Districts of Yerevan
The Districts of Yerevan refers to administrative divisions of Yerevan, the capital of Armenia.
Persian and Russian eras
Main districts
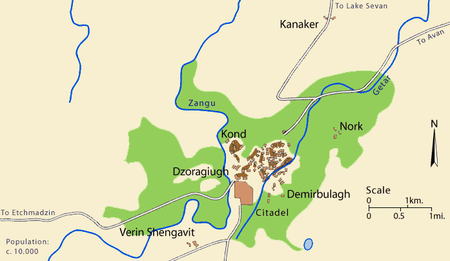
Since the 17th century, without the fortress and nearby villages (Noragyugh, Dzoragyugh and Nork), Yerevan was divided into three main quarters (mahlas; Persian: محله):
- Shahar (The Old City),
- Demir-Bulagh (Karahank)
- Kond (Tapabash).
The market (Ghantar) was separate, between Kond and Shahar.
| Shahar | 998 | 1,111 | 30 | 3,199 | 5,338 | |
| Kond | 1,176 | 374 | 18 | 2,537 | 195 | 4,300 |
| Demirbulagh | 230 | 1,595 | 1,825 | |||
Shahar
Shahar (Persian: شهر šahar) was the oldest and biggest quarter of Yerevan. It located in the north-eastern part of the city, between Amiryan St. and Khorenatsi St. It was, probably, populated since the Urartian times. During later centuries it was destroyed many times, but have always been populated. First time it was mentioned as old Yerevan or the old city of Yerevan by bishop Pilipos of Bjni in 1631:[2][3]
| “ | …after many searches I found it [the Bible] in the old city of Yerevan… Բազում որոնմամբ խուզեալ գտաք, զգանձս զայս անգին ի հին քաղաքն Երեւան բազում ժամանակաւ գերի տարեալ ումեք իբրեւ եօթանասնօք |
” |
Kond
Kond (Armenian: Կոնդ), so-named because of its high position. It was also known as Tapabashi (Turkish: tepe - hill, baş - head, top; "top of the hill") during the Persian rule. Kond located in the western part of Yerevan. According to Hovhannes Shahkhatunyants, an Armenian historian, Kond located in the western and southern hillsides and foot of a rocky hill with similar name. Its western border was Hrazdan River, and the northern border was the Kozern Cemetery. Kond, similar to Shahar, was populated by Armenians. The population of Kond became multiethnic, when about 100 Armenian Boshas moved to Kond.[4]
Demir-Bulagh
The third main quarter was Demir-Bulagh (Turkish: "demir" - iron, "bulağ" - source, meaning "iron source"') or Karahank (Armenian: Քարահանք, meaning "rock quarry" referring to a quarry of tufa and basalt there). It located in the south-eastern Yerevan. This district was inhabited, comparatively, later than other districts. Firstly, a quarry located here and was not inhabited. Later, Karahank was inhabited with newcomer Tatars (Azerbaijanis) and became part of Yerevan forming a separate district.[5][6] Demir-Bulagh become crowded in the 17th century, when terrified of the Persian invasions, many Turks from Nakhichevan moved to the areas north to the Yerevan Fortress. The majority of the population of the district were Muslims, few Armenians lived there.
Ghantar (the market)
Ghantar (Armenian: Ղանթար, meaning "big scales in a marketplace", from Arabic: قنطار, qinṭār) was the active and business center of Yerevan. Ghantar belonged to the City Administration. Later, in place of Ghantar was built a close market and was called Ghantar. In 1938, the Children's Park (called Kirov Park during the Soviet era) was built in the place of Ghantar.
Expansion in the mid-19th century


After Erivan was taken over by the Russian troops in 1827, many Armenians from northern Persia came to Eastern Armenia, including to Yerevan. The city was expanded. In the mid-19th century Yerevan had 6 districts:
- Shahar
- Kond
- Demir-Bulagh
- Dzoragyugh
- Nor tagh
- Shen tagh
- Nork
Yerevan has been expanded at the expense of two surrounding villages: Dzoragyugh and Nork.
