Haemanthus coccineus
| Haemanthus coccineus | |
|---|---|
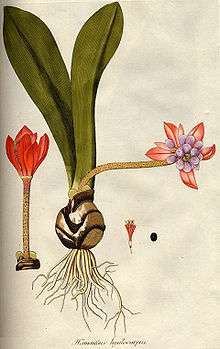 | |
| Haemanthus coccineus by Nikolaus Joseph von Jacquin | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Amaryllidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Amaryllidoideae |
| Genus: | Haemanthus |
| Species: | H. coccineus |
| Binomial name | |
| Haemanthus coccineus L. | |
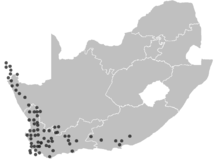 | |
| Distribution over South Africa | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Haemanthus coccineus, the blood flower, blood lily or paintbrush lily, is a bulbous geophyte in the genus Haemanthus, native to Southern Africa.
The generic name Haemanthus is derived from the Greek words haima for blood and anthos for flower; coccineus is the Latin word for red or scarlet. In the Afrikaans language it is known as bergajuin, bloedblom, and many other vernacular names.[2]
Distribution
Haemanthus coccineus is widespread throughout the winter rainfall region in Southern Africa - from the southern parts of Namibia, to South Africa in the Cape Peninsula, to the Keiskamma River in the Eastern Cape.[2] It is found in Renosterveld and Fynbos habitats.
It is an adaptable species, growing in a wide range of soils derived from sandstones, quartzites, granites, shales and limestones. It will survive annual rainfall ranging from 100–1,100 millimetres (3.9–43.3 in). The plant adapts to a wide range of altitudes, being found from coastal dunes to 1,200 metres (3,900 ft) high mountains.
It can be a 'gregarious species' found in clumps of hundreds, from the under the shelter of other shrubs on flat land, to in shady ravines and rock crevices.


Description
The flowerheads of Haemanthus coccineus emerge between February and April, with scarlet spathe valves on them like bright shaving brushes, make it a striking plant. The flowers are soon followed by translucent, fleshy berries. There are usually two large leaves per bulb, and occasionally three, which appear after flowering. [2]
The brilliant flowerheads account for its early appearance in Europe, being described by Carl Linnaeus in 1762. Together with Haemanthus sanguineus (Jacq.), this was the first Haemanthus to be introduced to European horticulture as an ornamental plant.
Despite Linnaeus' description, this same species was described under a host of different names (see gallery captions), which reflects more on taxonomic disorganisation than species variability. The plant figured on the left, was first described as Haemanthus hyalocarpus by Jacquin in 1804, and those in the gallery below, which are all H. coccineus, were first described under the caption names.
See also
References
- ↑ "The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species". Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- 1 2 3 Plantzafrica . accessed 11.11.2011
Gallery
- Haemanthus coccineus in botanical illustrations, with former synonyms:

Haemanthus coarctatus 
Haemanthus crassipes 
HaemanthusH. moschatus 
Haemanthus tigrinus
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Haemanthus coccineus. |
- Pacific Bulb Society | Haemanthus coccineus
- Plantzafrica.com Treatment: Haemanthus coccineus
- Haemanthus coccineus - International Bulb Society Photo Gallery
- Dressler, S.; Schmidt, M. & Zizka, G. (2014). [http://www.africanplants.senckenberg.de/root/index.php?submitForm=true&page_id=77&searchTextMenue=Haemanthus+coccineus&filterRegionIDs[]=6&filterRegionIDs[]=1&filterRegionIDs[]=2&filterRegionIDs[]=3&filterRegionIDs[]=5 "Haemanthus coccineus"]. African plants – a Photo Guide. Frankfurt/Main: Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg.