August Borsig

Johann Friedrich August Borsig (23 June 1804 – 6 July 1854) was a German businessman who founded the Borsig-Werke factory.
Borsig was born in Breslau (Wrocław), the son of cuirassier and carpenter foreman Johann George Borsig. After learning his father's trade, he first attended the Königliche Provinzial-Kunst- und Bauschule (Royal Provincial Art and Building school), then until fall of 1825 the Königliche Gewerbe-Institut (Royal Institute of Trade). He received his practical training in engine construction at the Neue Berliner Eisengießerei (New Iron Foundry of Berlin) of F. A. Egells, where one of his first tasks was the assembly of a steam engine in Waldenburg, Silesia. After the successful completion of this task, Borsig was made factory manager for eight years. In 1828, he married Louise Pahl; they had one son, Albert.
August Borsig and his company

From early on, Borsig was a supporter of railroads. Despite the lack of experience with railroads in Germany and the risks involved in the founding of a railroad machinery manufacturing company, Borsig used his savings to buy a site at Chausseestraße (in the Feuerland) near the Oranienburger Tor, neighboring his old company's factory, and founded his own machine factory, focusing on locomotives. The founding date was declared to be 22 July 1837, the day of the first successful casting in the foundry.
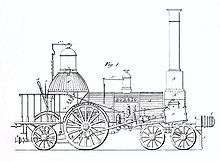
Despite tremendous costs, the first locomotive, bearing factory number 1 and the name BORSIG, was finished in 1840. This locomotive had an interior frame, a two-axle front pivoted bogie and an extra dead axle behind the only drive axle. On 21 July 1840, Borsig let it compete against a Stephenson-built locomotive on the Berlin-Jüterbog railroad. The Borsig locomotive won by 10 minutes, proving that in spite of the lack of experience, Germans could build locomotives that were at least as good as the British models, and so the import of locomotives and engineers was no longer necessary. After this victory, the number of orders rose quickly. A further six machines of this type were sold to the Berlin-Stettiner Eisenbahn and the Oberschlesische Eisenbahn in 1842.
In the beginning, the Borsig company also built steam engines for their own needs and machines for other companies as well as cast parts for art and construction. However, the focus soon shifted to locomotive building, and the name Borsig is connected with locomotives to this day. By 1843, railway companies in Prussia had ordered 18 locomotives, and in 1844, Borsig could exhibit his 24th locomotive at the Berlin industrial fair. The one hundredth locomotive was finished in 1846. Meanwhile, Borsig built the steam pump for the fountain at Sanssouci and participated in the building of the domes of the Nicolai Church in Potsdam and the Berliner Stadtschloss (Berlin City Palace). The company was expanding rapidly in those years, since new railways were being built all over Germany. In 1847, construction of the new Moabit ironworks started and they became operational in 1849. The machine factory and iron foundry in Kirchstraße was bought in 1850, and this put the total number of employees at the three Berlin factories at 1800, making Borsig's company one of the large-scale enterprises of its time.

The increasing number of orders also increased Borsig's private wealth, and he soon became a rich entrepreneur who was not averse to splendor and a patron for many artists. August Borsig was said to be a strict but just boss with a zest for action. For his workers, he set up a sickness fund, a funeral expense fund, and a savings bank. His company had an instruction room, a dining room and a bath with swimming pool.