Dzoragyugh
Dzoragyugh (Armenian: Ձորագյուղ, Dara-kend in Turkish and Azerbaijani) was a suburb and later a district of Yerevan. It located in the Hrazdan gorge, in the left steep coast. During the Persian rule it was officially translated as Dara-kend. According to Zakaria Sarkavag this village - which before becoming a district of Yerevan was a separate village - was called Khnkelo dzor.[7] According to Simeon I of Yerevan this village was called with two names: Dzoragyugh and Khnkadzor.[8] The Surb Sargis Church located in Dzoragygh and commonly was called the Church of Dzoragyugh. Dzoragyugh was called Khnkadzor or Khnkelo, because it was Yerevan's bishop's seat, the word "khunk" means 'incense' in Armenian. The population of Dzoragyugh was completely Armenian. Dzoragyugh had three smaller neighborhoods:
- Verin tagh (Վերին թաղ, "Upper district") or Karapi tagh (Քարափի թաղ, "The Bluff district") located on the left upland of Hrazdan, north-west from the fortress, in the surrounding area of the St. Sargis church.
- Storin tagh (Ստորին թաղ, "Lower district") or Dzori tagh (Ձորի թաղ, "The Gorge district") located on the left side of Hrazdan, in a precipitous gorge.
- The district of Karbi (Կարբիի թաղ) was, probably, the southern continuation of Storin tagh. Many people from Karbi village of Ashtarak lived there.[9]
Nork
Nork (Armenian: Նորք, Turkish: Çömlekçi, meaning "potter") was the second villages near Yerevan, that became its part in the 1830s. Because the pottery was common labor, the Turks called it Cholmakci (Çömlekçi). The population was completely Armenian. They were working in agriculture, vegetable-growing, farming, and pottery. There were smaller districts (mahlans) in Nork, too. Though Nork was inhabited since ancient times, but it was mentioned comparatively late.[10] There were two churches in Nork: Surb Astvatsatsin and Surb Simeon Tseruni (19th century).
And other two new districts were built: Nor tagh and Shen tagh.
Nor tagh
Nor tagh (Armenian: Նոր թաղ, meaning “new district”) located in the eastern part of Kond, in the surrounding are of the Hovhannes Tumanyan House-Museum. It was called ‘new’, because many immigrants from Atropatene were moved here after the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay. During the Persian rule, in the place of the Nor tagh were the Gardens of the Sardars, called Khanlubagh (Persian: باغ خان)
Shen tagh
Shen tagh (Armenian: Շեն թաղ) located in the surrounding areas of the English Park.
Soviet era

- Note: for the names of districts the Russian names are given, which was official at the time.
The first administrative division of Yerevan took place in 1936. Two districts were formed:
- Kirov District (Кировский район)
- Stalin District (Сталинский район)
The Spandaryan Distriсt (Спандарянский район) was formed in 1938 and the Molotov district (Молотовский район) in 1939. As of 1940 Yerevan had 4 districts:
- Kirov District (Кировский район)
- Molotov District (Молотовский район)
- Spandaryan District (Спандарянский район)
- Stalin District (Сталинский район)
The Kirov District was disintegrated in 1953 and Shahumyan District was formed in 1958 and was renamed to Ordzhonikidze District in 1961. So as of 1971 there were 6 districts in Yerevan:
- 26 Commissars District (Район им.26 Комиссаров)
- Lenin District (Ленинский район)
- Myasnikyan District (Мясникянский район)
- Ordzhonkidze District (Орджоникидзевский район)
- Spandaryan District (Спандарянский район)
- Ordzhonikidze District (Орджоникидзевский район)
The Soviet district (Советский район) was formed in 1972. And Mashtots district (Маштоцкий район) in 1986.[11]
Districts of Yerevan and their populations according to the last Soviet census of 1989:[12]
| |
|
|
|
| Soviet District | Советский район | Սովետական շրջան | 279,494 |
| Shahumyan district | Шаумянский район | Շահումյանի շրջան | 192,899 |
| 26 Commissars District | Район имени 26 комиссаров | 26 կոմիսարների շրջան | 186,754 |
| Lenin District | Ленинский район | Լենինի շրջան | 138,926 |
| Ordzhonikidze District | Орджоникидзевский район | Օրջոնիկիձեի շրջան | 133,038 |
| Mashtots District | Маштоцкий район | Մաշտոցի շրջան | 125,620 |
| Spandaryan District | Спандарянский район | Սպանդարյան շրջան | 80,580 |
| Myasnikyan District | Мясникянский район | Մյասնիկյանի շրջան | 64,228 |
| City of Yerevan | город Ереван | քաղաք Երևան | 1,201,539 |
|---|
Independent Armenia

Yerevan is divided into twelve "neighborhood communities" (թաղային համայնքներ), commonly translated as "districts",[13] each with an elected community leader. Each district is divided into neighborhoods (թաղամաս). Each district is divided into unofficial neighborhoods (թաղամասեր or թաղեր). The total area of the 12 districts of Yerevan is 227 km².
