, 2011, p. 111
- ↑ Stewart, 2011, pp. 110-111, 209
- ↑ McDonald, 2004, p. 115
- ↑ Daughan, 2011, p. 28
- 1 2 3 Taylor, 2010, pp. 180-182
- ↑ DiLorenzo, 1998, Yankee Confederates
- 1 2 3 Taylor, 2010, p. 182
- ↑ Daughan, 2011, p. 95
- ↑ Hickey, 1989 p. 84
- ↑ Taylor, 2010, p. 217
- ↑ Elting, 1991, p.119
- ↑ Hickey, 1989 p. 88
- ↑ Dictionary of American Biography, Vol. V, p.174
- ↑ American Antiquarian Society Members Directory
- ↑ Journal of the American Revolution
- ↑ Purcell, 2010, pp.164-168
- ↑ Fredriksen, 1999, p. 210
Bibliography
- Johnson, Allen; Malone, Dumas (Eds.) (1930). Dictionary of American Biography, Feb. 23, 1751 - Jun. 6, 1829, Vol. V,. Charles Scribner's Sons, New York.
- Dearborn, Henry; Putnam, Daniel (1818). An Account of the Battle of Bunker's Hill. Munroe & Francis, Boston.
- Biographical Directory of the United States Congress, 1774-2005: The Continental Congress, September 5, 1774, to October 21, 1788. Government Printing Office. 2005.
- Cray, Robert E. (2001). Bunker Hill Refought: Memory Wars and Partisan Conflicts, 1775-1825 (PDF). Historical Journal of Massachusetts.
- Dearborn, Henry; Peckham, Howard Henry (2009). Revolutionary War Journals of Henry Dearborn, 1775-1783. Heritage Books, 282 pages;. e'Book
- Daughan, George C. (2011). 1812, The Navy's War. Perseus Books, New York, 491 pages;.
- Elting, John R. (1991). Amateurs, To Arms! A Military History of the War of 1812. DaCapo Press. ISBN 0-306-80653-3.
- Fredriksen, John C. (1999). American Military Leaders. ABC-CLIO.
- Green (2009). The Guns of Independence: The Siege of Yorktown, 1781.
- Hickey, Donald R. (1989). The War of 1812, The Forgotten Conflict. University of Illinois Press, 454 pages;.
- McDonald, Forrest (2004). Thomas Jefferson's Military Academy: Founding West Point. University of Virginia Press.
- Philbrick, Nathaniel (2013). Bunker Hill: A City, A Siege, A Revolution. Penguin Books, 416 pages;.
- Purcell, Sarah J. (2010). Sealed with Blood: War, Sacrifice, and Memory in Revolutionary America. University of Pennsylvania Press., pages covering account
- Proceedings of the General Society of the Cincinnati, 1784-1884, Volume 1. Society of the Cincinnati, Philadelphia. 1887.
- Stewart, David O. (2011). American Emperor, Aaron Burr's challenge to Jefferson's America. Simon & Schuster, 411 pages;.
- Taylor, Alan (2010). The Civil War of 1812. Alfred A Knopf, New York, 623 pages;.
- Wheelan, Joseph (2005). Jefferson's Vendetta. Carrol and Graf Publishers, New York, 344 pages;.
- Willey, George Franklyn (1903). State Builders: An Illustrated Historical and Biographical Record of the State of New Hampshire. State Builders Publishing, Manchester, NH.
Website sources
- "Dearborn, H.A.S. (Henry Alexander Scammell), 1783-1851". New York Public library. Retrieved April 13, 2016.
- "Dearborn's 5 December 1801 letter to Jefferson". U.S. National Archives. 1801. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- "Henry Dearborn's Report on the War Department, [12 May 1801]". U.S. National Archives. 1801.
- "Thomas Jefferson to the Senate, 25 March 1802". U.S. National Archives. Retrieved March 23, 2016.
- "DEARBORN, Henry, (1751 - 1829)". U.S. Congress. Retrieved March 26, 2012.
- "Henery Dearborn". U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved March 26, 2016.
- "Henry Dearborn (Physiognotrace)". Thomas Jefferson Foundation. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- DiLorenzo, Thomas J. (1998). "Yankee Confederates". Retrieved March 29, 2016.
- "Bunker Hill Monument and Memory". Journal of the American Revolution. Retrieved April 15, 2016.
Further reading
- Dale, Ronald J. (2001). The Invasion of Canada: Battles of the War of 1812. James Lorimer & Company, 96 pages.
- Frothingham, Richard (1890). Battle of Bunker Hill. Little, Brown & Company, 136 pages. — eBook
- Livingston, William Farrand (1901). Israel Putnam: Pioneer, Ranger, and Major-general,1718-1790. G. P. Putnam's sons. — eBook
- Tarbox, Increase Niles (1876). Life of Israel Putnam. Lockwood, Brooks & Company, Boston. — eBook
- Winsor, Justin (1887). Narrative and Critical History of America, Volume 6. Houghton, Mifflin and Company, 777 pages. — eBook
External links
- Letters from Henry Dearborn, to Washington, Adams, Jefferson, etc.
- Bell, William Gardner (2005). "Henry Dearborn". Commanding Generals and Chiefs of Staff: Portraits and Biographical Sketchs. United States Army Center of Military History. pp. 72–73.
- George LaBarre Galleries : Henry Dearborn autographed as President, Republican Institution Certificate dated 1821.
| United States House of Representatives | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Theodore Sedgwick |
Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Massachusetts's 4th congressional district 1793–1795 Served alongside: George Thatcher, Peleg Wadsworth |
Succeeded by Dwight Foster |
| New constituency | Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Massachusetts's 12th congressional district 1795–1797 |
Succeeded by Isaac Parker |
| Political offices | ||
| Preceded by Samuel Dexter |
United States Secretary of War 1801–1809 |
Succeeded by William Eustis |
| Military offices | ||
| Preceded by James Wilkinson |
Senior Officer of the United States Army 1812–1815 |
Succeeded by Jacob Brown |
| Diplomatic posts | ||
| Preceded by John Appleton |
United States Minister to Portugal 1822–1824 |
Succeeded by Thomas Brent Acting |





