Distributor
Also visible are mounting/drive shaft (bottom), vacuum advance unit (right) and capacitor (centre)
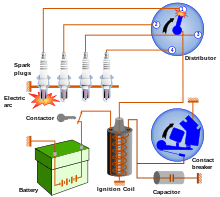
A distributor is an enclosed rotating shaft used in spark-ignition internal combustion engines that have mechanically-timed ignition. The distributor's main function is route secondary, or high voltage, current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs in the correct firing order, and for the correct amount of time. Except in magneto systems, the distributor also houses a mechanical or inductive breaker switch to open and close the ignition coil's primary circuit.
The first reliable battery operated ignition was developed by Dayton Engineering Laboratories Co. (Delco) and introduced in the 1910 Cadillac. This ignition was developed by Charles Kettering and was considered a wonder in its day. Atwater Kent invented his Unisparker ignition system about this time in competition with the Delco system.[1] By the end of the 20th centrury mechanical ignitions were disappearing from automotive applications in favor of inductive or capacitive electronic ignitions fully controlled engine control units (ECU), rather than directly timed to the engine's crankshaft speed.
Description
A distributor consists of a rotating arm or rotor inside the distributor cap, on top of the distributor shaft, but insulated from it and the body of the vehicle (ground). The distributor shaft is driven by a gear on the camshaft on most overhead valve engines, and attached directly to a camshaft on most overhead cam engines. (The distributor shaft may also drive the oil pump.) The metal part of the rotor contacts the high voltage cable from the ignition coil via a spring-loaded carbon brush on the underside of the distributor cap. The metal part of the rotor arm passes close to (but does not touch) the output contacts which connect via high tension leads to the spark plug of each cylinder. As the rotor spins within the distributor, electric current is able to jump the small gaps created between the rotor arm and the contacts due to the high voltage created by the ignition coil.[2]
The distributor shaft has a cam that operates the contact breaker. Opening the points causes a high induction voltage in the system's ignition coil.[2]
The distributor also houses the centrifugal advance unit: a set of hinged weights attached to the distributor shaft, that cause the breaker points mounting plate to slightly rotate and advance the spark timing with higher engine revolutions per minute (rpm). In addition, the distributor has a vacuum advance unit that advances the timing even further as a function of the vacuum in the inlet manifold. Usually there is also a capacitor attached to the distributor. The capacitor is connected parallel to the breaker points, to suppress sparking to prevent excessive wear of the points.
Around the 1970s the primary breaker points were largely replaced with a Hall effect sensor or optical sensor. As this is a non-contacting device and the ignition coil is controlled by solid state electronics, a great amount of maintenance in point adjustment and replacement was eliminated. This also eliminates any problem with breaker follower or cam wear, and by eliminating a side load it extends distributor shaft bearing life. The remaining secondary (high voltage) circuit stayed essentially the same, using an ignition coil and a rotary distributor.
Most distributors used on electronically fuel injected engines lack vacuum and centrifugal advance units. On such distributors, the timing advance is controlled electronically by the engine computer. This allows more accurate control of ignition timing, as well as the ability to alter timing based on factors other than engine speed and manifold vacuum (such as engine temperature). Additionally, eliminating vacuum and centrifugal advance results in a simpler and more reliable distributor.
Distributor cap
The distributor cap is the cover that protects the distributor's internal parts and holds the contacts between internal rotor and the spark plug wires.
The distributor cap has one post for each cylinder, and in points ignition systems there is a central post for the current from the ignition coil coming into the distributor. There are some exceptions however, as some engines (many Alfa Romeo cars, some 1980s Nissans) have two spark plugs per cylinder, so there are two leads coming out of the distributor per cylinder. Another implementation is the wasted spark system, where a single contact serves two leads, but in that case each lead connects one cylinder. In General Motors high energy ignition (HEI) systems there is no central post and the ignition coil sits on top of the distributor. Some Toyota and Honda engines also have their coil within the distributor cap. On the inside of the cap there is a terminal that corresponds to each post, and the plug terminals are arranged around the circumference of the cap according to the firing order in order to send the secondary voltage to the proper spark plug at the right time.
The rotor is attached to the top of the distributor shaft which is driven by the engine's camshaft and thus synchronized to it. Synchronization to the camshaft is required as the rotor must turn at exactly half the speed of the main crankshaft in the 4-stroke cycle. Often, the rotor and distributor are attached directly to the end of the one of (or the only) camshaft, at the opposite end to the timing drive belt. This rotor is pressed against a carbon brush on the center terminal of the distributor cap which connects to the ignition coil. The rotor is constructed such that the center tab is electrically connected to its outer edge so the current coming in to the center post travels through the carbon point to the outer edge of the rotor. As the camshaft rotates, the rotor spins and its outer edge passes each of the internal plug terminals to fire each spark plug in sequence.