| District | Armenian | Population (2001) | Area (km²) | Neighborhoods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ajapnyak | Աջափնյակ | |
25 | Ajapnyak, Norashen, Nazarbekyan, Silikyan, Lukashin, Vahagni, Anastasavan, Cheryomushki |
| Arabkir | Արաբկիր | |
12.35 | Nor Arabkir, Aygedzor, Mergelyan, Raykom, Power Plant |
| Avan | Ավան | |
8.37 | Avan, Avan-Arinj, Aghi Hank |
| Davtashen | Դավթաշեն | |
6.71 | Davtashen blocks, Huysi Avan |
| Erebuni | Էրեբունի | |
48.41 | Erebuni, Nor Aresh, Saritagh, Vardashen, Mushavan, Verin Jrashen, Nor Butaniya, Kayaran |
| Kanaker-Zeytun | Քանաքեր-Զեյթուն | |
8.10 | Kanaker, Nor Zeytun, Mounument |
| Kentron | Կենտրոն | |
14.20 | Pokr Kentron, Noragyugh, Nor Kilikia, Aygestan, Kond, Dzoragyugh |
| Malatia-Sebastia | Մալաթիա-Սեբաստիա | |
25.80 | Nor Malatia, Nor Sebastia, Zoravar Andranik, Shahumyan, Araratyan, Haghtanak |
| Nork-Marash | Նորք-Մարաշ | |
4.60 | Nork, Nor Marash |
| Nor Nork | Նոր Նորք | |
14.47 | Nor Nork, Bagrevand |
| Nubarashen | Նուբարաշեն | |
18.11 | Nubarashen |
| Shengavit | Շենգավիթ | |
40.50 | Nerkin Shengavit, Verin Shengavit, Nerkin Charbakh, Verin Charbakh, Noragavit, Aeratsia, South-Western |
See also
- History of Yerevan
- Yerevan
- Erebuni Fortress
- Armenian Oblast
- Erivan Governorate
- Khanate of Erevan
- History of Armenia
References
- ↑ (Armenian) Երևան քաղաքի բնակչության շարժընթացը 1824-1914թթ. Yerevan History Museum
- ↑ (Armenian) H. Tashyan, List of manuscripts (Ձեռագրաց ցուցակ)", p. 260
- ↑ (Armenian) Handes Amsorya («Հանդէս ամսօրեայ»), 1934, № 329 — 330
- ↑ (Armenian) Hovhannes Shahkhutyants, Ստորագրութիւն կաթուղիկէ Էջմիածնի և հինգ գաւառացն Արարատայ, volume II, p. 146
- ↑ (Russian) I. Chopin, Historical monument of the Armenian Oblast (Исторический памятник Армянской области), p. 464
- ↑ (Armenian) Yervand Shahaziz, The Old Yerevan (Հին Երևանը), pp. 173—174
- ↑ (Armenian) Zakaria Sarkavag, Պատմագրութիւն (History), volume II, pp. 32, 51
- ↑ (Armenian) Simeon of Yerevan, Jambr (Ջամբռ), p. 204
- ↑ (Armenian) Yervand Shahaziz, The Old Yerevan (Հին Երևանը), pp. 174-175
- ↑ (Armenian) Ghevont Alishan, Ayrarat (Այրարատ), p. 293
- ↑ (Russian) Административно-территориальное деление города Еревана
- ↑ (Russian) Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г.: Численность городского населения союзных республик, их территориальных единиц, городских поселений и городских районов по полу
- ↑ "The 12 district of Yerevan" (in Armenian). Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- Albert Parsadanyan. Intelligence Warehouse-2. Yerevan, VMV-Print, 2005, p. 150-152.
- (Armenian) Կամսար Ավետիսյան. ՀԱՅՐԵՆԱԳԻՏԱԿԱՆ ԷՏՅՈՒԴՆԵՐ - ԵՐԵՎԱՆԻ ՄԻԿՐՈՏՈՊՈՆԻՄԻԿԱՆ. Երևան, «Սովետական գրող» հրատարակչություն, 1979
- (Armenian) Կամսար Ավետիսյան. ՀԱՅՐԵՆԱԳԻՏԱԿԱՆ ԷՏՅՈՒԴՆԵՐ - ՀԱՅՐԵՆԻՔՈԻՄ ՎԵՐԱՀԱՍՏԱՏՎԱԾ ՏԵՂԱՆՈՒՆՆԵՐ. Երևան, «Սովետական գրող» հրատարակչություն, 1979
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Old Yerevan. |