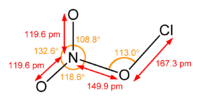
Chlorine nitrate
| |||
 | |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Chlorine nitrate | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Chloro nitrate | |||
| Other names
Nitryl hypochlorite | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 14545-72-3 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 102875 | ||
| PubChem | 114934 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| ClNO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 97.46 | ||
| Density | 1.65 g/cm3 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| EU classification (DSD) |
| ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Chlorine nitrate, with chemical formula ClNO3 is an important atmospheric gas present in the stratosphere. It is an important sink of chlorine that contributes to the depletion of ozone.
It explosively reacts with metals, metal chlorides, alcohols, ethers, and most organic materials. When it is heated to decomposition, it emits toxic fumes of Cl2 and NOx.
It can be produced by the reaction of dichlorine monoxide and dinitrogen pentoxide at 0 °C:
- Cl2O + N2O5 → 2 ClONO2
It can also react with alkenes:
- (CH3)2C=CH2 + ClONO2 → O2NOC(CH3)2CH2Cl
Chlorine nitrate reacts with metal chlorides:[1]
- 4 ClONO2 + TiCl4 → Ti(NO3)4 + 4 Cl2
References
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the Nitrate ion | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiNO3 | Be(NO3)2 | B(NO3)4− | C | N | O | FNO3 | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaNO3 | Mg(NO3)2 | Al(NO3)3 | Si | P | S | ClONO2 | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 | Sc(NO3)3 | Ti(NO3)4 | VO(NO3)3 | Cr(NO3)3 | Mn(NO3)2 | Fe(NO3)3 | Co(NO3)2, Co(NO3)3 |
Ni(NO3)2 | Cu(NO3)2 | Zn(NO3)2 | Ga(NO3)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||
| RbNO3 | Sr(NO3)2 | Y | Zr(NO3)4 | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd(NO3)2 | AgNO3 | Cd(NO3)2 | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe(NO3)2 | ||
| CsNO3 | Ba(NO3)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg2(NO3)2, Hg(NO3)2 |
Tl(NO3)3 | Pb(NO3)2 | Bi(NO3)3 BiO(NO3) |
Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce(NO3)3, Ce(NO3)4 |
Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd(NO3)3 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(NO3)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/16/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.