Conuber sordidum
| Conuber sordidum | |
|---|---|
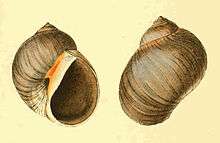 | |
| Conuber sordidum. From Zoological Illustrations, Volume II, Plate 79, by William Swainson (1821). | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| (unranked): | clade Caenogastropoda clade Hypsogastropoda clade Littorinimorpha |
| Superfamily: | Naticoidea |
| Family: | Naticidae |
| Genus: | Conuber[1] |
| Species: | C. sordidum |
| Binomial name | |
| Conuber sordidum (Swainson, 1821) | |
| Synonyms | |
Conuber sordidum (originally described as Natica sordida by Swainson) is a species of predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk family Naticidae, the moon snails.[2][3]
Distribution
East coast of Australia, from Victoria to Queensland. The species also occurs off Tasmania and New Zealand.[4]
Life habits
Conuber sordidum is predatory, feeding mostly on bivalves and gastropods.[5] The species is also known to prey on the soldier crab Mictyris longicarpus by drilling predation.[6][7] To catch soldier crabs, C. sordidum uses the same stereotyped behaviour as previously described for moon snails hunting shelled molluscan prey.[7]
Habitat
On intertidal muddy sand flats near mangroves or sea weed.[4]
References
- ↑ Finlay, H. J. and Marwick, J. (1937) The Wangaloan and Associated Molluscan Faunas of Kaitagata-Green Island Subdivision. New Zealand Geological Survey Branch, Palaeontological Bulletin No. 15, Wellington, p. 53.
- ↑ Swainson, W. (1820-1821) Zoological Illustrations, or original figures and descriptions of new, rare, or interesting animals, selected chiefly from the classes of ornithology, entomology, and conchology, and arranged on the principles of Cuvier and other modern zoologists. Vol. 2. London
- ↑ Huelsken, T., Tapken, D., Dahlmann, T., Wägele, H., Riginos, C., Hollmann, M. (2012). Systematics and phylogenetic species delimitation within Polinices s.l. (Caenogastropoda: Naticidae) based on molecular data and shell morphology. Organisms Diversity & Evolution. DOI: 10.1007/s13127-012-0111-5. ODE homepage
- 1 2 Conuber sordidus on Indo-Pacific Molluscan Database
- ↑ Bishop, M. J., Cole, M. R., Taylor, S. L., Wilkie, E. M. & Kelaher, B. P. (2008) Size-specific predation by dominant consumers maintains a 'trophic cul-de-sac'. Marine Ecology Progress Series 354, 75-83.
- ↑ Ann M. Cameron (1966). "Some aspects of the behaviour of the soldier crab, Mictyris longicarpus". Pacific Science. 20 (2): 224–234. hdl:10125/7754.
- 1 2 Huelsken, T. (2011) First evidence of drilling predation by Conuber sordidus (Swainson, 1821) (Gastropoda: Naticidae) on soldier crabs (Crustacea: Mictyridae). Molluscan Research, 31(2), 125-131.
External links
- Video of Conuber sordidus hunting Mictyris longicarpus on YouTube
- Philippe Bouchet (2012). "Conuber sordidum (Swainson, 1821)". World Register of Marine Species.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.