Hydrogenoxalate
Wireframe model of hydrogenoxalate
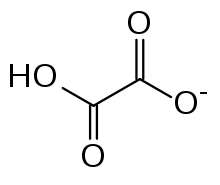
Hydrogenoxalate or hydrogen oxalate is an anion with chemical formula HC2O4− or HO2C–CO2−, derived from oxalic acid by the loss of a single proton; or, alternatively, from the oxalate anion C2O42− by addition of a proton.
The name is also used for any salt containing this anion, such as NaHC2O4, KHC2O4, or NH3HC2O4. Hydrogenoxalates may also be called (especially in older literature) binoxalates, acid oxalates, or monobasic oxalates.
See also
References
- Roland Tellgren and Ivar Olovsson (1971) The crystal structures of normal and deuterated sodium hydrogen oxalate monohydrate NaHC2O4·H2O and NaDC2O4·D2O. Hydrogen bond studies. XXXXVI. The Journal of chemical physics pp. 234–238.
- R. G. Delaplane, R. Tellgren and I. Olovsson (1984) Neutron diffraction study of sodium hydrogen oxalate monohydrate, NaHC2O4·H2O, at 120 K. Acta Crystallographica, volume C40, 1800–1803 doi:10.1107/S0108270184009616
- M. Hamadène, H. Kherfi, A. Guehria-Laidoudi (2006), The polymeric anhydrous rubidium hydrogen oxalate. Acta Crystallographica volume A62, p. s280
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/22/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.