Flooding (computer networking)
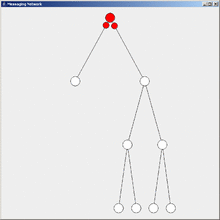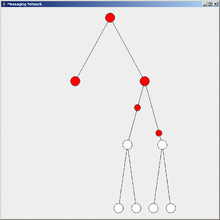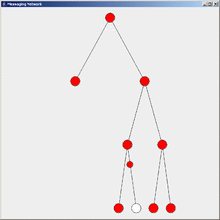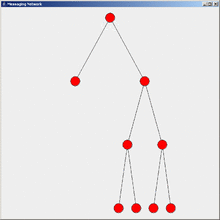
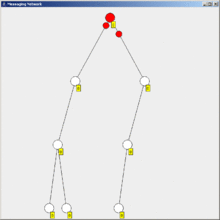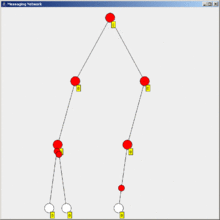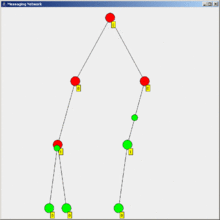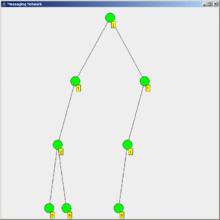
Flooding is a simple computer network routing algorithm in which every incoming packet is sent through every outgoing link except the one it arrived on.[1]
Flooding is used in bridging and in systems such as Usenet and peer-to-peer file sharing and as part of some routing protocols, including OSPF, DVMRP, and those used in ad-hoc wireless networks.[2]
Types
There are generally two types of flooding available, Uncontrolled Flooding and Controlled Flooding.
Uncontrolled Flooding is the fatal law of flooding. All nodes have neighbors and route packets indefinitely. More than two neighbours creates a broadcast storm.
Controlled Flooding has its own two algorithms to make it reliable, SNCF (Sequence Number Controlled Flooding) and RPF (Reverse Path Flooding). In SNCF, the node attaches its own address and sequence number to the packet, since every node has a memory of addresses and sequence numbers. If it receives a packet in memory, it drops it immediately while in RPF, the node will only send the packet forward. If it is received from the next node, it sends it back to the sender.
Algorithm
There are several variants of flooding algorithms. Most work roughly as follows:
- Each node acts as both a transmitter and a receiver.
- Each node tries to forward every message to every one of its neighbors except the source node.
This results in every message eventually being delivered to all reachable parts of the network.
Algorithms may need to be more complex than this, since, in some case, precautions have to be taken to avoid wasted duplicate deliveries and infinite loops, and to allow messages to eventually expire from the system. A variant of flooding called selective flooding partially addresses these issues by only sending packets to routers in the same direction. In selective flooding the routers don't send every incoming packet on every line but only on those lines which are going approximately in the right direction.
Advantages
- If a packet can be delivered, it will (probably multiple times).
- Since flooding naturally utilizes every path through the network, it will also use the shortest path.
- This algorithm is very simple to implement.
Disadvantages
- Flooding can be costly in terms of wasted bandwidth. While a message may only have one destination it has to be sent to every host. In the case of a ping flood or a denial of service attack, it can be harmful to the reliability of a computer network.
- Messages can become duplicated in the network further increasing the load on the networks bandwidth as well as requiring an increase in processing complexity to disregard duplicate messages.
- Duplicate packets may circulate forever, unless certain precautions are taken:
- Use a hop count or a time to live count and include it with each packet. This value should take into account the number of nodes that a packet may have to pass through on the way to its destination.
- Have each node keep track of every packet seen and only forward each packet once
- Enforce a network topology without loops
Examples
Open Shortest Path First - Used for transferring updates to the topology (LSAs)
See also
References
- ↑ A. Tanenbaum; D. Wetherall (23 March 2010). Computer Networks, 5th Edition. Pearson. p. 368-370. ISBN 978-0-13-212695-3.
- ↑ A. Rahman, W. Olesinski and P. Gburzynski. "Controlled Flooding in Wireless Ad-hoc Networks" (PDF). senserf.com. Retrieved 2015-10-15.
External links
- Ricochet A flooding networking app written in Java