Engines that use a mechanical distributor may fail if they run into deep puddles because any water that gets on to the distributor can short out the electric current that should go through the spark plugs, rerouting it directly to the body of the vehicle. This in turn causes the engine to stop as the fuel is not ignited in the cylinders.[3] This problem can be fixed by removing the distributor's cap and drying the cap, cam, rotor and the contacts by wiping with tissue paper or a clean rag, by blowing hot air on them, or using a moisture displacement spray e.g. WD-40 or similar. Oil, dirt or other contaminants can cause similar problems, so the distributor should be kept clean inside and outside to ensure reliable operation.[4] Some engines include a rubber o-ring or gasket between the distributor base and cap to help prevent this problem. The gasket is made of a material like Viton or butyl for a tight seal in extreme temperatures and chemical environments.[5] This gasket should not be discarded when replacing the cap. Most distributor caps have the position of the number 1 cylinder's terminal molded into the plastic. By referencing a firing order diagram and knowing the direction the rotor turns, (which can be seen by cranking the engine with the cap off) the spark plug wires can be correctly routed. Most distributor caps are designed so that they cannot be installed in the wrong position. Some older engine designs allow the cap to be installed in the wrong position by 180 degrees, however. The number 1 cylinder position on the cap should be noted before a cap is replaced.
The distributor cap is a prime example of a component that eventually succumbs to heat and vibration. It is a relatively easy and inexpensive part to replace if its bakelite housing does not break or crack first. Carbon deposit accumulation or erosion of its metal terminals may also cause distributor-cap failure.
As it is generally easy to remove and carry off, the distributor cap can be taken off as a means of theft prevention. Although not practical for everyday use, because it is essential for the starting and running of the engine, its removal thwarts any attempt at hot-wiring the vehicle.
|
Direct and distributorless ignition
Modern engine designs have abandoned the high-voltage distributor and coil, instead performing the distribution function in the primary circuit electronically and applying the primary (low-voltage) pulse to individual coils for each spark plug, or one coil for each pair of companion cylinders in an engine (two coils for a four-cylinder, three coils for a six-cylinder, four coils for an eight-cylinder, and so on).
In traditional remote distributorless systems, the coils are mounted together in a transformer oil filled 'coil pack', or separate coils for each cylinder, which are secured in a specified place in the engine compartment with wires to the spark plugs, similar to a distributor setup. General Motors, Ford, Chrysler, Hyundai, Subaru, Volkswagen and Toyota are among the automobile manufacturers known to have used coil packs. Coil packs by Delco for use with General Motors engines allow removal of the individual coils in case one should fail, but in most other remote distributorless coil pack setups, if a coil were to fail, replacement of the whole pack would be required to fix the problem.
More recent layouts utilize a coil located very near to (Coil-Near-Plugs) or directly on top of each spark plug (Direct Ignition, DI, coil-on-plug, or COP). This design avoids the need to transmit very high voltages, which is often a source of trouble, especially in damp conditions.
Both direct and remote distributorless systems also allow finer levels of ignition control by the engine computer, which helps to increase power output, decrease fuel consumption and emissions, and implement features such as cylinder deactivation. Spark plug wires, which need routine replacement due to wear, are also eliminated when the individual coils are mounted directly on top of each plug, since the power is transported a very short distance from the coil to the plug.
Wasted spark
Four-stroke 2-cylinder engines can be built without a distributor, as in the Citroen 2CV of 1948 and BMW boxer twin motorcycles. Both spark plugs of the boxer twin are fired simultaneously, resulting in a wasted spark on the cylinder currently on its exhaust stroke.[6]
Four-stroke 4-cylinder engines can be built without a distributor, as in the Citroen ID19. Two coils are used with one coil firing two of the spark plugs simultaneously, resulting in a wasted spark on the cylinder currently on its exhaust stroke, and the other coil used for the other two cylinders. This system has been scaled up to engines with virtually an unlimited number of cylinders.
Four-stroke one-cylinder engines can be built without a distributor, as in many lawn mowers. The spark plug is fired on every stroke, resulting in a wasted spark in the cylinder when on its exhaust stroke.
See also
References
- ↑ "Cadillac History | Kanter Car Tales". kanter-car-tales.com. Retrieved 2016-02-12.
- 1 2 "How the ignition system works". How a Car Works. Retrieved 2016-02-12.
- ↑ "Misfire from driving through "wave of water" likely result of wet distributor cap — a problem that's not costly to fix". Post and Courier. Retrieved 2016-02-12.
- ↑ mitmaks (2014-03-23), Cleaning distributor cap, retrieved 2016-02-12
- ↑ "Rubber Gaskets and Soft Gaskets - Mercer Gasket & Shim". Mercer Gasket & Shim. Retrieved 2016-02-12.
- ↑ "Citroen 2CV Special (1979)". NetCarShow.com. Retrieved 2016-02-12.
External links
| Look up distributor in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |




