Dithionic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
dithionic acid [1] | |
| Other names
hypodisulfuric acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 14970-71-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:29208 |
| ChemSpider | 25128 |
| PubChem | 26985 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H2S2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 162.14 g mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
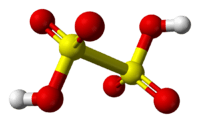
Dithionic acid, H2S2O6, is a chemical compound known only in solution.[2]
Salts
Dithionic acid is dibasic and salts called dithionates are known. No acid salts have been discovered. All dithionates are readily soluble in water.[2] They are mild oxidizing and mild reducing agents. The structure of dithionate ion is like ethane, but two SO3 groups adopt an almost eclipsed conformation. The S—S length is 2.15 Å; S—O bonds are rather short with bond length of 1.43 Å.
Synthesis
Dithionates can be made by oxidizing a sulfite (from the +4 to the +5 oxidation state), but on a larger scale they are made by oxidizing a cooled aqueous solution of sulfur dioxide with MnO2:
- 2MnO2 + 3SO2 → MnS2O6 + MnSO4
The manganese dithionate solution formed can then be converted to dithionate salts of other metals by metathesis reactions:
- Ba2+(aq) + MnS2O6(aq) + MnSO4(aq) → BaSO4(s)↓ + BaS2O6·2H2O(aq)
Concentrated solutions of dithionic acid can subsequently be obtained treating a barium dithionate solution with sulfuric acid:
- BaS2O6(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → H2S2O6(aq) + BaSO4(s)↓
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005). Cambridge (UK): RSC–IUPAC. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. p. 130. Electronic version.
- 1 2 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-08-037941-9. pp. 715-716
www.chemindustry.com/chemicals/1022920.html - CASNo reference