Diazene
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diazene | |||
| Other names
Diimide Diimine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3618-05-1 15626-43-4 (E)-diazene 15626-42-3 (Z)-diazene | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:30096 | ||
| ChemSpider | 10612167 | ||
| KEGG | C05360 | ||
| MeSH | Diazene | ||
| PubChem | 123195 | ||
| UNII | LM321PYV3Y | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 30.03 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Yellow gas | ||
| Melting point | −80 °C (−112 °F; 193 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions |
diphosphene dinitrogen difluoride | ||
| Other cations |
azo compounds | ||
| Related Binary azanes |
ammonia diazane triazane | ||
| Related compounds |
triazene tetrazene | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
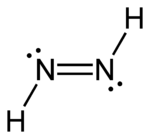
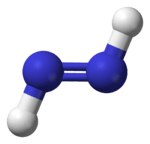
Diazene, also called diimine or diimide, is a compound having the formula (NH)2. It exists as two geometric isomers, E and Z. Diazene is also the parent member of the entire class of azo compounds with the formula (NR)2, where R is an organyl group. Thus, azobenzene is an example of an organic diazene.
Synthesis
The traditional route to diazene involves oxidation of hydrazine with hydrogen peroxide or air.[1] Alternatively the decarboxylation of azodicarboxylic acid affords diazene:[2]
- (NCO2H)2 → (NH)2 + 2 CO2
Diazene can also be efficiently generated by elimination of sulfonohydrazides using a suitable base. For example, 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonohydrazide eliminates diazene upon treatment with sodium bicarbonate, a very mild base.
Because of its instability, diazene is generated and used in-situ. A mixture of both the cis (Z-) and trans (E-) isomers is produced. Both isomers are unstable, and they undergo a slow interconversion. The trans isomer is more stable, but the cis isomer is the one that reacts with unsaturated substrates, therefore the equilibrium between them shifts towards the cis isomer due to Le Chatelier's principle. Some procedures call for the addition of carboxylic acids, which catalyse the cis–trans isomerization.[3] Diazene decomposes readily. Even at low temperatures, the more stable trans isomer rapidly undergoes various disproportionation reactions, primarily forming hydrazine and nitrogen gas:[4]
- 2 HN=NH → H2N–NH2 + N2
Because of this competing decomposition reaction, reductions with diazene typically require a large excess of the precursor reagent.
Applications to organic synthesis
cis-Diazene is occasionally useful as a reagent in organic synthesis.[3] It hydrogenates alkenes and alkynes with selective delivery of hydrogen from one face of the substrate resulting in the same stereoselectivty as metal-catalysed syn addition of H2. The only coproduct released is nitrogen gas. Although the method is cumbersome, the use of diazene avoids the need for high pressures or hydrogen gas and metal catalysts, which can be expensive.[5] The hydrogenation mechanism involves a six-membered C2H2N2 transition state:
Selectivity
Diazene is advantageous because of it selectively reduces alkenes and alkynes and is nonreactive toward many functional groups that would interfere with normal catalytic hydrogenation. Thus, peroxides, alkyl halides, and thiols are tolerated by diazene, but these same groups would typically be degraded by metal catalysts. The reagent preferentially reduces alkynes and unhindered or strained alkenes[1] to the corresponding alkenes and alkanes.[3]
Related
The dication diazene HNNH2+ is calculated to have the strongest known chemical bond. This ion can be thought of as doubly protonated nitrogen. The relative bond strength order (RBSO) is 3.38.[6] FNNH2+ and FNNF2+ have slightly lower strength bonds.[6]
References
- 1 2 Ohno, M.; Okamoto, M. (1973). "cis-Cyclododecene". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 5, p. 281
- ↑ Wiberg, E.; Holleman, A. F. (2001). "1.2.7: Diimine, N2H2". Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 628. ISBN 9780123526519.
- 1 2 3 Pasto, D. J. (2001). "Diimide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd235.
- ↑ Wiberg, Nils; Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, Egon, eds. (2001). "1.2.7 Diimine N2H2 [1.13.17]". Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. pp. 628–632. ISBN 978-0123526519.
- ↑ Miller, C. E. (1965). "Hydrogenation with Diimide". Journal of Chemical Education. 42 (5): 254–259. doi:10.1021/ed042p254.
- 1 2 Kalescky, Robert; Kraka, Elfi; Cremer, Dieter (12 September 2013). "Identification of the Strongest Bonds in Chemistry". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 117 (36): 8981–8995. doi:10.1021/jp406200w.