Eastern European Group
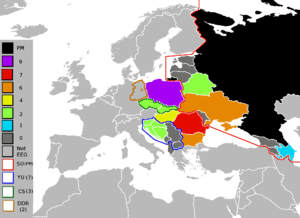
The Eastern European Group in 2012, with the years each member spent in the
United Nations Security Council, including former members represented as outlines
The Eastern European Group (EEG), also known as Countries with Economies in Transition (CEIT), is one of the five unofficial Regional Groups in the United Nations that act as voting blocs and negotiation forums. Regional voting blocs were formed in 1961 to encourage voting to various UN bodies from regional groups. The group consists of countries in Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, which form the area of the former Eastern Bloc. Europe is divided between the EEG and the Western European and Others Group. The group currently has 23 members.
History
Prior to the creation of the Regional Groups in 1966, the UNSC had an Eastern European and Asian Seat, that was taken between 1946 and 1966 by countries from Eastern Europe (including Greece and Turkey, members of the modern Western European and Others Group (WEOG)) and Asia (members of the modern Asia-Pacific Group). The Eastern European Group exists since 1966. It has changed significantly due to the dissolution of some of its members. These dissolutions are those of the Soviet Union (1991), Yugoslavia (1991-2006), and Czechoslovakia (1993). Also, through the German reunification, the Eastern European Group lost East Germany as its member. All the new countries created in Europe stayed in the bloc, and the Central Asian post-Soviet states joined the Asia-Pacific Group.
Members
Current members
Historical members
Representation
The Eastern European Group has two seats in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC); the permanent seat of Russia, and one elected seat, currently held by Lithuania. The Group further has 6 seats on the United Nations Economic and Social Council and 6 seats on the United Nations Human Rights Council. It is also eligible for having its nationals elected as President of the United Nations General Assembly in years ending with 2 and 7; most recently, Vuk Jeremić of Serbia was elected to this position in June 2012 and was the office holder of the Sixty-seventh session.
List of presidents of the United Nations General Assembly
List of presidents of the United Nations Security Council
Source[4][5][6][7][8][9]
Permanent seat
|
Elected seat
|
List of presidents of the United Nations Economic and Social Council
Timeline of membership
As the Eastern European Group changed significantly over time, the number of its members had also changed.
References
- ↑ Referred to by the United Nations as "The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia"
- ↑ Presidents of the General Assembly of the United Nations. Un.org. Retrieved on 2016-10-15.
- ↑ Referred to by the United Nations as "The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia"
- ↑ Presidents of the Security Council : 1946-1949, un.org.
- ↑ Presidents of the Security Council : 1950-1959, un.org.
- ↑ Presidents of the Security Council : 1960-1969, un.org.
- ↑ Presidents of the Security Council : 1970-1979, un.org.
- ↑ Presidents of the Security Council : 1980-1989, un.org.
- ↑ Presidents of the Security Council : 1990-1999, un.org.
- ↑ "Security Council Press Statement On Ethiopia And Eritrea". Un.org. Retrieved 2012-12-26.
- ↑ Press Conference By Security Council President
- ↑ Security Council Press Statement On Somalia
- ↑ Security Council Press Statement On Darfur
- ↑ Security Council Press Statement On United Nations Regional Centre For Preventive Diplomacy For Central Asia
- ↑ SECURITY COUNCIL, EXPRESSING DEEP CONCERN OVER ‘CONTINUOUS TERRORIST ATTACKS’, CALLS FOR RENEWAL OF GLOBAL SOLIDARITY AGAINST THREAT MANIFESTED AFTER 9/11
- ↑ Adopting Text On Middle East Conflict, Security Council Reaffirms Support For Annapolis Outcomes, Declares Negotiations ‘Irreversible’
- ↑ Security Council Press Statement On Sri Lanka
- ↑ Security Council Presidential Statement Reiterates Urgent Need For Renewed Efforts To Achieve Comprehensive Peace In Middle East
- ↑ Security Council Press Statement on Panel of Inquiry on 31 May Flotilla Incident
- ↑ Security Council Press Statement on Democratic Republic of the Congo
- ↑
- ↑ "SC/11269 - Security Council Press Statement on Lebanon". United Nations Department of Public Information, News and Media Division, New York. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- ↑ "SC/11279 - Security Council issues presidential statement applauding European Union's partnership with United Nations in resolving global challenges". United Nations Department of Public Information, News and Media Division, New York. Retrieved 22 February 2014.
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ http://www.un.org/en/sc/presidency/
- ↑ Presidents of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. Un.org. Retrieved on 2016-04-23.

