Exarchate of Africa
| Exarchate of Africa Exarchatus Africae | |||||
| Exarchate of the East Roman Empire | |||||
| |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Carthage | ||||
| Historical era | Early Middle Ages | ||||
| • | Foundation of Exarchate | 585/590 | |||
| • | First Arab invasion | 647 | |||
| • | Battle of Carthage (698) | 698 | |||
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Tunisia | ||||||||||||
| Prehistoric | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Ancient | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Early Islamic | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Medieval | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Early modern | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Modern | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| Part of a series on the |
| History of Algeria |
|---|
 |
|
|
|
|
Modern times |
|
|
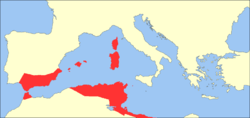
The Exarchate of Africa or of Carthage, after its capital, was the name of an administrative division of the Byzantine Empire encompassing its possessions on the Western Mediterranean, ruled by an exarch (viceroy). It was created by emperor Maurice in the late 580s and survived until the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb in the late 7th century.
History
Background
The Maghreb along with Corsica and Sardinia and the Balearic Islands were reconquered by the Byzantine Empire under Belisarius in the Vandalic War of 533 and reorganized as the Praetorian prefecture of Africa by Justinian I. It included the provinces of Africa Proconsularis, Byzacena, Tripolitania, Numidia, Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis, and was centered at Carthage. In the 560s, a Roman expedition succeeded in regaining parts of southern Spain, which were administered as the new province of Spania. After the death of Justinian, the Empire came into increasing attacks on all fronts, and the remoter provinces were often left to themselves to cope as best as they could, with Constantinople unable to provide assistance.
Establishment of the Exarchate

The Late Roman administrative system, as established by Diocletian, provided for a clear distinction between civil and military offices, primarily to lessen the possibility of rebellion by over-powerful provincial governors. Under Justinian I, the process was partially reversed for provinces which were judged to be especially vulnerable or in internal disorder. Capitalizing upon this precedent and taking it one step further, the emperor Maurice sometime between 585 and 590 created the office of exarch, which combined the supreme civil authority of a praetorian prefect and the military authority of a magister militum, and enjoyed considerable autonomy from Constantinople. Two exarchates were established, one in Italy, with seat at Ravenna (hence known as the Exarchate of Ravenna), and one in Africa, based at Carthage and including all imperial possessions in the Western Mediterranean. The first African exarch was the patricius Gennadius.[1]
Among the provincial changes, Tripolitania was detached from Africa and placed under the province of Egypt,[2] Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis were merged to form the new province of "Mauretania Prima", while Maretania Tingitana, effectively reduced to the city of Septum (Ceuta), was combined with the citadels of the Spanish coast (Spania) and the Balearic Islands to form "Mauretania Secunda".[1]
The Visigothic Kingdom was also a continuous threat. The African exarch was in possession of Mauretania II, which was little more than a tiny outpost in southern Spain. The conflict continued until the final conquest of the last Spanish strongholds in c. 624 by the Visigoths. The Byzantines retained only the fort of Septum (modern Ceuta), across the Strait of Gibraltar.
During the successful revolt of the exarch of Carthage, Heraclius the Elder, and his namesake son Heraclius in 608, the Berbers comprised a large portion of the fleet that transported Heraclius to Constantinople. Due to religious and political ambitions, the Exarch Gregory the Patrician (who was related by blood to the imperial family, through the emperor's cousin Nicetas) declared himself independent of Constantinople in 647. At this time the influence and power of the exarchate was exemplified in the forces gathered by Gregory in the battle of Sufetula also in that year where more than 100,000 men of Amazigh origin fought for Gregory.
The Arab Muslim conquest
The first Islamic expeditions began with an initiative from Egypt under the emir 'Amr ibn al-'As and his nephew Uqba ibn Nafi. Sensing Roman weakness they conquered Barca, in Cyrenaica, then successively on to Tripolitania where they encountered resistance.
Due to the unrest caused by theological disputes concerning Monothelitism and Monoenergism the Exarchate under Gregory the Patrician distanced itself from the empire in open revolt. Carthage being flooded with refugees from Egypt (especially Melkites), Palestine and Syria exacerbated religious tensions and further raised the alarm to Gregory of the approaching Arab threat.
Sensing that the more immediate danger came from the Muslim forces Gregory gathered his allies and initiated a confrontation with the Muslims and was defeated at the Battle of Sufetula, which was actually the capital of the exarchate since Gregory had moved to the interior for a better defense against Roman counter-offensives from the sea.
Afterwards the Exarchate became a semi-client state under a new Exarch called Gennadius. Attempting to maintain tributary status with Constantinople and Damascus strained the resources of the Exarchate and caused unrest amongst the population.
The peak of resistance reached by the Exarchate with assistance from the Berber allies of king Kusaila was the victory over the forces of Uqba ibn Nafi at the Battle of Vescera in 682. This victory caused the Muslim forces to retreat to Egypt, giving the Exarchate a decade's respite. The repeated confrontations took their toll on the dwindling and ever-divided resources of the Exarchate.
In 698, the Muslim commander Hasan ibn al-Nu'man and a force of 40,000 men crushed Roman Carthage. Many of its defenders were Visigoths sent to defend the Exarchate by their king, who also feared Muslim expansion. Many Visigoths fought to the death; in the ensuing battle Roman Carthage was again reduced to rubble, as it had been centuries earlier by the Romans.
The loss of the mainland African Exarchate was an enormous blow to the Byzantine empire in the Western Mediterranean because both Carthage and Egypt were Constantinople's main sources of manpower and grain. It was also an enormous blow because it permanently ended Roman presence in Africa.
Known Exarchs of Africa
| Tenure | Name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 591–598 | Gennadios (I) | Last magister militum per Africam and first Exarch, victory over the Roman-Berber realm of Altava. |
| 598 or 602–611 | Herakleios | |
| 641(?)–647/48 | Gregory | |
| 647/48–665 | Gennadios (II) | |
| after 665 | Eleutherios | Possibly Exarch of Carthage. The Arabic al-At'riyūn is commonly read as Eleutherios. He overthrew Gennadios. |
| about 711 | Julian, Count of Ceuta | Commander of Septem. According to some scholars, possibly last Exarch of Africa. |
Notes
- 1 2 Julien (1931, v.1, p.273)
- ↑ Hrbek 1992, p. 120
Sources
- Diehl, Charles (1896). L'Afrique Byzantine. Histoire de la Domination Byzantine en Afrique (533–709) (in French). Paris, France: Ernest Leroux.
- Hrbek, Ivan (1992). Africa from the Seventh to the Eleventh Century. James Currey Publishers.
- Julien, C.A. (1931) Histoire de l'Afrique du Nord, vol. 1 - Des origines a la conquête arabe, 1961 edition, Paris: Payot
- Pringle, Denys (1981). The Defence of Byzantine Africa from Justinian to the Arab Conquest: An Account of the Military History and Archaeology of the African Provinces in the Sixth and Seventh Century. Oxford, United Kingdom: British Archaeological Reports. ISBN 0-86054-119-3.