Folded spectrum method
In mathematics, the folded spectrum method (FSM) is an iterative method for solving large eigenvalue problems.
Here you always find a vector with an eigenvalue close to a search-value  . This means you can get a vector
. This means you can get a vector 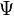 in the middle of the spectrum without solving the matrix.
in the middle of the spectrum without solving the matrix.
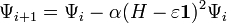 , with
, with 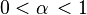 and
and 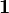 the Identity matrix.
the Identity matrix.
In contrast to the Conjugate gradient method, here the gradient calculates by twice multipling matrix 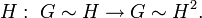
Literature
- J. K. L. MacDonald, Phys. Rev. 46, 828 - 828 (1934)
- W. Wang and A. Zunger, J. Phys. Chem. 98, 2158 (1994)
- W. Wang and A. Zunger, J. Chem. Phys. 100, 2394 (1994)
- http://www.sst.nrel.gov/topics/nano/escan.html
| ||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/17/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.