Chlorotoluene
Chlorotoluene is a group of three isomeric chemical compounds. They (ortho-chlorotoluene, meta-chlorotoluene, and para-chlorotoluene) consisist of a disubsituted benzene ring with one chlorine atom and one methyl group.
Chemical properties
The isomers differ in the location of the chlorine, but have the same chemical formula. All have very similar boiling points, although p-chlorotoluene has a much higher melting point due a more tightly-packed crystal structure.
| Chlorotoluene Isomers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | ||||
| Common name | o-chlorotoluene | m-chlorotoluene | p-chlorotoluene | |
| Structure | 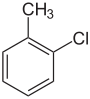 |
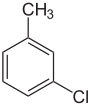 |
 | |
| Systematic name | 1-chloro-2-methylbenzene | 1-chloro-3-methylbenzene | 1-chloro-4-methylbenzene | |
| Molecular formula | C7H7Cl (C6H4ClCH3) | |||
| Molar mass | 126.586 g/mol | |||
| Appearance | clear, colorless liquid | |||
| CAS number | [95-49-8] | [108-41-8] | [106-43-4] | |
| Properties | ||||
| Density and phase | 1.073 g/mL, liquid | 1.072 g/mL, liquid | 1.069 g/mL, liquid | |
| Solubility in water | practically insoluble | |||
| Other solubilities | Soluble in non-polar solvents such as aromatic hydrocarbons | |||
| Melting point | −35 °C (−31 °F; 238 K) | −47 °C (−52.6 °F; 226 K) | 7 °C (44.6 °F; 280 K) | |
| Boiling point | 159 °C (318.2 °F; 432 K) | 162 °C (323.6 °F; 435 K) | 162 °C (323.6 °F; 435 K) | |
Benzyl chloride is an isomer, which has a chlorine substituted for one of the hydrogens of toluene's the methyl group, and it is sometimes named α-chlorotoluene.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.