Boeing Model 6D
| Model 6D | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | passenger flying-boat |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| First flight | April 1928[1] |
| Number built | 2 |
|
| |
The Boeing Model 6D (originally designated the Boeing B-1D) was an American pusher biplane flying-boat built by Boeing between 1928 and 1929.
Development and design

Boeing Model B1D or 6D
The Model 6D continued the designation series of the 1919 Boeing Model 6 but the only similarity was that they are both biplane pusher flying-boats. The 6D was designed in 1928 and 2 aircraft were built between May 1928 and April 1929. The 6Ds rectangular hull was constructed of wood with wood longerons, covered in spruce veneer. The wings were taken from the Model 40 and shortened. The pusher engine and wood propeller was mounted on the lower side of the upper wing.[2]
Specifications
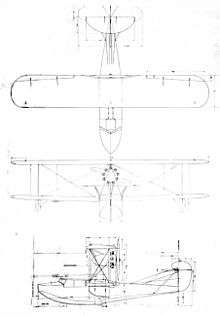
Boeing model B1D/6D drawing
Data from Bowers, 1966. pg. 136.
General characteristics
- Crew: 1 pilot
- Capacity: 3 passengers
- Length: 30 ft 9 in (9.37 m)
- Wingspan: 39 ft 8.25 in (12.10 m)
- Height: 12 ft in (3.66 m)
- Wing area: 466 ft2 (43.29 m2)
- Empty weight: 2,442 lb (1,017 kg)
- Gross weight: 3,442 lb (1,516 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Wright J-5, 220 hp (164 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 95 mph (153 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 80 mph (129 km/h)
- Range: 175 miles (282 km)
- Service ceiling: 12,000 ft (3,656 m)
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Boeing model 6D. |
- Bowers, Peter M. Boeing aircraft since 1916. London: Putnam Aeronautical Books, 1966.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.