Borsig had become sufficiently important by the end of the 1840s that he was able to weather the economic crisis of 1848-1852 with little damage. Starting 1851, foreign railway companies also began to order Borsig locomotives, among them the Warsaw-Vienna Railway and the Seeländische Eisenbahn. After the 500th locomotive had been completed in 1854, Borsig was made Geheimer Kommerzienrat (Secret Commerce Councillor). This allowed him to tighten his monopoly position, and 67 of the 68 new Prussian locomotives in 1854 came from Borsig factories.
Some years earlier, his magnificent villa in Berlin-Moabit had been completed, fulfilling a dream of Borsig's. However, he could not enjoy his wealth for very long. He died in Berlin on 6 July 1854, at the height of his power.
Further history of the company
After the death of August Borsig, the company was led and expanded by his son August Julius Albert Borsig.
On the occasion of the completion of the 1000th locomotive, a large celebration with many prominent guests was held, among them the explorer Alexander von Humboldt. At this time, the company that had started out with 50 workers, had 2800 employees. It continued its expansion, and moved some part of its production to Hindenburg in Silesia in 1862. In 1872, Borsig was the largest locomotive producer in Europe. Albert Borsig co-founded the Maschinenfabrik Deutschland on the Köln-Mindener Eisenbahn line in Dortmund but the most successful chapter in the Borsig business history ended with Albert's death in 1878.
The company continued to be led mostly by Borsig family members and continued to build large numbers of locomotives, but it began to lose market share to other traffic-related companies. The company moved to Tegel, a former suburb of Berlin. The works was inaugurated in 1898. The Tegel works area was one of the most modern facilities in Germany at that time. It had its own harbour where the ships brought the material for the locomotives. The works itself had long road with every production step at its place. The end of this production lane was the BORSIG Gate. The brand new locomotives left the works through this gate. The company also developed new products that are still part of the current manufacturing program: pressure vessels and compressors. The Great Depression made an end the success of BORSIG as a private company. By 1930, the company was on the verge of liquidation, the locomotive business was saved by a merger with AEG. Borsig built a number of famous locomotives, among which was the world speed record holder DRG Class 05, the first steam locomotive to hit 200 km/h. The last of a total of 16,352 locomotives was built in 1954. The rest of the company went to Rheinmetall.

BORSIG today
After World War II, the company was called Borsig AG, owned by Rheinmetall (as Rheinmetall-Borsig) and later by VIAG, a company owned by the German Federal Republic. In 1970, Borsig was sold to the private company Deutsche Babcock AG, later known as Babcock Borsig AG. In July 2002, Borsig had to reorganize due to the insolvency of its mother company, Babcock Borsig AG, Oberhausen. In 2004, Borsig bought ZM Zwickauer Maschinenfabrik, a manufacturer of reciprocating compressors and blowers, today known as BORSIG ZM Compression GmbH, situated in Meerane/Saxony. In 2006, Borsig bought the industrial boiler manufacturer DIM KWE, today BORSIG Boiler Systems GmbH. Today the BORSIG Group consists of six companies:
- BORSIG GmbH, the mother company, Berlin,
- BORSIG Process Heat Exchanger GmbH, Berlin, manufacturer of pressure vessels and heat exchangers,
- BORSIG ZM Compression GmbH, Meerane, manufacturer of compressors and blowers,
- BORSIG Membrane Technology GmbH, Gladbeck and Rheinfelden, manufacturer of membrane technology such as emission control systems or vapour recovery units,
- BORSIG Boiler Systems GmbH, Hamburg, industrial boilers and power plant engineering,
- BORSIG Service GmbH, Berlin and Gladbeck, industrial service.
In 2008 the whole BORSIG Group got a new owner, the KNM Group Berhad, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The actual product and service programme of the BORSIG Group consists of pressure vessels, heat exchangers, process gas waste heat recovery systems, quench coolers, scraped surface exchangers, reciprocating compressors for process gases, turbo compressors for process gases, reciprocating compressors for CNG filling stations, blowers and blowers systems, compressor valves, membrane technologies, such as emission control units, vapour recovery systems, gas conditioning, advanced separations, industrial boilers, power plant engineering, power plant services and industrial services.
See also
References
This article is based on a translation of the German article August Borsig, which cites the following references:
- Rheinmetall-Borsig Aktiengesellschaft (Hrsg.): Deutscher Maschinenbau 1837-1937 im Spiegel des Werkes Borsig. Berlin, 1937
- Galm, Ulla: August Borsig. Stapp, Berlin 1987, ISBN 3-87776-167-4
- Kutschik, Dietrich: Lokomotiven von Borsig: Eine Darstellung der Lokomotivgeschichte der Firma A. Borsig und der Nachfolgefirmen. Transpress, Verlag für Verkehrswesen, Berlin 1985
- Kutschik, Dietrich; Wenzel, Hansjürgen; Koch, Matthias: Borsig. Lokomotiven für die Welt. EK Verlag, Freiburg 1986, ISBN 3-88255-111-9
- Pierson, Kurt: Borsig, ein Name geht um die Welt: die Geschichte des Hauses Borsig und seiner Lokomotiven. Rembrandt Verlag Berlin, 1973, ISBN 3-7925-0204-6
External links
- August Borsig in the German National Library catalogue
- Alte Borsig GmbH
- http://www.borsig.de
|